Compare commits
No commits in common. 'master' and 'master' have entirely different histories.
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
---
|
|
||||||
name: Bug report
|
|
||||||
about: Create a report to help us improve
|
|
||||||
title: ''
|
|
||||||
labels: bug
|
|
||||||
assignees: ''
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Describe the bug**
|
|
||||||
A clear and concise description of what the bug is.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**To Reproduce**
|
|
||||||
Steps to reproduce the behavior (you can also attach your script):
|
|
||||||
1. Go to '...'
|
|
||||||
2. Click on '....'
|
|
||||||
3. Scroll down to '....'
|
|
||||||
4. See error
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Expected behavior**
|
|
||||||
A clear and concise description of what you expected to happen.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Screenshots**
|
|
||||||
If applicable, add screenshots to help explain your problem.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Desktop (please complete the following information):**
|
|
||||||
- OS: [e.g. iOS]
|
|
||||||
- CoastSat Version [e.g. 22]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Additional context**
|
|
||||||
Add any other context about the problem here.
|
|
||||||
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
---
|
|
||||||
name: Feature request
|
|
||||||
about: Suggest an idea for this project
|
|
||||||
title: ''
|
|
||||||
labels: enhancement
|
|
||||||
assignees: ''
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Is your feature request related to a problem? Please describe.**
|
|
||||||
A clear and concise description of what the problem is. Ex. I'm always frustrated when [...]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Describe the solution you'd like**
|
|
||||||
A clear and concise description of what you want to happen.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Describe alternatives you've considered**
|
|
||||||
A clear and concise description of any alternative solutions or features you've considered.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Additional context**
|
|
||||||
Add any other context or screenshots about the feature request here.
|
|
||||||
@ -1,674 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
|
|
||||||
Version 3, 29 June 2007
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc. <https://fsf.org/>
|
|
||||||
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
|
|
||||||
of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Preamble
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The GNU General Public License is a free, copyleft license for
|
|
||||||
software and other kinds of works.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The licenses for most software and other practical works are designed
|
|
||||||
to take away your freedom to share and change the works. By contrast,
|
|
||||||
the GNU General Public License is intended to guarantee your freedom to
|
|
||||||
share and change all versions of a program--to make sure it remains free
|
|
||||||
software for all its users. We, the Free Software Foundation, use the
|
|
||||||
GNU General Public License for most of our software; it applies also to
|
|
||||||
any other work released this way by its authors. You can apply it to
|
|
||||||
your programs, too.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not
|
|
||||||
price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you
|
|
||||||
have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge for
|
|
||||||
them if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it if you
|
|
||||||
want it, that you can change the software or use pieces of it in new
|
|
||||||
free programs, and that you know you can do these things.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To protect your rights, we need to prevent others from denying you
|
|
||||||
these rights or asking you to surrender the rights. Therefore, you have
|
|
||||||
certain responsibilities if you distribute copies of the software, or if
|
|
||||||
you modify it: responsibilities to respect the freedom of others.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether
|
|
||||||
gratis or for a fee, you must pass on to the recipients the same
|
|
||||||
freedoms that you received. You must make sure that they, too, receive
|
|
||||||
or can get the source code. And you must show them these terms so they
|
|
||||||
know their rights.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Developers that use the GNU GPL protect your rights with two steps:
|
|
||||||
(1) assert copyright on the software, and (2) offer you this License
|
|
||||||
giving you legal permission to copy, distribute and/or modify it.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For the developers' and authors' protection, the GPL clearly explains
|
|
||||||
that there is no warranty for this free software. For both users' and
|
|
||||||
authors' sake, the GPL requires that modified versions be marked as
|
|
||||||
changed, so that their problems will not be attributed erroneously to
|
|
||||||
authors of previous versions.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Some devices are designed to deny users access to install or run
|
|
||||||
modified versions of the software inside them, although the manufacturer
|
|
||||||
can do so. This is fundamentally incompatible with the aim of
|
|
||||||
protecting users' freedom to change the software. The systematic
|
|
||||||
pattern of such abuse occurs in the area of products for individuals to
|
|
||||||
use, which is precisely where it is most unacceptable. Therefore, we
|
|
||||||
have designed this version of the GPL to prohibit the practice for those
|
|
||||||
products. If such problems arise substantially in other domains, we
|
|
||||||
stand ready to extend this provision to those domains in future versions
|
|
||||||
of the GPL, as needed to protect the freedom of users.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Finally, every program is threatened constantly by software patents.
|
|
||||||
States should not allow patents to restrict development and use of
|
|
||||||
software on general-purpose computers, but in those that do, we wish to
|
|
||||||
avoid the special danger that patents applied to a free program could
|
|
||||||
make it effectively proprietary. To prevent this, the GPL assures that
|
|
||||||
patents cannot be used to render the program non-free.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and
|
|
||||||
modification follow.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
0. Definitions.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"This License" refers to version 3 of the GNU General Public License.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"Copyright" also means copyright-like laws that apply to other kinds of
|
|
||||||
works, such as semiconductor masks.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"The Program" refers to any copyrightable work licensed under this
|
|
||||||
License. Each licensee is addressed as "you". "Licensees" and
|
|
||||||
"recipients" may be individuals or organizations.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To "modify" a work means to copy from or adapt all or part of the work
|
|
||||||
in a fashion requiring copyright permission, other than the making of an
|
|
||||||
exact copy. The resulting work is called a "modified version" of the
|
|
||||||
earlier work or a work "based on" the earlier work.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A "covered work" means either the unmodified Program or a work based
|
|
||||||
on the Program.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To "propagate" a work means to do anything with it that, without
|
|
||||||
permission, would make you directly or secondarily liable for
|
|
||||||
infringement under applicable copyright law, except executing it on a
|
|
||||||
computer or modifying a private copy. Propagation includes copying,
|
|
||||||
distribution (with or without modification), making available to the
|
|
||||||
public, and in some countries other activities as well.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To "convey" a work means any kind of propagation that enables other
|
|
||||||
parties to make or receive copies. Mere interaction with a user through
|
|
||||||
a computer network, with no transfer of a copy, is not conveying.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
An interactive user interface displays "Appropriate Legal Notices"
|
|
||||||
to the extent that it includes a convenient and prominently visible
|
|
||||||
feature that (1) displays an appropriate copyright notice, and (2)
|
|
||||||
tells the user that there is no warranty for the work (except to the
|
|
||||||
extent that warranties are provided), that licensees may convey the
|
|
||||||
work under this License, and how to view a copy of this License. If
|
|
||||||
the interface presents a list of user commands or options, such as a
|
|
||||||
menu, a prominent item in the list meets this criterion.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. Source Code.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The "source code" for a work means the preferred form of the work
|
|
||||||
for making modifications to it. "Object code" means any non-source
|
|
||||||
form of a work.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A "Standard Interface" means an interface that either is an official
|
|
||||||
standard defined by a recognized standards body, or, in the case of
|
|
||||||
interfaces specified for a particular programming language, one that
|
|
||||||
is widely used among developers working in that language.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The "System Libraries" of an executable work include anything, other
|
|
||||||
than the work as a whole, that (a) is included in the normal form of
|
|
||||||
packaging a Major Component, but which is not part of that Major
|
|
||||||
Component, and (b) serves only to enable use of the work with that
|
|
||||||
Major Component, or to implement a Standard Interface for which an
|
|
||||||
implementation is available to the public in source code form. A
|
|
||||||
"Major Component", in this context, means a major essential component
|
|
||||||
(kernel, window system, and so on) of the specific operating system
|
|
||||||
(if any) on which the executable work runs, or a compiler used to
|
|
||||||
produce the work, or an object code interpreter used to run it.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The "Corresponding Source" for a work in object code form means all
|
|
||||||
the source code needed to generate, install, and (for an executable
|
|
||||||
work) run the object code and to modify the work, including scripts to
|
|
||||||
control those activities. However, it does not include the work's
|
|
||||||
System Libraries, or general-purpose tools or generally available free
|
|
||||||
programs which are used unmodified in performing those activities but
|
|
||||||
which are not part of the work. For example, Corresponding Source
|
|
||||||
includes interface definition files associated with source files for
|
|
||||||
the work, and the source code for shared libraries and dynamically
|
|
||||||
linked subprograms that the work is specifically designed to require,
|
|
||||||
such as by intimate data communication or control flow between those
|
|
||||||
subprograms and other parts of the work.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The Corresponding Source need not include anything that users
|
|
||||||
can regenerate automatically from other parts of the Corresponding
|
|
||||||
Source.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The Corresponding Source for a work in source code form is that
|
|
||||||
same work.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2. Basic Permissions.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
All rights granted under this License are granted for the term of
|
|
||||||
copyright on the Program, and are irrevocable provided the stated
|
|
||||||
conditions are met. This License explicitly affirms your unlimited
|
|
||||||
permission to run the unmodified Program. The output from running a
|
|
||||||
covered work is covered by this License only if the output, given its
|
|
||||||
content, constitutes a covered work. This License acknowledges your
|
|
||||||
rights of fair use or other equivalent, as provided by copyright law.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You may make, run and propagate covered works that you do not
|
|
||||||
convey, without conditions so long as your license otherwise remains
|
|
||||||
in force. You may convey covered works to others for the sole purpose
|
|
||||||
of having them make modifications exclusively for you, or provide you
|
|
||||||
with facilities for running those works, provided that you comply with
|
|
||||||
the terms of this License in conveying all material for which you do
|
|
||||||
not control copyright. Those thus making or running the covered works
|
|
||||||
for you must do so exclusively on your behalf, under your direction
|
|
||||||
and control, on terms that prohibit them from making any copies of
|
|
||||||
your copyrighted material outside their relationship with you.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Conveying under any other circumstances is permitted solely under
|
|
||||||
the conditions stated below. Sublicensing is not allowed; section 10
|
|
||||||
makes it unnecessary.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
3. Protecting Users' Legal Rights From Anti-Circumvention Law.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
No covered work shall be deemed part of an effective technological
|
|
||||||
measure under any applicable law fulfilling obligations under article
|
|
||||||
11 of the WIPO copyright treaty adopted on 20 December 1996, or
|
|
||||||
similar laws prohibiting or restricting circumvention of such
|
|
||||||
measures.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
When you convey a covered work, you waive any legal power to forbid
|
|
||||||
circumvention of technological measures to the extent such circumvention
|
|
||||||
is effected by exercising rights under this License with respect to
|
|
||||||
the covered work, and you disclaim any intention to limit operation or
|
|
||||||
modification of the work as a means of enforcing, against the work's
|
|
||||||
users, your or third parties' legal rights to forbid circumvention of
|
|
||||||
technological measures.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
4. Conveying Verbatim Copies.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You may convey verbatim copies of the Program's source code as you
|
|
||||||
receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuously and
|
|
||||||
appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate copyright notice;
|
|
||||||
keep intact all notices stating that this License and any
|
|
||||||
non-permissive terms added in accord with section 7 apply to the code;
|
|
||||||
keep intact all notices of the absence of any warranty; and give all
|
|
||||||
recipients a copy of this License along with the Program.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You may charge any price or no price for each copy that you convey,
|
|
||||||
and you may offer support or warranty protection for a fee.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
5. Conveying Modified Source Versions.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You may convey a work based on the Program, or the modifications to
|
|
||||||
produce it from the Program, in the form of source code under the
|
|
||||||
terms of section 4, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
a) The work must carry prominent notices stating that you modified
|
|
||||||
it, and giving a relevant date.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
b) The work must carry prominent notices stating that it is
|
|
||||||
released under this License and any conditions added under section
|
|
||||||
7. This requirement modifies the requirement in section 4 to
|
|
||||||
"keep intact all notices".
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
c) You must license the entire work, as a whole, under this
|
|
||||||
License to anyone who comes into possession of a copy. This
|
|
||||||
License will therefore apply, along with any applicable section 7
|
|
||||||
additional terms, to the whole of the work, and all its parts,
|
|
||||||
regardless of how they are packaged. This License gives no
|
|
||||||
permission to license the work in any other way, but it does not
|
|
||||||
invalidate such permission if you have separately received it.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
d) If the work has interactive user interfaces, each must display
|
|
||||||
Appropriate Legal Notices; however, if the Program has interactive
|
|
||||||
interfaces that do not display Appropriate Legal Notices, your
|
|
||||||
work need not make them do so.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A compilation of a covered work with other separate and independent
|
|
||||||
works, which are not by their nature extensions of the covered work,
|
|
||||||
and which are not combined with it such as to form a larger program,
|
|
||||||
in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, is called an
|
|
||||||
"aggregate" if the compilation and its resulting copyright are not
|
|
||||||
used to limit the access or legal rights of the compilation's users
|
|
||||||
beyond what the individual works permit. Inclusion of a covered work
|
|
||||||
in an aggregate does not cause this License to apply to the other
|
|
||||||
parts of the aggregate.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
6. Conveying Non-Source Forms.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You may convey a covered work in object code form under the terms
|
|
||||||
of sections 4 and 5, provided that you also convey the
|
|
||||||
machine-readable Corresponding Source under the terms of this License,
|
|
||||||
in one of these ways:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
a) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
|
|
||||||
(including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by the
|
|
||||||
Corresponding Source fixed on a durable physical medium
|
|
||||||
customarily used for software interchange.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
b) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
|
|
||||||
(including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by a
|
|
||||||
written offer, valid for at least three years and valid for as
|
|
||||||
long as you offer spare parts or customer support for that product
|
|
||||||
model, to give anyone who possesses the object code either (1) a
|
|
||||||
copy of the Corresponding Source for all the software in the
|
|
||||||
product that is covered by this License, on a durable physical
|
|
||||||
medium customarily used for software interchange, for a price no
|
|
||||||
more than your reasonable cost of physically performing this
|
|
||||||
conveying of source, or (2) access to copy the
|
|
||||||
Corresponding Source from a network server at no charge.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
c) Convey individual copies of the object code with a copy of the
|
|
||||||
written offer to provide the Corresponding Source. This
|
|
||||||
alternative is allowed only occasionally and noncommercially, and
|
|
||||||
only if you received the object code with such an offer, in accord
|
|
||||||
with subsection 6b.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
d) Convey the object code by offering access from a designated
|
|
||||||
place (gratis or for a charge), and offer equivalent access to the
|
|
||||||
Corresponding Source in the same way through the same place at no
|
|
||||||
further charge. You need not require recipients to copy the
|
|
||||||
Corresponding Source along with the object code. If the place to
|
|
||||||
copy the object code is a network server, the Corresponding Source
|
|
||||||
may be on a different server (operated by you or a third party)
|
|
||||||
that supports equivalent copying facilities, provided you maintain
|
|
||||||
clear directions next to the object code saying where to find the
|
|
||||||
Corresponding Source. Regardless of what server hosts the
|
|
||||||
Corresponding Source, you remain obligated to ensure that it is
|
|
||||||
available for as long as needed to satisfy these requirements.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
e) Convey the object code using peer-to-peer transmission, provided
|
|
||||||
you inform other peers where the object code and Corresponding
|
|
||||||
Source of the work are being offered to the general public at no
|
|
||||||
charge under subsection 6d.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A separable portion of the object code, whose source code is excluded
|
|
||||||
from the Corresponding Source as a System Library, need not be
|
|
||||||
included in conveying the object code work.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A "User Product" is either (1) a "consumer product", which means any
|
|
||||||
tangible personal property which is normally used for personal, family,
|
|
||||||
or household purposes, or (2) anything designed or sold for incorporation
|
|
||||||
into a dwelling. In determining whether a product is a consumer product,
|
|
||||||
doubtful cases shall be resolved in favor of coverage. For a particular
|
|
||||||
product received by a particular user, "normally used" refers to a
|
|
||||||
typical or common use of that class of product, regardless of the status
|
|
||||||
of the particular user or of the way in which the particular user
|
|
||||||
actually uses, or expects or is expected to use, the product. A product
|
|
||||||
is a consumer product regardless of whether the product has substantial
|
|
||||||
commercial, industrial or non-consumer uses, unless such uses represent
|
|
||||||
the only significant mode of use of the product.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"Installation Information" for a User Product means any methods,
|
|
||||||
procedures, authorization keys, or other information required to install
|
|
||||||
and execute modified versions of a covered work in that User Product from
|
|
||||||
a modified version of its Corresponding Source. The information must
|
|
||||||
suffice to ensure that the continued functioning of the modified object
|
|
||||||
code is in no case prevented or interfered with solely because
|
|
||||||
modification has been made.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you convey an object code work under this section in, or with, or
|
|
||||||
specifically for use in, a User Product, and the conveying occurs as
|
|
||||||
part of a transaction in which the right of possession and use of the
|
|
||||||
User Product is transferred to the recipient in perpetuity or for a
|
|
||||||
fixed term (regardless of how the transaction is characterized), the
|
|
||||||
Corresponding Source conveyed under this section must be accompanied
|
|
||||||
by the Installation Information. But this requirement does not apply
|
|
||||||
if neither you nor any third party retains the ability to install
|
|
||||||
modified object code on the User Product (for example, the work has
|
|
||||||
been installed in ROM).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The requirement to provide Installation Information does not include a
|
|
||||||
requirement to continue to provide support service, warranty, or updates
|
|
||||||
for a work that has been modified or installed by the recipient, or for
|
|
||||||
the User Product in which it has been modified or installed. Access to a
|
|
||||||
network may be denied when the modification itself materially and
|
|
||||||
adversely affects the operation of the network or violates the rules and
|
|
||||||
protocols for communication across the network.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Corresponding Source conveyed, and Installation Information provided,
|
|
||||||
in accord with this section must be in a format that is publicly
|
|
||||||
documented (and with an implementation available to the public in
|
|
||||||
source code form), and must require no special password or key for
|
|
||||||
unpacking, reading or copying.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
7. Additional Terms.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"Additional permissions" are terms that supplement the terms of this
|
|
||||||
License by making exceptions from one or more of its conditions.
|
|
||||||
Additional permissions that are applicable to the entire Program shall
|
|
||||||
be treated as though they were included in this License, to the extent
|
|
||||||
that they are valid under applicable law. If additional permissions
|
|
||||||
apply only to part of the Program, that part may be used separately
|
|
||||||
under those permissions, but the entire Program remains governed by
|
|
||||||
this License without regard to the additional permissions.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
When you convey a copy of a covered work, you may at your option
|
|
||||||
remove any additional permissions from that copy, or from any part of
|
|
||||||
it. (Additional permissions may be written to require their own
|
|
||||||
removal in certain cases when you modify the work.) You may place
|
|
||||||
additional permissions on material, added by you to a covered work,
|
|
||||||
for which you have or can give appropriate copyright permission.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, for material you
|
|
||||||
add to a covered work, you may (if authorized by the copyright holders of
|
|
||||||
that material) supplement the terms of this License with terms:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
a) Disclaiming warranty or limiting liability differently from the
|
|
||||||
terms of sections 15 and 16 of this License; or
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
b) Requiring preservation of specified reasonable legal notices or
|
|
||||||
author attributions in that material or in the Appropriate Legal
|
|
||||||
Notices displayed by works containing it; or
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
c) Prohibiting misrepresentation of the origin of that material, or
|
|
||||||
requiring that modified versions of such material be marked in
|
|
||||||
reasonable ways as different from the original version; or
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
d) Limiting the use for publicity purposes of names of licensors or
|
|
||||||
authors of the material; or
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
e) Declining to grant rights under trademark law for use of some
|
|
||||||
trade names, trademarks, or service marks; or
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
f) Requiring indemnification of licensors and authors of that
|
|
||||||
material by anyone who conveys the material (or modified versions of
|
|
||||||
it) with contractual assumptions of liability to the recipient, for
|
|
||||||
any liability that these contractual assumptions directly impose on
|
|
||||||
those licensors and authors.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
All other non-permissive additional terms are considered "further
|
|
||||||
restrictions" within the meaning of section 10. If the Program as you
|
|
||||||
received it, or any part of it, contains a notice stating that it is
|
|
||||||
governed by this License along with a term that is a further
|
|
||||||
restriction, you may remove that term. If a license document contains
|
|
||||||
a further restriction but permits relicensing or conveying under this
|
|
||||||
License, you may add to a covered work material governed by the terms
|
|
||||||
of that license document, provided that the further restriction does
|
|
||||||
not survive such relicensing or conveying.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you add terms to a covered work in accord with this section, you
|
|
||||||
must place, in the relevant source files, a statement of the
|
|
||||||
additional terms that apply to those files, or a notice indicating
|
|
||||||
where to find the applicable terms.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Additional terms, permissive or non-permissive, may be stated in the
|
|
||||||
form of a separately written license, or stated as exceptions;
|
|
||||||
the above requirements apply either way.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
8. Termination.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You may not propagate or modify a covered work except as expressly
|
|
||||||
provided under this License. Any attempt otherwise to propagate or
|
|
||||||
modify it is void, and will automatically terminate your rights under
|
|
||||||
this License (including any patent licenses granted under the third
|
|
||||||
paragraph of section 11).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
However, if you cease all violation of this License, then your
|
|
||||||
license from a particular copyright holder is reinstated (a)
|
|
||||||
provisionally, unless and until the copyright holder explicitly and
|
|
||||||
finally terminates your license, and (b) permanently, if the copyright
|
|
||||||
holder fails to notify you of the violation by some reasonable means
|
|
||||||
prior to 60 days after the cessation.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Moreover, your license from a particular copyright holder is
|
|
||||||
reinstated permanently if the copyright holder notifies you of the
|
|
||||||
violation by some reasonable means, this is the first time you have
|
|
||||||
received notice of violation of this License (for any work) from that
|
|
||||||
copyright holder, and you cure the violation prior to 30 days after
|
|
||||||
your receipt of the notice.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Termination of your rights under this section does not terminate the
|
|
||||||
licenses of parties who have received copies or rights from you under
|
|
||||||
this License. If your rights have been terminated and not permanently
|
|
||||||
reinstated, you do not qualify to receive new licenses for the same
|
|
||||||
material under section 10.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
9. Acceptance Not Required for Having Copies.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You are not required to accept this License in order to receive or
|
|
||||||
run a copy of the Program. Ancillary propagation of a covered work
|
|
||||||
occurring solely as a consequence of using peer-to-peer transmission
|
|
||||||
to receive a copy likewise does not require acceptance. However,
|
|
||||||
nothing other than this License grants you permission to propagate or
|
|
||||||
modify any covered work. These actions infringe copyright if you do
|
|
||||||
not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or propagating a
|
|
||||||
covered work, you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
10. Automatic Licensing of Downstream Recipients.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Each time you convey a covered work, the recipient automatically
|
|
||||||
receives a license from the original licensors, to run, modify and
|
|
||||||
propagate that work, subject to this License. You are not responsible
|
|
||||||
for enforcing compliance by third parties with this License.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
An "entity transaction" is a transaction transferring control of an
|
|
||||||
organization, or substantially all assets of one, or subdividing an
|
|
||||||
organization, or merging organizations. If propagation of a covered
|
|
||||||
work results from an entity transaction, each party to that
|
|
||||||
transaction who receives a copy of the work also receives whatever
|
|
||||||
licenses to the work the party's predecessor in interest had or could
|
|
||||||
give under the previous paragraph, plus a right to possession of the
|
|
||||||
Corresponding Source of the work from the predecessor in interest, if
|
|
||||||
the predecessor has it or can get it with reasonable efforts.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You may not impose any further restrictions on the exercise of the
|
|
||||||
rights granted or affirmed under this License. For example, you may
|
|
||||||
not impose a license fee, royalty, or other charge for exercise of
|
|
||||||
rights granted under this License, and you may not initiate litigation
|
|
||||||
(including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that
|
|
||||||
any patent claim is infringed by making, using, selling, offering for
|
|
||||||
sale, or importing the Program or any portion of it.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
11. Patents.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A "contributor" is a copyright holder who authorizes use under this
|
|
||||||
License of the Program or a work on which the Program is based. The
|
|
||||||
work thus licensed is called the contributor's "contributor version".
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A contributor's "essential patent claims" are all patent claims
|
|
||||||
owned or controlled by the contributor, whether already acquired or
|
|
||||||
hereafter acquired, that would be infringed by some manner, permitted
|
|
||||||
by this License, of making, using, or selling its contributor version,
|
|
||||||
but do not include claims that would be infringed only as a
|
|
||||||
consequence of further modification of the contributor version. For
|
|
||||||
purposes of this definition, "control" includes the right to grant
|
|
||||||
patent sublicenses in a manner consistent with the requirements of
|
|
||||||
this License.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Each contributor grants you a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free
|
|
||||||
patent license under the contributor's essential patent claims, to
|
|
||||||
make, use, sell, offer for sale, import and otherwise run, modify and
|
|
||||||
propagate the contents of its contributor version.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In the following three paragraphs, a "patent license" is any express
|
|
||||||
agreement or commitment, however denominated, not to enforce a patent
|
|
||||||
(such as an express permission to practice a patent or covenant not to
|
|
||||||
sue for patent infringement). To "grant" such a patent license to a
|
|
||||||
party means to make such an agreement or commitment not to enforce a
|
|
||||||
patent against the party.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you convey a covered work, knowingly relying on a patent license,
|
|
||||||
and the Corresponding Source of the work is not available for anyone
|
|
||||||
to copy, free of charge and under the terms of this License, through a
|
|
||||||
publicly available network server or other readily accessible means,
|
|
||||||
then you must either (1) cause the Corresponding Source to be so
|
|
||||||
available, or (2) arrange to deprive yourself of the benefit of the
|
|
||||||
patent license for this particular work, or (3) arrange, in a manner
|
|
||||||
consistent with the requirements of this License, to extend the patent
|
|
||||||
license to downstream recipients. "Knowingly relying" means you have
|
|
||||||
actual knowledge that, but for the patent license, your conveying the
|
|
||||||
covered work in a country, or your recipient's use of the covered work
|
|
||||||
in a country, would infringe one or more identifiable patents in that
|
|
||||||
country that you have reason to believe are valid.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If, pursuant to or in connection with a single transaction or
|
|
||||||
arrangement, you convey, or propagate by procuring conveyance of, a
|
|
||||||
covered work, and grant a patent license to some of the parties
|
|
||||||
receiving the covered work authorizing them to use, propagate, modify
|
|
||||||
or convey a specific copy of the covered work, then the patent license
|
|
||||||
you grant is automatically extended to all recipients of the covered
|
|
||||||
work and works based on it.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A patent license is "discriminatory" if it does not include within
|
|
||||||
the scope of its coverage, prohibits the exercise of, or is
|
|
||||||
conditioned on the non-exercise of one or more of the rights that are
|
|
||||||
specifically granted under this License. You may not convey a covered
|
|
||||||
work if you are a party to an arrangement with a third party that is
|
|
||||||
in the business of distributing software, under which you make payment
|
|
||||||
to the third party based on the extent of your activity of conveying
|
|
||||||
the work, and under which the third party grants, to any of the
|
|
||||||
parties who would receive the covered work from you, a discriminatory
|
|
||||||
patent license (a) in connection with copies of the covered work
|
|
||||||
conveyed by you (or copies made from those copies), or (b) primarily
|
|
||||||
for and in connection with specific products or compilations that
|
|
||||||
contain the covered work, unless you entered into that arrangement,
|
|
||||||
or that patent license was granted, prior to 28 March 2007.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Nothing in this License shall be construed as excluding or limiting
|
|
||||||
any implied license or other defenses to infringement that may
|
|
||||||
otherwise be available to you under applicable patent law.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
12. No Surrender of Others' Freedom.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
|
|
||||||
otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
|
|
||||||
excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot convey a
|
|
||||||
covered work so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this
|
|
||||||
License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you may
|
|
||||||
not convey it at all. For example, if you agree to terms that obligate you
|
|
||||||
to collect a royalty for further conveying from those to whom you convey
|
|
||||||
the Program, the only way you could satisfy both those terms and this
|
|
||||||
License would be to refrain entirely from conveying the Program.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
13. Use with the GNU Affero General Public License.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, you have
|
|
||||||
permission to link or combine any covered work with a work licensed
|
|
||||||
under version 3 of the GNU Affero General Public License into a single
|
|
||||||
combined work, and to convey the resulting work. The terms of this
|
|
||||||
License will continue to apply to the part which is the covered work,
|
|
||||||
but the special requirements of the GNU Affero General Public License,
|
|
||||||
section 13, concerning interaction through a network will apply to the
|
|
||||||
combination as such.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
14. Revised Versions of this License.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of
|
|
||||||
the GNU General Public License from time to time. Such new versions will
|
|
||||||
be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to
|
|
||||||
address new problems or concerns.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
|
|
||||||
Program specifies that a certain numbered version of the GNU General
|
|
||||||
Public License "or any later version" applies to it, you have the
|
|
||||||
option of following the terms and conditions either of that numbered
|
|
||||||
version or of any later version published by the Free Software
|
|
||||||
Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of the
|
|
||||||
GNU General Public License, you may choose any version ever published
|
|
||||||
by the Free Software Foundation.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If the Program specifies that a proxy can decide which future
|
|
||||||
versions of the GNU General Public License can be used, that proxy's
|
|
||||||
public statement of acceptance of a version permanently authorizes you
|
|
||||||
to choose that version for the Program.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Later license versions may give you additional or different
|
|
||||||
permissions. However, no additional obligations are imposed on any
|
|
||||||
author or copyright holder as a result of your choosing to follow a
|
|
||||||
later version.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
15. Disclaimer of Warranty.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY
|
|
||||||
APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT
|
|
||||||
HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY
|
|
||||||
OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
|
|
||||||
THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
|
|
||||||
PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM
|
|
||||||
IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF
|
|
||||||
ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
16. Limitation of Liability.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING
|
|
||||||
WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MODIFIES AND/OR CONVEYS
|
|
||||||
THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY
|
|
||||||
GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE
|
|
||||||
USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF
|
|
||||||
DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD
|
|
||||||
PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS),
|
|
||||||
EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
|
|
||||||
SUCH DAMAGES.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
17. Interpretation of Sections 15 and 16.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If the disclaimer of warranty and limitation of liability provided
|
|
||||||
above cannot be given local legal effect according to their terms,
|
|
||||||
reviewing courts shall apply local law that most closely approximates
|
|
||||||
an absolute waiver of all civil liability in connection with the
|
|
||||||
Program, unless a warranty or assumption of liability accompanies a
|
|
||||||
copy of the Program in return for a fee.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the greatest
|
|
||||||
possible use to the public, the best way to achieve this is to make it
|
|
||||||
free software which everyone can redistribute and change under these terms.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is safest
|
|
||||||
to attach them to the start of each source file to most effectively
|
|
||||||
state the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least
|
|
||||||
the "copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<one line to give the program's name and a brief idea of what it does.>
|
|
||||||
Copyright (C) <year> <name of author>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
|
||||||
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
|
|
||||||
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
|
|
||||||
(at your option) any later version.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
|
||||||
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
|
||||||
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
|
||||||
GNU General Public License for more details.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
|
|
||||||
along with this program. If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If the program does terminal interaction, make it output a short
|
|
||||||
notice like this when it starts in an interactive mode:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<program> Copyright (C) <year> <name of author>
|
|
||||||
This program comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details type `show w'.
|
|
||||||
This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it
|
|
||||||
under certain conditions; type `show c' for details.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The hypothetical commands `show w' and `show c' should show the appropriate
|
|
||||||
parts of the General Public License. Of course, your program's commands
|
|
||||||
might be different; for a GUI interface, you would use an "about box".
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or school,
|
|
||||||
if any, to sign a "copyright disclaimer" for the program, if necessary.
|
|
||||||
For more information on this, and how to apply and follow the GNU GPL, see
|
|
||||||
<https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The GNU General Public License does not permit incorporating your program
|
|
||||||
into proprietary programs. If your program is a subroutine library, you
|
|
||||||
may consider it more useful to permit linking proprietary applications with
|
|
||||||
the library. If this is what you want to do, use the GNU Lesser General
|
|
||||||
Public License instead of this License. But first, please read
|
|
||||||
<https://www.gnu.org/licenses/why-not-lgpl.html>.
|
|
||||||
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
@ -1,436 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cells": [
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# Train a new classifier for CoastSat\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"In this notebook the CoastSat classifier is trained using satellite images from new sites. This can improve the accuracy of the shoreline detection if the users are experiencing issues with the default classifier."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"#### Initial settings"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"code_folding": [],
|
|
||||||
"run_control": {
|
|
||||||
"marked": false
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# load modules\n",
|
|
||||||
"%load_ext autoreload\n",
|
|
||||||
"%autoreload 2\n",
|
|
||||||
"import os, sys\n",
|
|
||||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
|
||||||
"import pickle\n",
|
|
||||||
"import warnings\n",
|
|
||||||
"warnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\n",
|
|
||||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"# sklearn modules\n",
|
|
||||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
|
|
||||||
"from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier\n",
|
|
||||||
"from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score\n",
|
|
||||||
"from sklearn.externals import joblib\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"# coastsat modules\n",
|
|
||||||
"sys.path.insert(0, os.pardir)\n",
|
|
||||||
"from coastsat import SDS_download, SDS_preprocess, SDS_shoreline, SDS_tools, SDS_classify\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"# plotting params\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 14\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.rcParams['xtick.labelsize'] = 12\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.rcParams['ytick.labelsize'] = 12\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.rcParams['axes.titlesize'] = 12\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.rcParams['axes.labelsize'] = 12\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"# filepaths \n",
|
|
||||||
"filepath_images = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data')\n",
|
|
||||||
"filepath_train = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'training_data')\n",
|
|
||||||
"filepath_models = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'models')\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"# settings\n",
|
|
||||||
"settings ={'filepath_train':filepath_train, # folder where the labelled images will be stored\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'cloud_thresh':0.9, # percentage of cloudy pixels accepted on the image\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'cloud_mask_issue':True, # set to True if problems with the default cloud mask \n",
|
|
||||||
" 'inputs':{'filepath':filepath_images}, # folder where the images are stored\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'labels':{'sand':1,'white-water':2,'water':3,'other land features':4}, # labels for the classifier\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'colors':{'sand':[1, 0.65, 0],'white-water':[1,0,1],'water':[0.1,0.1,0.7],'other land features':[0.8,0.8,0.1]},\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'tolerance':0.01, # this is the pixel intensity tolerance, when using flood fill for sandy pixels\n",
|
|
||||||
" # set to 0 to select one pixel at a time\n",
|
|
||||||
" }\n",
|
|
||||||
" \n",
|
|
||||||
"# read kml files for the training sites\n",
|
|
||||||
"filepath_sites = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'training_sites')\n",
|
|
||||||
"train_sites = os.listdir(filepath_sites)\n",
|
|
||||||
"print('Sites for training:\\n%s\\n'%train_sites)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"### 1. Download images\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"For each site on which you want to train the classifier, save a .kml file with the region of interest (5 vertices clockwise, first and last points are the same, can be created from Google myMaps) in the folder *\\training_sites*.\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"You only need a few images (~10) to train the classifier."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"code_folding": []
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# dowload images at the sites\n",
|
|
||||||
"dates = ['2019-01-01', '2019-07-01']\n",
|
|
||||||
"sat_list = 'L8'\n",
|
|
||||||
"for site in train_sites:\n",
|
|
||||||
" polygon = SDS_tools.polygon_from_kml(os.path.join(filepath_sites,site))\n",
|
|
||||||
" sitename = site[:site.find('.')] \n",
|
|
||||||
" inputs = {'polygon':polygon, 'dates':dates, 'sat_list':sat_list,\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'sitename':sitename, 'filepath':filepath_images}\n",
|
|
||||||
" print(sitename)\n",
|
|
||||||
" metadata = SDS_download.retrieve_images(inputs)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"### 2. Label images\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"Label the images into 4 classes: sand, white-water, water and other land features.\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"The labelled images are saved in the *filepath_train* and can be visualised afterwards for quality control. If yo make a mistake, don't worry, this can be fixed later by deleting the labelled image."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"code_folding": [],
|
|
||||||
"run_control": {
|
|
||||||
"marked": true
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# label the images with an interactive annotator\n",
|
|
||||||
"%matplotlib qt\n",
|
|
||||||
"for site in train_sites:\n",
|
|
||||||
" settings['inputs']['sitename'] = site[:site.find('.')] \n",
|
|
||||||
" # load metadata\n",
|
|
||||||
" metadata = SDS_download.get_metadata(settings['inputs'])\n",
|
|
||||||
" # label images\n",
|
|
||||||
" SDS_classify.label_images(metadata,settings)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"### 3. Train Classifier\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"A Multilayer Perceptron is trained with *scikit-learn*. To train the classifier, the training data needs to be loaded.\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"You can use the data that was labelled here and/or the original CoastSat training data."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# load labelled images\n",
|
|
||||||
"features = SDS_classify.load_labels(train_sites, settings)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# you can also load the original CoastSat training data (and optionally merge it with your labelled data)\n",
|
|
||||||
"with open(os.path.join(settings['filepath_train'], 'CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl'), 'rb') as f:\n",
|
|
||||||
" features_original = pickle.load(f)\n",
|
|
||||||
"for key in features_original.keys():\n",
|
|
||||||
" print('%s : %d pixels'%(key,len(features_original[key])))"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"Run this section to combine the original training data with your labelled data:"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"code_folding": []
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# add the white-water data from the original training data\n",
|
|
||||||
"features['white-water'] = np.append(features['white-water'], features_original['white-water'], axis=0)\n",
|
|
||||||
"# or merge all the classes\n",
|
|
||||||
"# for key in features.keys():\n",
|
|
||||||
"# features[key] = np.append(features[key], features_original[key], axis=0)\n",
|
|
||||||
"# features = features_original \n",
|
|
||||||
"for key in features.keys():\n",
|
|
||||||
" print('%s : %d pixels'%(key,len(features[key])))"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"[OPTIONAL] As the classes do not have the same number of pixels, it is good practice to subsample the very large classes (in this case 'water' and 'other land features'):"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# subsample randomly the land and water classes\n",
|
|
||||||
"# as the most important class is 'sand', the number of samples should be close to the number of sand pixels\n",
|
|
||||||
"n_samples = 5000\n",
|
|
||||||
"for key in ['water', 'other land features']:\n",
|
|
||||||
" features[key] = features[key][np.random.choice(features[key].shape[0], n_samples, replace=False),:]\n",
|
|
||||||
"# print classes again\n",
|
|
||||||
"for key in features.keys():\n",
|
|
||||||
" print('%s : %d pixels'%(key,len(features[key])))"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"When the labelled data is ready, format it into X, a matrix of features, and y, a vector of labels:"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"code_folding": [],
|
|
||||||
"run_control": {
|
|
||||||
"marked": true
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# format into X (features) and y (labels) \n",
|
|
||||||
"classes = ['sand','white-water','water','other land features']\n",
|
|
||||||
"labels = [1,2,3,0]\n",
|
|
||||||
"X,y = SDS_classify.format_training_data(features, classes, labels)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"Divide the dataset into train and test: train on 70% of the data and evaluate on the other 30%:"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"code_folding": [],
|
|
||||||
"run_control": {
|
|
||||||
"marked": true
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# divide in train and test and evaluate the classifier\n",
|
|
||||||
"X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, shuffle=True, random_state=0)\n",
|
|
||||||
"classifier = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(100,50), solver='adam')\n",
|
|
||||||
"classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)\n",
|
|
||||||
"print('Accuracy: %0.4f' % classifier.score(X_test,y_test))"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"[OPTIONAL] A more robust evaluation is 10-fold cross-validation (may take a few minutes to run):"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"code_folding": [],
|
|
||||||
"run_control": {
|
|
||||||
"marked": true
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# cross-validation\n",
|
|
||||||
"scores = cross_val_score(classifier, X, y, cv=10)\n",
|
|
||||||
"print('Accuracy: %0.4f (+/- %0.4f)' % (scores.mean(), scores.std() * 2))"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"Plot a confusion matrix:"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"code_folding": []
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# plot confusion matrix\n",
|
|
||||||
"%matplotlib inline\n",
|
|
||||||
"y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)\n",
|
|
||||||
"SDS_classify.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred,\n",
|
|
||||||
" classes=['other land features','sand','white-water','water'],\n",
|
|
||||||
" normalize=False);"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"When satisfied with the accuracy and confusion matrix, train the model using ALL the training data and save it:"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# train with all the data and save the final classifier\n",
|
|
||||||
"classifier = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(100,50), solver='adam')\n",
|
|
||||||
"classifier.fit(X,y)\n",
|
|
||||||
"joblib.dump(classifier, os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_test.pkl'))"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"### 4. Evaluate the classifier\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"Load a classifier that you have trained (specify the classifiers filename) and evaluate it on the satellite images.\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"This section will save the output of the classification for each site in a directory named \\evaluation."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# load and evaluate a classifier\n",
|
|
||||||
"%matplotlib qt\n",
|
|
||||||
"classifier = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_test.pkl'))\n",
|
|
||||||
"settings['output_epsg'] = 3857\n",
|
|
||||||
"settings['min_beach_area'] = 4500\n",
|
|
||||||
"settings['buffer_size'] = 200\n",
|
|
||||||
"settings['min_length_sl'] = 200\n",
|
|
||||||
"settings['cloud_thresh'] = 0.5\n",
|
|
||||||
"# visualise the classified images\n",
|
|
||||||
"for site in train_sites:\n",
|
|
||||||
" settings['inputs']['sitename'] = site[:site.find('.')] \n",
|
|
||||||
" # load metadata\n",
|
|
||||||
" metadata = SDS_download.get_metadata(settings['inputs'])\n",
|
|
||||||
" # plot the classified images\n",
|
|
||||||
" SDS_classify.evaluate_classifier(classifier,metadata,settings)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
],
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"kernelspec": {
|
|
||||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
|
||||||
"language": "python",
|
|
||||||
"name": "python3"
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"language_info": {
|
|
||||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
|
||||||
"name": "ipython",
|
|
||||||
"version": 3
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
|
||||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
|
||||||
"name": "python",
|
|
||||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
|
||||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
|
||||||
"version": "3.7.3"
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"toc": {
|
|
||||||
"base_numbering": 1,
|
|
||||||
"nav_menu": {},
|
|
||||||
"number_sections": false,
|
|
||||||
"sideBar": true,
|
|
||||||
"skip_h1_title": false,
|
|
||||||
"title_cell": "Table of Contents",
|
|
||||||
"title_sidebar": "Contents",
|
|
||||||
"toc_cell": false,
|
|
||||||
"toc_position": {},
|
|
||||||
"toc_section_display": true,
|
|
||||||
"toc_window_display": false
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"varInspector": {
|
|
||||||
"cols": {
|
|
||||||
"lenName": 16,
|
|
||||||
"lenType": 16,
|
|
||||||
"lenVar": 40
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"kernels_config": {
|
|
||||||
"python": {
|
|
||||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": "",
|
|
||||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "del ",
|
|
||||||
"library": "var_list.py",
|
|
||||||
"varRefreshCmd": "print(var_dic_list())"
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"r": {
|
|
||||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": ") ",
|
|
||||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "rm(",
|
|
||||||
"library": "var_list.r",
|
|
||||||
"varRefreshCmd": "cat(var_dic_list()) "
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"types_to_exclude": [
|
|
||||||
"module",
|
|
||||||
"function",
|
|
||||||
"builtin_function_or_method",
|
|
||||||
"instance",
|
|
||||||
"_Feature"
|
|
||||||
],
|
|
||||||
"window_display": false
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
|
||||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
### Train a new CoastSat classifier
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
CoastSat's shoreline mapping alogorithm uses an image classification scheme to label each pixel into 4 classes: sand, water, white-water and other land features. While this classifier has been trained using a wide range of different beaches, it may be that it does not perform very well at specific sites that it has never seen before.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For this reason, we provide the possibility to re-train the classifier by adding labelled data from new sites. This can be done very quickly and easily by using this [Jupyter Notebook](https://github.com/kvos/CoastSat/blob/CoastSat-classifier/classification/train_new_classifier.ipynb).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Let's take this example, Playa Chañaral in the Atacama desert, Chile. At this beach, the sand is extremely white and the default classifier is not able to label correctly the sand pixels:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
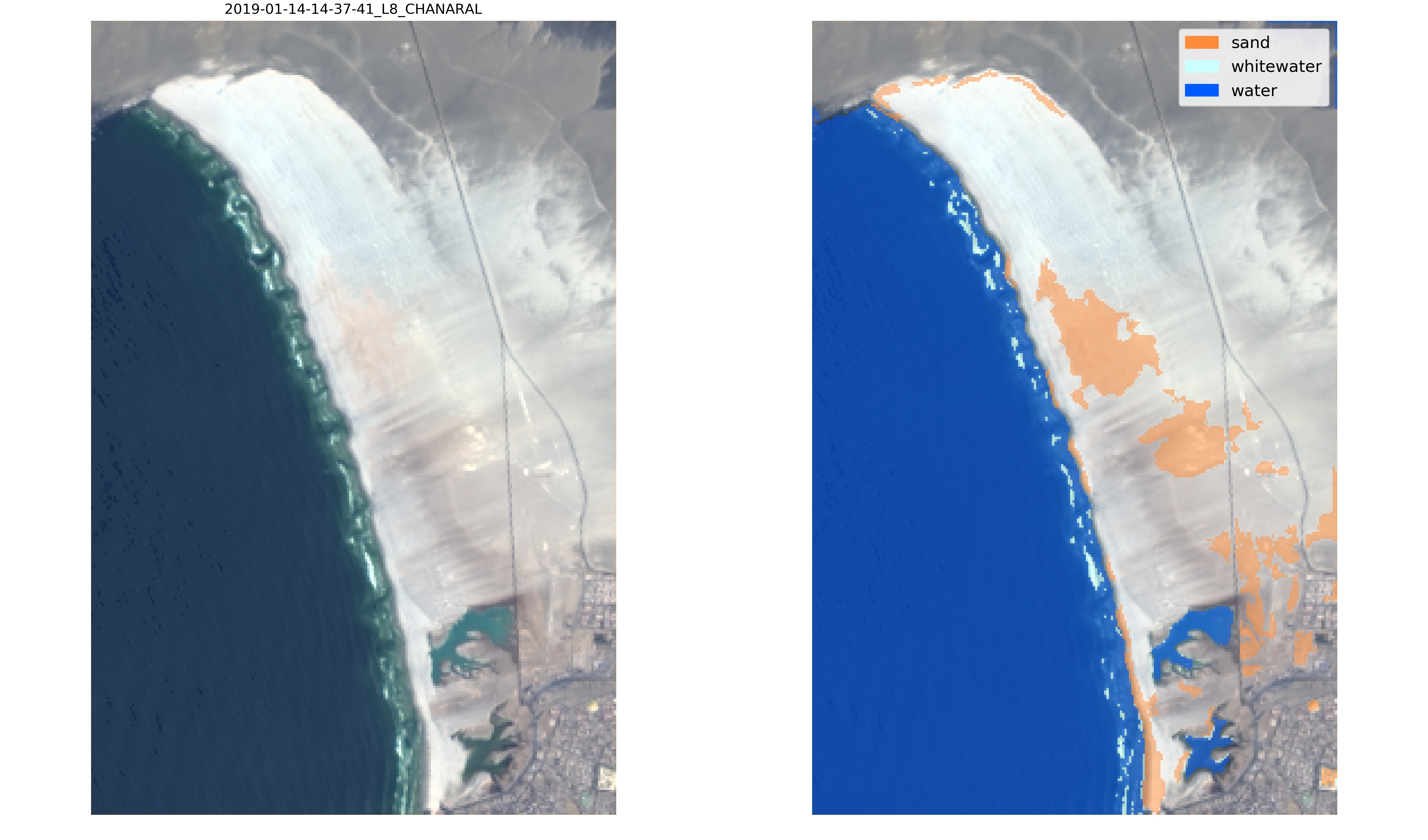
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To overcome this issue, we can generate training data for this site by labelling new images.
|
|
||||||
Download the new images to be labelled and then call the function `SDS_classify.label_images(metadata,settings)`, an interactive tool will pop up for quick and efficient labelling:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You only need to label sand pixels, as water and white-water looks the same everywhere in the world. You can label 2-3 images in a few minutes with the interactive tool and then the new labels can be used to re-train the classifier. The labelling tool uses *flood fill* to speed up the selection of sand pixels and you can tune the tolerance of the *flood fill* function in `settings['tolerance']`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You can then train a classifier with the newly labelled data.
|
|
||||||
Different classification schemes exist, in this example we use a Multilayer Perceptron (Neural Network) with 2 layers, one of 100 neurons and one of 50 neurons. The training data is first divided in train and split, so that we can evaluate the accuracy of the classifier and plot a confusion matrix.
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, shuffle=True, random_state=0)
|
|
||||||
classifier = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(100,50), solver='adam')
|
|
||||||
classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
|
|
||||||
print('Accuracy: %0.4f' % classifier.score(X_test,y_test))
|
|
||||||
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
|
|
||||||
label_names = ['other land features','sand','white-water','water']
|
|
||||||
SDS_classify.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred,classes=label_names,normalize=False);
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/7217258/69406723-d9c2eb00-0d56-11ea-9eff-4422dc377638.png" alt="confusion_matrix" width="400"/>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Finally, the new classifier can be applied to the satellite images, for visual inspection by calling the function `SDS_classify.evaluate_classifier(classifier,metadata,settings)` which will save the classified images in */evaluation*:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
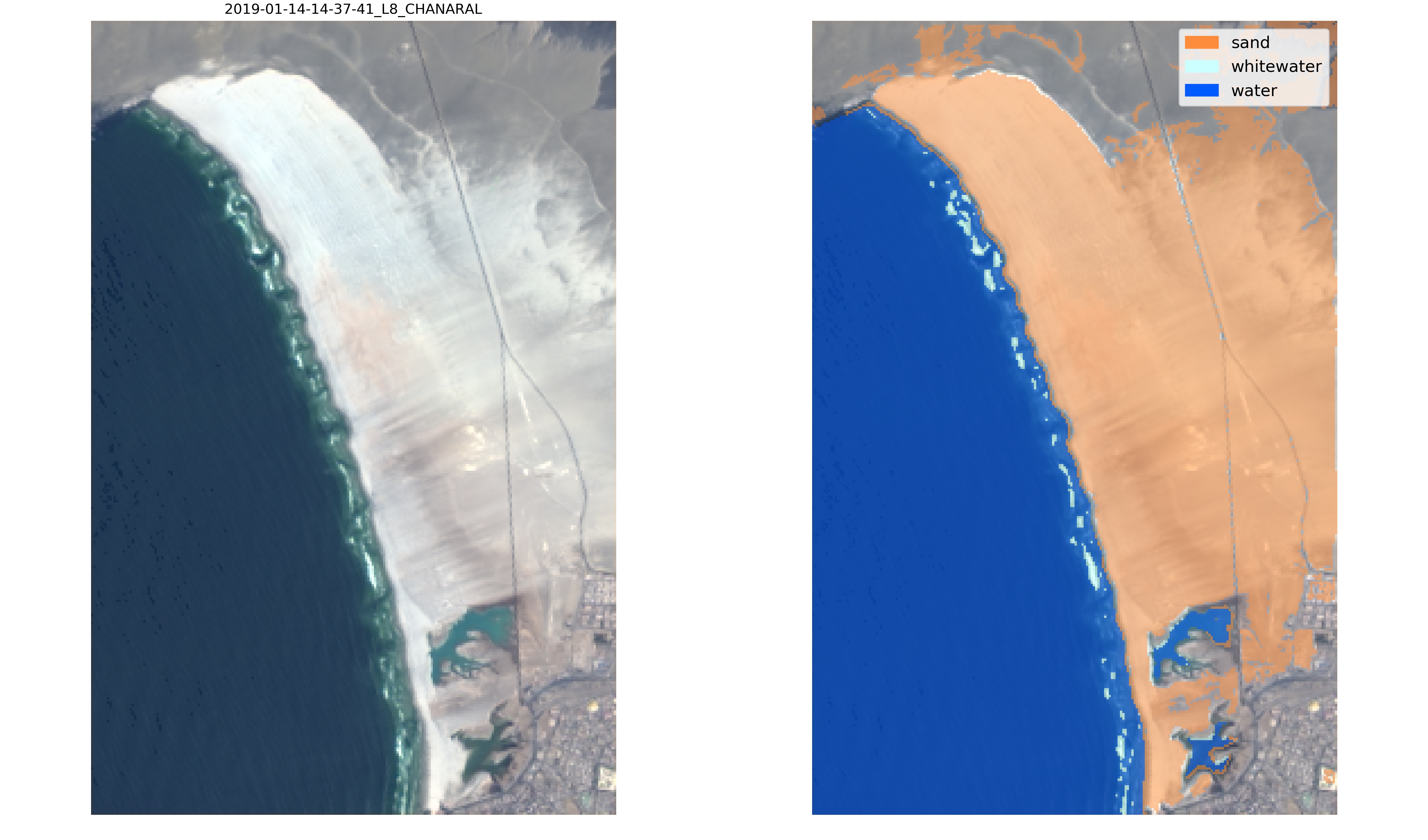
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now, this new classifier labels correctly the sandy pixels of the Atacama desert and will provide more accurate satellite-derived shorelines at this beach!
|
|
||||||
Binary file not shown.
@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
|
||||||
<kml xmlns="http://www.opengis.net/kml/2.2">
|
|
||||||
<Document>
|
|
||||||
<name>site5</name>
|
|
||||||
<Style id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal">
|
|
||||||
<LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>ff000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<width>1.2</width>
|
|
||||||
</LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>4d000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<fill>1</fill>
|
|
||||||
<outline>1</outline>
|
|
||||||
</PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
<text><![CDATA[<h3>$[name]</h3>]]></text>
|
|
||||||
</BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
</Style>
|
|
||||||
<Style id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight">
|
|
||||||
<LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>ff000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<width>1.8</width>
|
|
||||||
</LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>4d000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<fill>1</fill>
|
|
||||||
<outline>1</outline>
|
|
||||||
</PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
<text><![CDATA[<h3>$[name]</h3>]]></text>
|
|
||||||
</BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
</Style>
|
|
||||||
<StyleMap id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc">
|
|
||||||
<Pair>
|
|
||||||
<key>normal</key>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
</Pair>
|
|
||||||
<Pair>
|
|
||||||
<key>highlight</key>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
</Pair>
|
|
||||||
</StyleMap>
|
|
||||||
<Placemark>
|
|
||||||
<name>Polygon</name>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
<Polygon>
|
|
||||||
<outerBoundaryIs>
|
|
||||||
<LinearRing>
|
|
||||||
<tessellate>1</tessellate>
|
|
||||||
<coordinates>
|
|
||||||
153.6170468,-28.6510018,0
|
|
||||||
153.6134419,-28.6621487,0
|
|
||||||
153.6297498,-28.6665921,0
|
|
||||||
153.6333547,-28.655295,0
|
|
||||||
153.6170468,-28.6510018,0
|
|
||||||
</coordinates>
|
|
||||||
</LinearRing>
|
|
||||||
</outerBoundaryIs>
|
|
||||||
</Polygon>
|
|
||||||
</Placemark>
|
|
||||||
</Document>
|
|
||||||
</kml>
|
|
||||||
@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
|
||||||
<kml xmlns="http://www.opengis.net/kml/2.2">
|
|
||||||
<Document>
|
|
||||||
<name>site2</name>
|
|
||||||
<Style id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal">
|
|
||||||
<LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>ff000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<width>1.2</width>
|
|
||||||
</LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>4d000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<fill>1</fill>
|
|
||||||
<outline>1</outline>
|
|
||||||
</PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
<text><![CDATA[<h3>$[name]</h3>]]></text>
|
|
||||||
</BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
</Style>
|
|
||||||
<Style id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight">
|
|
||||||
<LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>ff000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<width>1.8</width>
|
|
||||||
</LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>4d000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<fill>1</fill>
|
|
||||||
<outline>1</outline>
|
|
||||||
</PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
<text><![CDATA[<h3>$[name]</h3>]]></text>
|
|
||||||
</BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
</Style>
|
|
||||||
<StyleMap id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc">
|
|
||||||
<Pair>
|
|
||||||
<key>normal</key>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
</Pair>
|
|
||||||
<Pair>
|
|
||||||
<key>highlight</key>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
</Pair>
|
|
||||||
</StyleMap>
|
|
||||||
<Placemark>
|
|
||||||
<name>Polygon</name>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
<Polygon>
|
|
||||||
<outerBoundaryIs>
|
|
||||||
<LinearRing>
|
|
||||||
<tessellate>1</tessellate>
|
|
||||||
<coordinates>
|
|
||||||
151.7604354,-32.9330576,0
|
|
||||||
151.7480758,-32.9411254,0
|
|
||||||
151.7612079,-32.953226,0
|
|
||||||
151.7750266,-32.9451592,0
|
|
||||||
151.7604354,-32.9330576,0
|
|
||||||
</coordinates>
|
|
||||||
</LinearRing>
|
|
||||||
</outerBoundaryIs>
|
|
||||||
</Polygon>
|
|
||||||
</Placemark>
|
|
||||||
</Document>
|
|
||||||
</kml>
|
|
||||||
@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
|
||||||
<kml xmlns="http://www.opengis.net/kml/2.2">
|
|
||||||
<Document>
|
|
||||||
<name>site4</name>
|
|
||||||
<Style id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal">
|
|
||||||
<LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>ff000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<width>1.2</width>
|
|
||||||
</LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>4d000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<fill>1</fill>
|
|
||||||
<outline>1</outline>
|
|
||||||
</PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
<text><![CDATA[<h3>$[name]</h3>]]></text>
|
|
||||||
</BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
</Style>
|
|
||||||
<Style id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight">
|
|
||||||
<LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>ff000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<width>1.8</width>
|
|
||||||
</LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>4d000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<fill>1</fill>
|
|
||||||
<outline>1</outline>
|
|
||||||
</PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
<text><![CDATA[<h3>$[name]</h3>]]></text>
|
|
||||||
</BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
</Style>
|
|
||||||
<StyleMap id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc">
|
|
||||||
<Pair>
|
|
||||||
<key>normal</key>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
</Pair>
|
|
||||||
<Pair>
|
|
||||||
<key>highlight</key>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
</Pair>
|
|
||||||
</StyleMap>
|
|
||||||
<Placemark>
|
|
||||||
<name>Polygon</name>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
<Polygon>
|
|
||||||
<outerBoundaryIs>
|
|
||||||
<LinearRing>
|
|
||||||
<tessellate>1</tessellate>
|
|
||||||
<coordinates>
|
|
||||||
153.0949026,-30.3586611,0
|
|
||||||
153.0927568,-30.3715099,0
|
|
||||||
153.1108242,-30.3727688,0
|
|
||||||
153.1124979,-30.3600312,0
|
|
||||||
153.0949026,-30.3586611,0
|
|
||||||
</coordinates>
|
|
||||||
</LinearRing>
|
|
||||||
</outerBoundaryIs>
|
|
||||||
</Polygon>
|
|
||||||
</Placemark>
|
|
||||||
</Document>
|
|
||||||
</kml>
|
|
||||||
@ -1,624 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
This module contains functions to label satellite images, use the labels to
|
|
||||||
train a pixel-wise classifier and evaluate the classifier
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# load modules
|
|
||||||
import os
|
|
||||||
import numpy as np
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.cm as cm
|
|
||||||
from matplotlib.widgets import LassoSelector
|
|
||||||
from matplotlib import path
|
|
||||||
import pickle
|
|
||||||
import pdb
|
|
||||||
import warnings
|
|
||||||
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# image processing modules
|
|
||||||
from skimage.segmentation import flood
|
|
||||||
from skimage import morphology
|
|
||||||
from pylab import ginput
|
|
||||||
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
|
|
||||||
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# CoastSat modules
|
|
||||||
from coastsat import SDS_preprocess, SDS_shoreline, SDS_tools
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class SelectFromImage(object):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Class used to draw the lassos on the images with two methods:
|
|
||||||
- onselect: save the pixels inside the selection
|
|
||||||
- disconnect: stop drawing lassos on the image
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
# initialize lasso selection class
|
|
||||||
def __init__(self, ax, implot, color=[1,1,1]):
|
|
||||||
self.canvas = ax.figure.canvas
|
|
||||||
self.implot = implot
|
|
||||||
self.array = implot.get_array()
|
|
||||||
xv, yv = np.meshgrid(np.arange(self.array.shape[1]),np.arange(self.array.shape[0]))
|
|
||||||
self.pix = np.vstack( (xv.flatten(), yv.flatten()) ).T
|
|
||||||
self.ind = []
|
|
||||||
self.im_bool = np.zeros((self.array.shape[0], self.array.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
self.color = color
|
|
||||||
self.lasso = LassoSelector(ax, onselect=self.onselect)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def onselect(self, verts):
|
|
||||||
# find pixels contained in the lasso
|
|
||||||
p = path.Path(verts)
|
|
||||||
self.ind = p.contains_points(self.pix, radius=1)
|
|
||||||
# color selected pixels
|
|
||||||
array_list = []
|
|
||||||
for k in range(self.array.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
array2d = self.array[:,:,k]
|
|
||||||
lin = np.arange(array2d.size)
|
|
||||||
new_array2d = array2d.flatten()
|
|
||||||
new_array2d[lin[self.ind]] = self.color[k]
|
|
||||||
array_list.append(new_array2d.reshape(array2d.shape))
|
|
||||||
self.array = np.stack(array_list,axis=2)
|
|
||||||
self.implot.set_data(self.array)
|
|
||||||
self.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
# update boolean image with selected pixels
|
|
||||||
vec_bool = self.im_bool.flatten()
|
|
||||||
vec_bool[lin[self.ind]] = 1
|
|
||||||
self.im_bool = vec_bool.reshape(self.im_bool.shape)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def disconnect(self):
|
|
||||||
self.lasso.disconnect_events()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def label_images(metadata,settings):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Load satellite images and interactively label different classes (hard-coded)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2019
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
metadata: dict
|
|
||||||
contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'cloud_thresh': float
|
|
||||||
value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
|
|
||||||
the cropped image that is accepted
|
|
||||||
'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
|
|
||||||
True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
|
|
||||||
are erroneously being masked on the images
|
|
||||||
'labels': dict
|
|
||||||
list of label names (key) and label numbers (value) for each class
|
|
||||||
'flood_fill': boolean
|
|
||||||
True to use the flood_fill functionality when labelling sand pixels
|
|
||||||
'tolerance': float
|
|
||||||
tolerance value for flood fill when labelling the sand pixels
|
|
||||||
'filepath_train': str
|
|
||||||
directory in which to save the labelled data
|
|
||||||
'inputs': dict
|
|
||||||
input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
Stores the labelled data in the specified directory
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
filepath_train = settings['filepath_train']
|
|
||||||
# initialize figure
|
|
||||||
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=[17,10], tight_layout=True,sharex=True,
|
|
||||||
sharey=True)
|
|
||||||
mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
|
|
||||||
mng.window.showMaximized()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop through satellites
|
|
||||||
for satname in metadata.keys():
|
|
||||||
filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
|
|
||||||
filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
|
|
||||||
# loop through images
|
|
||||||
for i in range(len(filenames)):
|
|
||||||
# image filename
|
|
||||||
fn = SDS_tools.get_filenames(filenames[i],filepath, satname)
|
|
||||||
# read and preprocess image
|
|
||||||
im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn, satname, settings['cloud_mask_issue'])
|
|
||||||
# calculate cloud cover
|
|
||||||
cloud_cover = np.divide(sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int))),
|
|
||||||
(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
# skip image if cloud cover is above threshold
|
|
||||||
if cloud_cover > settings['cloud_thresh'] or cloud_cover == 1:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
# get individual RGB image
|
|
||||||
im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
|
|
||||||
im_NDVI = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,3], im_ms[:,:,2], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
im_NDWI = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,3], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
# initialise labels
|
|
||||||
im_viz = im_RGB.copy()
|
|
||||||
im_labels = np.zeros([im_RGB.shape[0],im_RGB.shape[1]])
|
|
||||||
# show RGB image
|
|
||||||
ax.axis('off')
|
|
||||||
ax.imshow(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
implot = ax.imshow(im_viz, alpha=0.6)
|
|
||||||
filename = filenames[i][:filenames[i].find('.')][:-4]
|
|
||||||
ax.set_title(filename)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
# select image to label
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
# set a key event to accept/reject the detections (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/15033071)
|
|
||||||
# this variable needs to be immuatable so we can access it after the keypress event
|
|
||||||
key_event = {}
|
|
||||||
def press(event):
|
|
||||||
# store what key was pressed in the dictionary
|
|
||||||
key_event['pressed'] = event.key
|
|
||||||
# let the user press a key, right arrow to keep the image, left arrow to skip it
|
|
||||||
# to break the loop the user can press 'escape'
|
|
||||||
while True:
|
|
||||||
btn_keep = ax.text(1.1, 0.9, 'keep ⇨', size=12, ha="right", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=ax.transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
btn_skip = ax.text(-0.1, 0.9, '⇦ skip', size=12, ha="left", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=ax.transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
btn_esc = ax.text(0.5, 0, '<esc> to quit', size=12, ha="center", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=ax.transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
|
|
||||||
plt.waitforbuttonpress()
|
|
||||||
# after button is pressed, remove the buttons
|
|
||||||
btn_skip.remove()
|
|
||||||
btn_keep.remove()
|
|
||||||
btn_esc.remove()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# keep/skip image according to the pressed key, 'escape' to break the loop
|
|
||||||
if key_event.get('pressed') == 'right':
|
|
||||||
skip_image = False
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'left':
|
|
||||||
skip_image = True
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
|
|
||||||
plt.close()
|
|
||||||
raise StopIteration('User cancelled labelling images')
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
plt.waitforbuttonpress()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if user decided to skip show the next image
|
|
||||||
if skip_image:
|
|
||||||
ax.clear()
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
# otherwise label this image
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
# digitize sandy pixels
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
ax.set_title('Click on SAND pixels (flood fill activated, tolerance = %.2f)\nwhen finished press <Enter>'%settings['tolerance'])
|
|
||||||
# create erase button, if you click there it delets the last selection
|
|
||||||
btn_erase = ax.text(im_ms.shape[1], 0, 'Erase', size=20, ha='right', va='top',
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
color_sand = settings['colors']['sand']
|
|
||||||
sand_pixels = []
|
|
||||||
while 1:
|
|
||||||
seed = ginput(n=1, timeout=0, show_clicks=True)
|
|
||||||
# if empty break the loop and go to next label
|
|
||||||
if len(seed) == 0:
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# round to pixel location
|
|
||||||
seed = np.round(seed[0]).astype(int)
|
|
||||||
# if user clicks on erase, delete the last selection
|
|
||||||
if seed[0] > 0.95*im_ms.shape[1] and seed[1] < 0.05*im_ms.shape[0]:
|
|
||||||
if len(sand_pixels) > 0:
|
|
||||||
im_labels[sand_pixels[-1]] = 0
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_viz[sand_pixels[-1],k] = im_RGB[sand_pixels[-1],k]
|
|
||||||
implot.set_data(im_viz)
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
del sand_pixels[-1]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# otherwise label the selected sand pixels
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# flood fill the NDVI and the NDWI
|
|
||||||
fill_NDVI = flood(im_NDVI, (seed[1],seed[0]), tolerance=settings['tolerance'])
|
|
||||||
fill_NDWI = flood(im_NDWI, (seed[1],seed[0]), tolerance=settings['tolerance'])
|
|
||||||
# compute the intersection of the two masks
|
|
||||||
fill_sand = np.logical_and(fill_NDVI, fill_NDWI)
|
|
||||||
im_labels[fill_sand] = settings['labels']['sand']
|
|
||||||
sand_pixels.append(fill_sand)
|
|
||||||
# show the labelled pixels
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_viz[im_labels==settings['labels']['sand'],k] = color_sand[k]
|
|
||||||
implot.set_data(im_viz)
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
# digitize white-water pixels
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
color_ww = settings['colors']['white-water']
|
|
||||||
ax.set_title('Click on individual WHITE-WATER pixels (no flood fill)\nwhen finished press <Enter>')
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
ww_pixels = []
|
|
||||||
while 1:
|
|
||||||
seed = ginput(n=1, timeout=0, show_clicks=True)
|
|
||||||
# if empty break the loop and go to next label
|
|
||||||
if len(seed) == 0:
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# round to pixel location
|
|
||||||
seed = np.round(seed[0]).astype(int)
|
|
||||||
# if user clicks on erase, delete the last labelled pixels
|
|
||||||
if seed[0] > 0.95*im_ms.shape[1] and seed[1] < 0.05*im_ms.shape[0]:
|
|
||||||
if len(ww_pixels) > 0:
|
|
||||||
im_labels[ww_pixels[-1][1],ww_pixels[-1][0]] = 0
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_viz[ww_pixels[-1][1],ww_pixels[-1][0],k] = im_RGB[ww_pixels[-1][1],ww_pixels[-1][0],k]
|
|
||||||
implot.set_data(im_viz)
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
del ww_pixels[-1]
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
im_labels[seed[1],seed[0]] = settings['labels']['white-water']
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_viz[seed[1],seed[0],k] = color_ww[k]
|
|
||||||
implot.set_data(im_viz)
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
ww_pixels.append(seed)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
im_sand_ww = im_viz.copy()
|
|
||||||
btn_erase.set(text='<Esc> to Erase', fontsize=12)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
# digitize water pixels (with lassos)
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
color_water = settings['colors']['water']
|
|
||||||
ax.set_title('Click and hold to draw lassos and select WATER pixels\nwhen finished press <Enter>')
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
selector_water = SelectFromImage(ax, implot, color_water)
|
|
||||||
key_event = {}
|
|
||||||
while True:
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
|
|
||||||
plt.waitforbuttonpress()
|
|
||||||
if key_event.get('pressed') == 'enter':
|
|
||||||
selector_water.disconnect()
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
|
|
||||||
selector_water.array = im_sand_ww
|
|
||||||
implot.set_data(selector_water.array)
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
selector_water.implot = implot
|
|
||||||
selector_water.im_bool = np.zeros((selector_water.array.shape[0], selector_water.array.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
selector_water.ind=[]
|
|
||||||
# update im_viz and im_labels
|
|
||||||
im_viz = selector_water.array
|
|
||||||
selector_water.im_bool = selector_water.im_bool.astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
im_labels[selector_water.im_bool] = settings['labels']['water']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
im_sand_ww_water = im_viz.copy()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
# digitize land pixels (with lassos)
|
|
||||||
##############################################################
|
|
||||||
color_land = settings['colors']['other land features']
|
|
||||||
ax.set_title('Click and hold to draw lassos and select OTHER LAND pixels\nwhen finished press <Enter>')
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
selector_land = SelectFromImage(ax, implot, color_land)
|
|
||||||
key_event = {}
|
|
||||||
while True:
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
|
|
||||||
plt.waitforbuttonpress()
|
|
||||||
if key_event.get('pressed') == 'enter':
|
|
||||||
selector_land.disconnect()
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
|
|
||||||
selector_land.array = im_sand_ww_water
|
|
||||||
implot.set_data(selector_land.array)
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
selector_land.implot = implot
|
|
||||||
selector_land.im_bool = np.zeros((selector_land.array.shape[0], selector_land.array.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
selector_land.ind=[]
|
|
||||||
# update im_viz and im_labels
|
|
||||||
im_viz = selector_land.array
|
|
||||||
selector_land.im_bool = selector_land.im_bool.astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
im_labels[selector_land.im_bool] = settings['labels']['other land features']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save labelled image
|
|
||||||
ax.set_title(filename)
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
|
|
||||||
fp = os.path.join(filepath_train,settings['inputs']['sitename'])
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(fp):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(fp)
|
|
||||||
fig.savefig(os.path.join(fp,filename+'.jpg'), dpi=150)
|
|
||||||
ax.clear()
|
|
||||||
# save labels and features
|
|
||||||
features = dict([])
|
|
||||||
for key in settings['labels'].keys():
|
|
||||||
im_bool = im_labels == settings['labels'][key]
|
|
||||||
features[key] = SDS_shoreline.calculate_features(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_bool)
|
|
||||||
training_data = {'labels':im_labels, 'features':features, 'label_ids':settings['labels']}
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(fp, filename + '.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
|
|
||||||
pickle.dump(training_data,f)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# close figure when finished
|
|
||||||
plt.close(fig)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def load_labels(train_sites, settings):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Load the labelled data from the different training sites
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2019
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
train_sites: list of str
|
|
||||||
sites to be loaded
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'labels': dict
|
|
||||||
list of label names (key) and label numbers (value) for each class
|
|
||||||
'filepath_train': str
|
|
||||||
directory in which to save the labelled data
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
features: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the features for each labelled pixel
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
filepath_train = settings['filepath_train']
|
|
||||||
# initialize the features dict
|
|
||||||
features = dict([])
|
|
||||||
n_features = 20
|
|
||||||
first_row = np.nan*np.ones((1,n_features))
|
|
||||||
for key in settings['labels'].keys():
|
|
||||||
features[key] = first_row
|
|
||||||
# loop through each site
|
|
||||||
for site in train_sites:
|
|
||||||
sitename = site[:site.find('.')]
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_train,sitename)
|
|
||||||
if os.path.exists(filepath):
|
|
||||||
list_files = os.listdir(filepath)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
# make a new list with only the .pkl files (no .jpg)
|
|
||||||
list_files_pkl = []
|
|
||||||
for file in list_files:
|
|
||||||
if '.pkl' in file:
|
|
||||||
list_files_pkl.append(file)
|
|
||||||
# load and append the training data to the features dict
|
|
||||||
for file in list_files_pkl:
|
|
||||||
# read file
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath, file), 'rb') as f:
|
|
||||||
labelled_data = pickle.load(f)
|
|
||||||
for key in labelled_data['features'].keys():
|
|
||||||
if len(labelled_data['features'][key])>0: # check that is not empty
|
|
||||||
# append rows
|
|
||||||
features[key] = np.append(features[key],
|
|
||||||
labelled_data['features'][key], axis=0)
|
|
||||||
# remove the first row (initialized with nans) and print how many pixels
|
|
||||||
print('Number of pixels per class in training data:')
|
|
||||||
for key in features.keys():
|
|
||||||
features[key] = features[key][1:,:]
|
|
||||||
print('%s : %d pixels'%(key,len(features[key])))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return features
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def format_training_data(features, classes, labels):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Format the labelled data in an X features matrix and a y labels vector, so
|
|
||||||
that it can be used for training an ML model.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2019
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
features: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the features for each labelled pixel
|
|
||||||
classes: list of str
|
|
||||||
names of the classes
|
|
||||||
labels: list of int
|
|
||||||
int value associated with each class (in the same order as classes)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
X: np.array
|
|
||||||
matrix features along the columns and pixels along the rows
|
|
||||||
y: np.array
|
|
||||||
vector with the labels corresponding to each row of X
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# initialize X and y
|
|
||||||
X = np.nan*np.ones((1,features[classes[0]].shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
y = np.nan*np.ones((1,1))
|
|
||||||
# append row of features to X and corresponding label to y
|
|
||||||
for i,key in enumerate(classes):
|
|
||||||
y = np.append(y, labels[i]*np.ones((features[key].shape[0],1)), axis=0)
|
|
||||||
X = np.append(X, features[key], axis=0)
|
|
||||||
# remove first row
|
|
||||||
X = X[1:,:]; y = y[1:]
|
|
||||||
# replace nans with something close to 0
|
|
||||||
# training algotihms cannot handle nans
|
|
||||||
X[np.isnan(X)] = 1e-9
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return X, y
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def plot_confusion_matrix(y_true,y_pred,classes,normalize=False,cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Function copied from the scikit-learn examples (https://scikit-learn.org/stable/)
|
|
||||||
This function plots a confusion matrix.
|
|
||||||
Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
# compute confusion matrix
|
|
||||||
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
|
|
||||||
if normalize:
|
|
||||||
cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
|
|
||||||
print("Normalized confusion matrix")
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
print('Confusion matrix, without normalization')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# plot confusion matrix
|
|
||||||
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6), tight_layout=True)
|
|
||||||
im = ax.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
|
|
||||||
# ax.figure.colorbar(im, ax=ax)
|
|
||||||
ax.set(xticks=np.arange(cm.shape[1]),
|
|
||||||
yticks=np.arange(cm.shape[0]), ylim=[3.5,-0.5],
|
|
||||||
xticklabels=classes, yticklabels=classes,
|
|
||||||
ylabel='True label',
|
|
||||||
xlabel='Predicted label')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# rotate the tick labels and set their alignment.
|
|
||||||
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=45, ha="right",
|
|
||||||
rotation_mode="anchor")
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop over data dimensions and create text annotations.
|
|
||||||
fmt = '.2f' if normalize else 'd'
|
|
||||||
thresh = cm.max() / 2.
|
|
||||||
for i in range(cm.shape[0]):
|
|
||||||
for j in range(cm.shape[1]):
|
|
||||||
ax.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt),
|
|
||||||
ha="center", va="center",
|
|
||||||
color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black",
|
|
||||||
fontsize=12)
|
|
||||||
fig.tight_layout()
|
|
||||||
return ax
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def evaluate_classifier(classifier, metadata, settings):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Apply the image classifier to all the images and save the classified images.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2019
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
classifier: joblib object
|
|
||||||
classifier model to be used for image classification
|
|
||||||
metadata: dict
|
|
||||||
contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'inputs': dict
|
|
||||||
input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
|
|
||||||
'cloud_thresh': float
|
|
||||||
value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
|
|
||||||
the cropped image that is accepted
|
|
||||||
'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
|
|
||||||
True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
|
|
||||||
are erroneously being masked on the images
|
|
||||||
'output_epsg': int
|
|
||||||
output spatial reference system as EPSG code
|
|
||||||
'buffer_size': int
|
|
||||||
size of the buffer (m) around the sandy pixels over which the pixels
|
|
||||||
are considered in the thresholding algorithm
|
|
||||||
'min_beach_area': int
|
|
||||||
minimum allowable object area (in metres^2) for the class 'sand',
|
|
||||||
the area is converted to number of connected pixels
|
|
||||||
'min_length_sl': int
|
|
||||||
minimum length (in metres) of shoreline contour to be valid
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
Saves .jpg images with the output of the classification in the folder ./detection
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create folder called evaluation
|
|
||||||
fp = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'evaluation')
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(fp):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(fp)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# initialize figure (not interactive)
|
|
||||||
plt.ioff()
|
|
||||||
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=[17,10],sharex=True, sharey=True,
|
|
||||||
constrained_layout=True)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create colormap for labels
|
|
||||||
cmap = cm.get_cmap('tab20c')
|
|
||||||
colorpalette = cmap(np.arange(0,13,1))
|
|
||||||
colours = np.zeros((3,4))
|
|
||||||
colours[0,:] = colorpalette[5]
|
|
||||||
colours[1,:] = np.array([204/255,1,1,1])
|
|
||||||
colours[2,:] = np.array([0,91/255,1,1])
|
|
||||||
# loop through satellites
|
|
||||||
for satname in metadata.keys():
|
|
||||||
filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
|
|
||||||
filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# load classifiers and
|
|
||||||
if satname in ['L5','L7','L8']:
|
|
||||||
pixel_size = 15
|
|
||||||
elif satname == 'S2':
|
|
||||||
pixel_size = 10
|
|
||||||
# convert settings['min_beach_area'] and settings['buffer_size'] from metres to pixels
|
|
||||||
buffer_size_pixels = np.ceil(settings['buffer_size']/pixel_size)
|
|
||||||
min_beach_area_pixels = np.ceil(settings['min_beach_area']/pixel_size**2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop through images
|
|
||||||
for i in range(len(filenames)):
|
|
||||||
# image filename
|
|
||||||
fn = SDS_tools.get_filenames(filenames[i],filepath, satname)
|
|
||||||
# read and preprocess image
|
|
||||||
im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn, satname, settings['cloud_mask_issue'])
|
|
||||||
image_epsg = metadata[satname]['epsg'][i]
|
|
||||||
# calculate cloud cover
|
|
||||||
cloud_cover = np.divide(sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int))),
|
|
||||||
(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
# skip image if cloud cover is above threshold
|
|
||||||
if cloud_cover > settings['cloud_thresh']:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
# calculate a buffer around the reference shoreline (if any has been digitised)
|
|
||||||
im_ref_buffer = SDS_shoreline.create_shoreline_buffer(cloud_mask.shape, georef, image_epsg,
|
|
||||||
pixel_size, settings)
|
|
||||||
# classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
|
|
||||||
im_classif, im_labels = SDS_shoreline.classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask,
|
|
||||||
min_beach_area_pixels, classifier)
|
|
||||||
# there are two options to map the contours:
|
|
||||||
# if there are pixels in the 'sand' class --> use find_wl_contours2 (enhanced)
|
|
||||||
# otherwise use find_wl_contours2 (traditional)
|
|
||||||
try: # use try/except structure for long runs
|
|
||||||
if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) < 10 :
|
|
||||||
# compute MNDWI image (SWIR-G)
|
|
||||||
im_mndwi = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
# find water contours on MNDWI grayscale image
|
|
||||||
contours_mwi = SDS_shoreline.find_wl_contours1(im_mndwi, cloud_mask, im_ref_buffer)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# use classification to refine threshold and extract the sand/water interface
|
|
||||||
contours_wi, contours_mwi = SDS_shoreline.find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels,
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask, buffer_size_pixels, im_ref_buffer)
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
print('Could not map shoreline for this image: ' + filenames[i])
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
# process the water contours into a shoreline
|
|
||||||
shoreline = SDS_shoreline.process_shoreline(contours_mwi, cloud_mask, georef, image_epsg, settings)
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
sl_pix = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(SDS_tools.convert_epsg(shoreline,
|
|
||||||
settings['output_epsg'],
|
|
||||||
image_epsg)[:,[0,1]], georef)
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
# if try fails, just add nan into the shoreline vector so the next parts can still run
|
|
||||||
sl_pix = np.array([[np.nan, np.nan],[np.nan, np.nan]])
|
|
||||||
# make a plot
|
|
||||||
im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
|
|
||||||
# create classified image
|
|
||||||
im_class = np.copy(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
for k in range(0,im_labels.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],0] = colours[k,0]
|
|
||||||
im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],1] = colours[k,1]
|
|
||||||
im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],2] = colours[k,2]
|
|
||||||
# show images
|
|
||||||
ax[0].imshow(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
ax[1].imshow(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
ax[1].imshow(im_class, alpha=0.5)
|
|
||||||
ax[0].axis('off')
|
|
||||||
ax[1].axis('off')
|
|
||||||
filename = filenames[i][:filenames[i].find('.')][:-4]
|
|
||||||
ax[0].set_title(filename)
|
|
||||||
ax[0].plot(sl_pix[:,0], sl_pix[:,1], 'k.', markersize=3)
|
|
||||||
ax[1].plot(sl_pix[:,0], sl_pix[:,1], 'k.', markersize=3)
|
|
||||||
# save figure
|
|
||||||
fig.savefig(os.path.join(fp,settings['inputs']['sitename'] + filename[:19] +'.jpg'), dpi=150)
|
|
||||||
# clear axes
|
|
||||||
for cax in fig.axes:
|
|
||||||
cax.clear()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# close the figure at the end
|
|
||||||
plt.close()
|
|
||||||
@ -1,957 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
This module contains all the functions needed to download the satellite images
|
|
||||||
from the Google Earth Engine server
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# load modules
|
|
||||||
import os
|
|
||||||
import numpy as np
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
|
||||||
import pdb
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# earth engine modules
|
|
||||||
import ee
|
|
||||||
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
|
|
||||||
import zipfile
|
|
||||||
import copy
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# additional modules
|
|
||||||
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
|
|
||||||
import pytz
|
|
||||||
import pickle
|
|
||||||
from skimage import morphology, transform
|
|
||||||
from scipy import ndimage
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# CoastSat modules
|
|
||||||
from coastsat import SDS_preprocess, SDS_tools, gdal_merge
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def download_tif(image, polygon, bandsId, filepath):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Downloads a .TIF image from the ee server and stores it in a temp file
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
image: ee.Image
|
|
||||||
Image object to be downloaded
|
|
||||||
polygon: list
|
|
||||||
polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted
|
|
||||||
longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column
|
|
||||||
bandsId: list of dict
|
|
||||||
list of bands to be downloaded
|
|
||||||
filepath: location where the temporary file should be saved
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
Downloads an image in a file named data.tif
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
url = ee.data.makeDownloadUrl(ee.data.getDownloadId({
|
|
||||||
'image': image.serialize(),
|
|
||||||
'region': polygon,
|
|
||||||
'bands': bandsId,
|
|
||||||
'filePerBand': 'false',
|
|
||||||
'name': 'data',
|
|
||||||
}))
|
|
||||||
local_zip, headers = urlretrieve(url)
|
|
||||||
with zipfile.ZipFile(local_zip) as local_zipfile:
|
|
||||||
return local_zipfile.extract('data.tif', filepath)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def retrieve_images(inputs):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Downloads all images from Landsat 5, Landsat 7, Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2
|
|
||||||
covering the area of interest and acquired between the specified dates.
|
|
||||||
The downloaded images are in .TIF format and organised in subfolders, divided
|
|
||||||
by satellite mission. The bands are also subdivided by pixel resolution.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
inputs: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'sitename': str
|
|
||||||
name of the site
|
|
||||||
'polygon': list
|
|
||||||
polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted,
|
|
||||||
longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column,
|
|
||||||
there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point:
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
polygon = [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
|
|
||||||
[151.3, -33.7]]]
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
'dates': list of str
|
|
||||||
list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in
|
|
||||||
format 'yyyy-mm-dd':
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
dates = ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
'sat_list': list of str
|
|
||||||
list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include:
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
sat_list = ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
'filepath_data': str
|
|
||||||
filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
metadata: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded:
|
|
||||||
date, filename, georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# initialise connection with GEE server
|
|
||||||
ee.Initialize()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read inputs dictionnary
|
|
||||||
sitename = inputs['sitename']
|
|
||||||
polygon = inputs['polygon']
|
|
||||||
dates = inputs['dates']
|
|
||||||
sat_list= inputs['sat_list']
|
|
||||||
filepath_data = inputs['filepath']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# format in which the images are downloaded
|
|
||||||
suffix = '.tif'
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# initialize metadata dictionnary (stores information about each image)
|
|
||||||
metadata = dict([])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create a new directory for this site
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(filepath_data,sitename)):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(os.path.join(filepath_data,sitename))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('Downloading images:')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
# download L5 images
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if 'L5' in sat_list or 'Landsat5' in sat_list:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
satname = 'L5'
|
|
||||||
# create a subfolder to store L5 images
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, satname, '30m')
|
|
||||||
filepath_meta = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, satname, 'meta')
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath)
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_meta):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_meta)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Landsat 5 collection
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
input_col = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LT05/C01/T1_TOA')
|
|
||||||
# filter by location and dates
|
|
||||||
flt_col = input_col.filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Polygon(polygon)).filterDate(dates[0],dates[1])
|
|
||||||
# get all images in the filtered collection
|
|
||||||
im_all = flt_col.getInfo().get('features')
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove very cloudy images (>95% cloud)
|
|
||||||
cloud_cover = [_['properties']['CLOUD_COVER'] for _ in im_all]
|
|
||||||
if np.any([_ > 95 for _ in cloud_cover]):
|
|
||||||
idx_delete = np.where([_ > 95 for _ in cloud_cover])[0]
|
|
||||||
im_col = [x for k,x in enumerate(im_all) if k not in idx_delete]
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
im_col = im_all
|
|
||||||
n_img = len(im_col)
|
|
||||||
# print how many images there are
|
|
||||||
print('%s: %d images'%(satname,n_img))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop trough images
|
|
||||||
timestamps = []
|
|
||||||
acc_georef = []
|
|
||||||
filenames = []
|
|
||||||
all_names = []
|
|
||||||
im_epsg = []
|
|
||||||
for i in range(n_img):
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
# find each image in ee database
|
|
||||||
im = ee.Image(im_col[i]['id'])
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
# read metadata
|
|
||||||
im_dic = im_col[i]
|
|
||||||
# get bands
|
|
||||||
im_bands = im_dic['bands']
|
|
||||||
# get time of acquisition (UNIX time)
|
|
||||||
t = im_dic['properties']['system:time_start']
|
|
||||||
# convert to datetime
|
|
||||||
im_timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(t/1000, tz=pytz.utc)
|
|
||||||
timestamps.append(im_timestamp)
|
|
||||||
im_date = im_timestamp.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S')
|
|
||||||
# get EPSG code of reference system
|
|
||||||
im_epsg.append(int(im_dic['bands'][0]['crs'][5:]))
|
|
||||||
# get geometric accuracy
|
|
||||||
if 'GEOMETRIC_RMSE_MODEL' in im_dic['properties'].keys():
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(im_dic['properties']['GEOMETRIC_RMSE_MODEL'])
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(12) # default value of accuracy (RMSE = 12m)
|
|
||||||
# delete dimensions key from dictionnary, otherwise the entire image is extracted
|
|
||||||
for j in range(len(im_bands)): del im_bands[j]['dimensions']
|
|
||||||
# bands for L5
|
|
||||||
ms_bands = [im_bands[0], im_bands[1], im_bands[2], im_bands[3], im_bands[4], im_bands[7]]
|
|
||||||
# filenames for the images
|
|
||||||
filename = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + suffix
|
|
||||||
# if two images taken at the same date add 'dup' in the name (duplicate)
|
|
||||||
if any(filename in _ for _ in all_names):
|
|
||||||
filename = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_dup' + suffix
|
|
||||||
all_names.append(filename)
|
|
||||||
filenames.append(filename)
|
|
||||||
# download .TIF image
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
local_data = download_tif(im, polygon, ms_bands, filepath)
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
# update filename
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, filename))
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
os.remove(os.path.join(filepath, filename))
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, filename))
|
|
||||||
# write metadata in .txt file
|
|
||||||
filename_txt = filename.replace('.tif','')
|
|
||||||
metadict = {'filename':filename,'acc_georef':acc_georef[i],
|
|
||||||
'epsg':im_epsg[i]}
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath_meta,filename_txt + '.txt'), 'w') as f:
|
|
||||||
for key in metadict.keys():
|
|
||||||
f.write('%s\t%s\n'%(key,metadict[key]))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('\r%d%%' % (int(((i+1)/n_img)*100)), end='')
|
|
||||||
print('')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# sort metadata (downloaded images are sorted by date in directory)
|
|
||||||
timestamps_sorted = sorted(timestamps)
|
|
||||||
idx_sorted = sorted(range(len(timestamps)), key=timestamps.__getitem__)
|
|
||||||
acc_georef_sorted = [acc_georef[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
filenames_sorted = [filenames[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
im_epsg_sorted = [im_epsg[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
# save into dict
|
|
||||||
metadata[satname] = {'dates':timestamps_sorted, 'acc_georef':acc_georef_sorted,
|
|
||||||
'epsg':im_epsg_sorted, 'filenames':filenames_sorted}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
# download L7 images
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if 'L7' in sat_list or 'Landsat7' in sat_list:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
satname = 'L7'
|
|
||||||
# create subfolders (one for 30m multispectral bands and one for 15m pan bands)
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'L7')
|
|
||||||
filepath_pan = os.path.join(filepath, 'pan')
|
|
||||||
filepath_ms = os.path.join(filepath, 'ms')
|
|
||||||
filepath_meta = os.path.join(filepath, 'meta')
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_pan):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_pan)
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_ms):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_ms)
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_meta):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_meta)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# landsat 7 collection
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
input_col = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LE07/C01/T1_RT_TOA')
|
|
||||||
# filter by location and dates
|
|
||||||
flt_col = input_col.filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Polygon(polygon)).filterDate(dates[0],dates[1])
|
|
||||||
# get all images in the filtered collection
|
|
||||||
im_all = flt_col.getInfo().get('features')
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove very cloudy images (>95% cloud)
|
|
||||||
cloud_cover = [_['properties']['CLOUD_COVER'] for _ in im_all]
|
|
||||||
if np.any([_ > 95 for _ in cloud_cover]):
|
|
||||||
idx_delete = np.where([_ > 95 for _ in cloud_cover])[0]
|
|
||||||
im_col = [x for k,x in enumerate(im_all) if k not in idx_delete]
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
im_col = im_all
|
|
||||||
n_img = len(im_col)
|
|
||||||
# print how many images there are
|
|
||||||
print('%s: %d images'%(satname,n_img))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop trough images
|
|
||||||
timestamps = []
|
|
||||||
acc_georef = []
|
|
||||||
filenames = []
|
|
||||||
all_names = []
|
|
||||||
im_epsg = []
|
|
||||||
for i in range(n_img):
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
# find each image in ee database
|
|
||||||
im = ee.Image(im_col[i]['id'])
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
# read metadata
|
|
||||||
im_dic = im_col[i]
|
|
||||||
# get bands
|
|
||||||
im_bands = im_dic['bands']
|
|
||||||
# get time of acquisition (UNIX time)
|
|
||||||
t = im_dic['properties']['system:time_start']
|
|
||||||
# convert to datetime
|
|
||||||
im_timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(t/1000, tz=pytz.utc)
|
|
||||||
timestamps.append(im_timestamp)
|
|
||||||
im_date = im_timestamp.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S')
|
|
||||||
# get EPSG code of reference system
|
|
||||||
im_epsg.append(int(im_dic['bands'][0]['crs'][5:]))
|
|
||||||
# get geometric accuracy
|
|
||||||
if 'GEOMETRIC_RMSE_MODEL' in im_dic['properties'].keys():
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(im_dic['properties']['GEOMETRIC_RMSE_MODEL'])
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(12) # default value of accuracy (RMSE = 12m)
|
|
||||||
# delete dimensions key from dictionnary, otherwise the entire image is extracted
|
|
||||||
for j in range(len(im_bands)): del im_bands[j]['dimensions']
|
|
||||||
# bands for L7
|
|
||||||
pan_band = [im_bands[8]]
|
|
||||||
ms_bands = [im_bands[0], im_bands[1], im_bands[2], im_bands[3], im_bands[4], im_bands[9]]
|
|
||||||
# filenames for the images
|
|
||||||
filename_pan = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_pan' + suffix
|
|
||||||
filename_ms = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_ms' + suffix
|
|
||||||
# if two images taken at the same date add 'dup' in the name
|
|
||||||
if any(filename_pan in _ for _ in all_names):
|
|
||||||
filename_pan = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_pan' + '_dup' + suffix
|
|
||||||
filename_ms = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_ms' + '_dup' + suffix
|
|
||||||
all_names.append(filename_pan)
|
|
||||||
filenames.append(filename_pan)
|
|
||||||
# download .TIF image
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
local_data_pan = download_tif(im, polygon, pan_band, filepath_pan)
|
|
||||||
local_data_ms = download_tif(im, polygon, ms_bands, filepath_ms)
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
# update filename
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data_pan, os.path.join(filepath_pan, filename_pan))
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
os.remove(os.path.join(filepath_pan, filename_pan))
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data_pan, os.path.join(filepath_pan, filename_pan))
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data_ms, os.path.join(filepath_ms, filename_ms))
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
os.remove(os.path.join(filepath_ms, filename_ms))
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data_ms, os.path.join(filepath_ms, filename_ms))
|
|
||||||
# write metadata in .txt file
|
|
||||||
filename_txt = filename_pan.replace('_pan','').replace('.tif','')
|
|
||||||
metadict = {'filename':filename_pan,'acc_georef':acc_georef[i],
|
|
||||||
'epsg':im_epsg[i]}
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath_meta,filename_txt + '.txt'), 'w') as f:
|
|
||||||
for key in metadict.keys():
|
|
||||||
f.write('%s\t%s\n'%(key,metadict[key]))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('\r%d%%' % (int(((i+1)/n_img)*100)), end='')
|
|
||||||
print('')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# sort metadata (dowloaded images are sorted by date in directory)
|
|
||||||
timestamps_sorted = sorted(timestamps)
|
|
||||||
idx_sorted = sorted(range(len(timestamps)), key=timestamps.__getitem__)
|
|
||||||
acc_georef_sorted = [acc_georef[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
filenames_sorted = [filenames[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
im_epsg_sorted = [im_epsg[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
# save into dict
|
|
||||||
metadata[satname] = {'dates':timestamps_sorted, 'acc_georef':acc_georef_sorted,
|
|
||||||
'epsg':im_epsg_sorted, 'filenames':filenames_sorted}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
# download L8 images
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if 'L8' in sat_list or 'Landsat8' in sat_list:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
satname = 'L8'
|
|
||||||
# create subfolders (one for 30m multispectral bands and one for 15m pan bands)
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'L8')
|
|
||||||
filepath_pan = os.path.join(filepath, 'pan')
|
|
||||||
filepath_ms = os.path.join(filepath, 'ms')
|
|
||||||
filepath_meta = os.path.join(filepath, 'meta')
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_pan):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_pan)
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_ms):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_ms)
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_meta):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_meta)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# landsat 8 collection
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
input_col = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LC08/C01/T1_RT_TOA')
|
|
||||||
# filter by location and dates
|
|
||||||
flt_col = input_col.filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Polygon(polygon)).filterDate(dates[0],dates[1])
|
|
||||||
# get all images in the filtered collection
|
|
||||||
im_all = flt_col.getInfo().get('features')
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove very cloudy images (>95% cloud)
|
|
||||||
cloud_cover = [_['properties']['CLOUD_COVER'] for _ in im_all]
|
|
||||||
if np.any([_ > 95 for _ in cloud_cover]):
|
|
||||||
idx_delete = np.where([_ > 95 for _ in cloud_cover])[0]
|
|
||||||
im_col = [x for k,x in enumerate(im_all) if k not in idx_delete]
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
im_col = im_all
|
|
||||||
n_img = len(im_col)
|
|
||||||
# print how many images there are
|
|
||||||
print('%s: %d images'%(satname,n_img))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop trough images
|
|
||||||
timestamps = []
|
|
||||||
acc_georef = []
|
|
||||||
filenames = []
|
|
||||||
all_names = []
|
|
||||||
im_epsg = []
|
|
||||||
for i in range(n_img):
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
# find each image in ee database
|
|
||||||
im = ee.Image(im_col[i]['id'])
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
# read metadata
|
|
||||||
im_dic = im_col[i]
|
|
||||||
# get bands
|
|
||||||
im_bands = im_dic['bands']
|
|
||||||
# get time of acquisition (UNIX time)
|
|
||||||
t = im_dic['properties']['system:time_start']
|
|
||||||
# convert to datetime
|
|
||||||
im_timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(t/1000, tz=pytz.utc)
|
|
||||||
timestamps.append(im_timestamp)
|
|
||||||
im_date = im_timestamp.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S')
|
|
||||||
# get EPSG code of reference system
|
|
||||||
im_epsg.append(int(im_dic['bands'][0]['crs'][5:]))
|
|
||||||
# get geometric accuracy
|
|
||||||
if 'GEOMETRIC_RMSE_MODEL' in im_dic['properties'].keys():
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(im_dic['properties']['GEOMETRIC_RMSE_MODEL'])
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(12) # default value of accuracy (RMSE = 12m)
|
|
||||||
# delete dimensions key from dictionnary, otherwise the entire image is extracted
|
|
||||||
for j in range(len(im_bands)): del im_bands[j]['dimensions']
|
|
||||||
# bands for L8
|
|
||||||
pan_band = [im_bands[7]]
|
|
||||||
ms_bands = [im_bands[1], im_bands[2], im_bands[3], im_bands[4], im_bands[5], im_bands[11]]
|
|
||||||
# filenames for the images
|
|
||||||
filename_pan = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_pan' + suffix
|
|
||||||
filename_ms = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_ms' + suffix
|
|
||||||
# if two images taken at the same date add 'dup' in the name
|
|
||||||
if any(filename_pan in _ for _ in all_names):
|
|
||||||
filename_pan = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_pan' + '_dup' + suffix
|
|
||||||
filename_ms = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_ms' + '_dup' + suffix
|
|
||||||
all_names.append(filename_pan)
|
|
||||||
filenames.append(filename_pan)
|
|
||||||
# download .TIF image
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
local_data_pan = download_tif(im, polygon, pan_band, filepath_pan)
|
|
||||||
local_data_ms = download_tif(im, polygon, ms_bands, filepath_ms)
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# update filename
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data_pan, os.path.join(filepath_pan, filename_pan))
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
os.remove(os.path.join(filepath_pan, filename_pan))
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data_pan, os.path.join(filepath_pan, filename_pan))
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data_ms, os.path.join(filepath_ms, filename_ms))
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
os.remove(os.path.join(filepath_ms, filename_ms))
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data_ms, os.path.join(filepath_ms, filename_ms))
|
|
||||||
# write metadata in .txt file
|
|
||||||
filename_txt = filename_pan.replace('_pan','').replace('.tif','')
|
|
||||||
metadict = {'filename':filename_pan,'acc_georef':acc_georef[i],
|
|
||||||
'epsg':im_epsg[i]}
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath_meta,filename_txt + '.txt'), 'w') as f:
|
|
||||||
for key in metadict.keys():
|
|
||||||
f.write('%s\t%s\n'%(key,metadict[key]))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('\r%d%%' % (int(((i+1)/n_img)*100)), end='')
|
|
||||||
print('')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# sort metadata (dowloaded images are sorted by date in directory)
|
|
||||||
timestamps_sorted = sorted(timestamps)
|
|
||||||
idx_sorted = sorted(range(len(timestamps)), key=timestamps.__getitem__)
|
|
||||||
acc_georef_sorted = [acc_georef[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
filenames_sorted = [filenames[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
im_epsg_sorted = [im_epsg[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
metadata[satname] = {'dates':timestamps_sorted, 'acc_georef':acc_georef_sorted,
|
|
||||||
'epsg':im_epsg_sorted, 'filenames':filenames_sorted}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
# download S2 images
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if 'S2' in sat_list or 'Sentinel2' in sat_list:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
satname = 'S2'
|
|
||||||
# create subfolders for the 10m, 20m and 60m multipectral bands
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'S2')
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(filepath, '10m')):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(os.path.join(filepath, '10m'))
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(filepath, '20m')):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(os.path.join(filepath, '20m'))
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(filepath, '60m')):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(os.path.join(filepath, '60m'))
|
|
||||||
filepath_meta = os.path.join(filepath, 'meta')
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_meta):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_meta)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Sentinel2 collection
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
input_col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2')
|
|
||||||
# filter by location and dates
|
|
||||||
flt_col = input_col.filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Polygon(polygon)).filterDate(dates[0],dates[1])
|
|
||||||
# get all images in the filtered collection
|
|
||||||
im_all = flt_col.getInfo().get('features')
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove duplicates in the collection (there are many in S2 collection)
|
|
||||||
timestamps = [datetime.fromtimestamp(_['properties']['system:time_start']/1000,
|
|
||||||
tz=pytz.utc) for _ in im_all]
|
|
||||||
# utm zone projection
|
|
||||||
utm_zones = np.array([int(_['bands'][0]['crs'][5:]) for _ in im_all])
|
|
||||||
utm_zone_selected = np.max(np.unique(utm_zones))
|
|
||||||
# find the images that were acquired at the same time but have different utm zones
|
|
||||||
idx_all = np.arange(0,len(im_all),1)
|
|
||||||
idx_covered = np.ones(len(im_all)).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
idx_delete = []
|
|
||||||
i = 0
|
|
||||||
while 1:
|
|
||||||
same_time = np.abs([(timestamps[i]-_).total_seconds() for _ in timestamps]) < 60*60*24
|
|
||||||
idx_same_time = np.where(same_time)[0]
|
|
||||||
same_utm = utm_zones == utm_zone_selected
|
|
||||||
idx_temp = np.where([same_time[j] == True and same_utm[j] == False for j in idx_all])[0]
|
|
||||||
idx_keep = idx_same_time[[_ not in idx_temp for _ in idx_same_time ]]
|
|
||||||
# if more than 2 images with same date and same utm, drop the last ones
|
|
||||||
if len(idx_keep) > 2:
|
|
||||||
idx_temp = np.append(idx_temp,idx_keep[-(len(idx_keep)-2):])
|
|
||||||
for j in idx_temp:
|
|
||||||
idx_delete.append(j)
|
|
||||||
idx_covered[idx_same_time] = False
|
|
||||||
if np.any(idx_covered):
|
|
||||||
i = np.where(idx_covered)[0][0]
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
# update the collection by deleting all those images that have same timestamp and different
|
|
||||||
# utm projection
|
|
||||||
im_all_updated = [x for k,x in enumerate(im_all) if k not in idx_delete]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove very cloudy images (>95% cloud)
|
|
||||||
cloud_cover = [_['properties']['CLOUDY_PIXEL_PERCENTAGE'] for _ in im_all_updated]
|
|
||||||
if np.any([_ > 95 for _ in cloud_cover]):
|
|
||||||
idx_delete = np.where([_ > 95 for _ in cloud_cover])[0]
|
|
||||||
im_col = [x for k,x in enumerate(im_all_updated) if k not in idx_delete]
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
im_col = im_all_updated
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
n_img = len(im_col)
|
|
||||||
# print how many images there are
|
|
||||||
print('%s: %d images'%(satname,n_img))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop trough images
|
|
||||||
timestamps = []
|
|
||||||
acc_georef = []
|
|
||||||
filenames = []
|
|
||||||
all_names = []
|
|
||||||
im_epsg = []
|
|
||||||
for i in range(n_img):
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
# find each image in ee database
|
|
||||||
im = ee.Image(im_col[i]['id'])
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
# read metadata
|
|
||||||
im_dic = im_col[i]
|
|
||||||
# get bands
|
|
||||||
im_bands = im_dic['bands']
|
|
||||||
# get time of acquisition (UNIX time)
|
|
||||||
t = im_dic['properties']['system:time_start']
|
|
||||||
# convert to datetime
|
|
||||||
im_timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(t/1000, tz=pytz.utc)
|
|
||||||
im_date = im_timestamp.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S')
|
|
||||||
# delete dimensions key from dictionnary, otherwise the entire image is extracted
|
|
||||||
for j in range(len(im_bands)): del im_bands[j]['dimensions']
|
|
||||||
# bands for S2
|
|
||||||
bands10 = [im_bands[1], im_bands[2], im_bands[3], im_bands[7]]
|
|
||||||
bands20 = [im_bands[11]]
|
|
||||||
bands60 = [im_bands[15]]
|
|
||||||
# filenames for images
|
|
||||||
filename10 = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_' + '10m' + suffix
|
|
||||||
filename20 = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_' + '20m' + suffix
|
|
||||||
filename60 = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_' + '60m' + suffix
|
|
||||||
# if two images taken at the same date skip the second image (they are the same)
|
|
||||||
if any(filename10 in _ for _ in all_names):
|
|
||||||
filename10 = filename10[:filename10.find('.')] + '_dup' + suffix
|
|
||||||
filename20 = filename20[:filename20.find('.')] + '_dup' + suffix
|
|
||||||
filename60 = filename60[:filename60.find('.')] + '_dup' + suffix
|
|
||||||
all_names.append(filename10)
|
|
||||||
filenames.append(filename10)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# download .TIF image and update filename
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
local_data = download_tif(im, polygon, bands10, os.path.join(filepath, '10m'))
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, '10m', filename10))
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
os.remove(os.path.join(filepath, '10m', filename10))
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, '10m', filename10))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
local_data = download_tif(im, polygon, bands20, os.path.join(filepath, '20m'))
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, '20m', filename20))
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
os.remove(os.path.join(filepath, '20m', filename20))
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, '20m', filename20))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
while count_loop < 1:
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
local_data = download_tif(im, polygon, bands60, os.path.join(filepath, '60m'))
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 1
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
count_loop = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, '60m', filename60))
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
os.remove(os.path.join(filepath, '60m', filename60))
|
|
||||||
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, '60m', filename60))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save timestamp, epsg code and georeferencing accuracy (1 if passed 0 if not passed)
|
|
||||||
timestamps.append(im_timestamp)
|
|
||||||
im_epsg.append(int(im_dic['bands'][0]['crs'][5:]))
|
|
||||||
# Sentinel-2 products don't provide a georeferencing accuracy (RMSE as in Landsat)
|
|
||||||
# but they have a flag indicating if the geometric quality control was passed or failed
|
|
||||||
# if passed a value of 1 is stored if failed a value of -1 is stored in the metadata
|
|
||||||
if 'GEOMETRIC_QUALITY_FLAG' in im_dic['properties'].keys():
|
|
||||||
if im_dic['properties']['GEOMETRIC_QUALITY_FLAG'] == 'PASSED':
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(1)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(-1)
|
|
||||||
elif 'quality_check' in im_dic['properties'].keys():
|
|
||||||
if im_dic['properties']['quality_check'] == 'PASSED':
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(1)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(-1)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
acc_georef.append(-1)
|
|
||||||
# write metadata in .txt file
|
|
||||||
filename_txt = filename10.replace('_10m','').replace('.tif','')
|
|
||||||
metadict = {'filename':filename10,'acc_georef':acc_georef[i],
|
|
||||||
'epsg':im_epsg[i]}
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath_meta,filename_txt + '.txt'), 'w') as f:
|
|
||||||
for key in metadict.keys():
|
|
||||||
f.write('%s\t%s\n'%(key,metadict[key]))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('\r%d%%' % (int(((i+1)/n_img)*100)), end='')
|
|
||||||
print('')
|
|
||||||
# sort metadata (dowloaded images are sorted by date in directory)
|
|
||||||
timestamps_sorted = sorted(timestamps)
|
|
||||||
idx_sorted = sorted(range(len(timestamps)), key=timestamps.__getitem__)
|
|
||||||
acc_georef_sorted = [acc_georef[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
filenames_sorted = [filenames[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
im_epsg_sorted = [im_epsg[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
metadata[satname] = {'dates':timestamps_sorted, 'acc_georef':acc_georef_sorted,
|
|
||||||
'epsg':im_epsg_sorted, 'filenames':filenames_sorted}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# merge overlapping images (necessary only if the polygon is at the boundary of an image)
|
|
||||||
if 'S2' in metadata.keys():
|
|
||||||
metadata = merge_overlapping_images(metadata,inputs)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save metadata dict
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename)
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_metadata' + '.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
|
|
||||||
pickle.dump(metadata, f)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return metadata
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def merge_overlapping_images(metadata,inputs):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Merge simultaneous overlapping images that cover the area of interest.
|
|
||||||
When the area of interest is located at the boundary between 2 images, there
|
|
||||||
will be overlap between the 2 images and both will be downloaded from Google
|
|
||||||
Earth Engine. This function merges the 2 images, so that the area of interest
|
|
||||||
is covered by only 1 image.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
metadata: dict
|
|
||||||
contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
|
|
||||||
inputs: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'sitename': str
|
|
||||||
name of the site
|
|
||||||
'polygon': list
|
|
||||||
polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted,
|
|
||||||
longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column,
|
|
||||||
there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point:
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
polygon = [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
|
|
||||||
[151.3, -33.7]]]
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
'dates': list of str
|
|
||||||
list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in
|
|
||||||
format 'yyyy-mm-dd':
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
dates = ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
'sat_list': list of str
|
|
||||||
list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include:
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
sat_list = ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
'filepath_data': str
|
|
||||||
filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
metadata_updated: dict
|
|
||||||
updated metadata
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# only for Sentinel-2 at this stage (not sure if this is needed for Landsat images)
|
|
||||||
sat = 'S2'
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(inputs['filepath'], inputs['sitename'])
|
|
||||||
filenames = metadata[sat]['filenames']
|
|
||||||
# find the pairs of images that are within 5 minutes of each other
|
|
||||||
time_delta = 5*60 # 5 minutes in seconds
|
|
||||||
dates = metadata[sat]['dates'].copy()
|
|
||||||
pairs = []
|
|
||||||
for i,date in enumerate(metadata[sat]['dates']):
|
|
||||||
# dummy value so it does not match it again
|
|
||||||
dates[i] = pytz.utc.localize(datetime(1,1,1) + timedelta(days=i+1))
|
|
||||||
# calculate time difference
|
|
||||||
time_diff = np.array([np.abs((date - _).total_seconds()) for _ in dates])
|
|
||||||
# find the matching times and add to pairs list
|
|
||||||
boolvec = time_diff <= time_delta
|
|
||||||
if np.sum(boolvec) == 0:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
idx_dup = np.where(boolvec)[0][0]
|
|
||||||
pairs.append([i,idx_dup])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# for each pair of image, create a mask and add no_data into the .tif file (this is needed before merging .tif files)
|
|
||||||
for i,pair in enumerate(pairs):
|
|
||||||
fn_im = []
|
|
||||||
for index in range(len(pair)):
|
|
||||||
# get filenames of all the files corresponding to the each image in the pair
|
|
||||||
fn_im.append([os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', '10m', filenames[pair[index]]),
|
|
||||||
os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', '20m', filenames[pair[index]].replace('10m','20m')),
|
|
||||||
os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', '60m', filenames[pair[index]].replace('10m','60m')),
|
|
||||||
os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', 'meta', filenames[pair[index]].replace('_10m','').replace('.tif','.txt'))])
|
|
||||||
# read that image
|
|
||||||
im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn_im[index], sat, False)
|
|
||||||
# im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# in Sentinel2 images close to the edge of the image there are some artefacts,
|
|
||||||
# that are squares with constant pixel intensities. They need to be masked in the
|
|
||||||
# raster (GEOTIFF). It can be done using the image standard deviation, which
|
|
||||||
# indicates values close to 0 for the artefacts.
|
|
||||||
if len(im_ms) > 0:
|
|
||||||
# calculate image std for the first 10m band
|
|
||||||
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_ms[:,:,0],1)
|
|
||||||
# convert to binary
|
|
||||||
im_binary = np.logical_or(im_std < 1e-6, np.isnan(im_std))
|
|
||||||
# dilate to fill the edges (which have high std)
|
|
||||||
mask10 = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
|
|
||||||
# mask all 10m bands
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_ms[mask10,k] = np.nan
|
|
||||||
# mask the 10m .tif file (add no_data where mask is True)
|
|
||||||
SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][0], mask10)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create another mask for the 20m band (SWIR1)
|
|
||||||
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_extra,1)
|
|
||||||
im_binary = np.logical_or(im_std < 1e-6, np.isnan(im_std))
|
|
||||||
mask20 = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
|
|
||||||
im_extra[mask20] = np.nan
|
|
||||||
# mask the 20m .tif file (im_extra)
|
|
||||||
SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][1], mask20)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# use the 20m mask to create a mask for the 60m QA band (by resampling)
|
|
||||||
mask60 = ndimage.zoom(mask20,zoom=1/3,order=0)
|
|
||||||
mask60 = transform.resize(mask60, im_QA.shape, mode='constant', order=0,
|
|
||||||
preserve_range=True)
|
|
||||||
mask60 = mask60.astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
# mask the 60m .tif file (im_QA)
|
|
||||||
SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][2], mask60)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# make a figure for quality control
|
|
||||||
# fig,ax= plt.subplots(2,2,tight_layout=True)
|
|
||||||
# ax[0,0].imshow(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
# ax[0,0].set_title('RGB original')
|
|
||||||
# ax[1,0].imshow(mask10)
|
|
||||||
# ax[1,0].set_title('Mask 10m')
|
|
||||||
# ax[0,1].imshow(mask20)
|
|
||||||
# ax[0,1].set_title('Mask 20m')
|
|
||||||
# ax[1,1].imshow(mask60)
|
|
||||||
# ax[1,1].set_title('Mask 60 m')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# once all the pairs of .tif files have been masked with no_data, merge the using gdal_merge
|
|
||||||
fn_merged = os.path.join(filepath, 'merged.tif')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# merge masked 10m bands and remove duplicate file
|
|
||||||
gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', '0', fn_im[0][0], fn_im[1][0]])
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_im[0][0], 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.remove(fn_im[0][0])
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_im[1][0], 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.remove(fn_im[1][0])
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_merged, 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.rename(fn_merged, fn_im[0][0])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# merge masked 20m band (SWIR band)
|
|
||||||
gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', '0', fn_im[0][1], fn_im[1][1]])
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_im[0][1], 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.remove(fn_im[0][1])
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_im[1][1], 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.remove(fn_im[1][1])
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_merged, 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.rename(fn_merged, fn_im[0][1])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# merge QA band (60m band)
|
|
||||||
gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', '0', fn_im[0][2], fn_im[1][2]])
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_im[0][2], 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.remove(fn_im[0][2])
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_im[1][2], 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.remove(fn_im[1][2])
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_merged, 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.rename(fn_merged, fn_im[0][2])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove the metadata .txt file of the duplicate image
|
|
||||||
os.chmod(fn_im[1][3], 0o777)
|
|
||||||
os.remove(fn_im[1][3])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('%d pairs of overlapping Sentinel-2 images were merged' % len(pairs))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# update the metadata dict
|
|
||||||
metadata_updated = copy.deepcopy(metadata)
|
|
||||||
idx_removed = []
|
|
||||||
idx_kept = []
|
|
||||||
for pair in pairs: idx_removed.append(pair[1])
|
|
||||||
for idx in np.arange(0,len(metadata[sat]['dates'])):
|
|
||||||
if not idx in idx_removed: idx_kept.append(idx)
|
|
||||||
for key in metadata_updated[sat].keys():
|
|
||||||
metadata_updated[sat][key] = [metadata_updated[sat][key][_] for _ in idx_kept]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return metadata_updated
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_metadata(inputs):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Gets the metadata from the downloaded images by parsing .txt files located
|
|
||||||
in the \meta subfolder.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
inputs: dict with the following fields
|
|
||||||
'sitename': str
|
|
||||||
name of the site
|
|
||||||
'filepath_data': str
|
|
||||||
filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
metadata: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded:
|
|
||||||
date, filename, georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
# directory containing the images
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(inputs['filepath'],inputs['sitename'])
|
|
||||||
# initialize metadata dict
|
|
||||||
metadata = dict([])
|
|
||||||
# loop through the satellite missions
|
|
||||||
for satname in ['L5','L7','L8','S2']:
|
|
||||||
# if a folder has been created for the given satellite mission
|
|
||||||
if satname in os.listdir(filepath):
|
|
||||||
# update the metadata dict
|
|
||||||
metadata[satname] = {'filenames':[], 'acc_georef':[], 'epsg':[], 'dates':[]}
|
|
||||||
# directory where the metadata .txt files are stored
|
|
||||||
filepath_meta = os.path.join(filepath, satname, 'meta')
|
|
||||||
# get the list of filenames and sort it chronologically
|
|
||||||
filenames_meta = os.listdir(filepath_meta)
|
|
||||||
filenames_meta.sort()
|
|
||||||
# loop through the .txt files
|
|
||||||
for im_meta in filenames_meta:
|
|
||||||
# read them and extract the metadata info: filename, georeferencing accuracy
|
|
||||||
# epsg code and date
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath_meta, im_meta), 'r') as f:
|
|
||||||
filename = f.readline().split('\t')[1].replace('\n','')
|
|
||||||
acc_georef = float(f.readline().split('\t')[1].replace('\n',''))
|
|
||||||
epsg = int(f.readline().split('\t')[1].replace('\n',''))
|
|
||||||
date_str = filename[0:19]
|
|
||||||
date = pytz.utc.localize(datetime(int(date_str[:4]),int(date_str[5:7]),
|
|
||||||
int(date_str[8:10]),int(date_str[11:13]),
|
|
||||||
int(date_str[14:16]),int(date_str[17:19])))
|
|
||||||
# store the information in the metadata dict
|
|
||||||
metadata[satname]['filenames'].append(filename)
|
|
||||||
metadata[satname]['acc_georef'].append(acc_georef)
|
|
||||||
metadata[satname]['epsg'].append(epsg)
|
|
||||||
metadata[satname]['dates'].append(date)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save a .pkl file containing the metadata dict
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath, inputs['sitename'] + '_metadata' + '.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
|
|
||||||
pickle.dump(metadata, f)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return metadata
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -1,893 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
This module contains all the functions needed to preprocess the satellite images
|
|
||||||
before the shorelines can be extracted. This includes creating a cloud mask and
|
|
||||||
pansharpening/downsampling the multispectral bands.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# load modules
|
|
||||||
import os
|
|
||||||
import numpy as np
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
|
||||||
import pdb
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# image processing modules
|
|
||||||
import skimage.transform as transform
|
|
||||||
import skimage.morphology as morphology
|
|
||||||
import sklearn.decomposition as decomposition
|
|
||||||
import skimage.exposure as exposure
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# other modules
|
|
||||||
from osgeo import gdal
|
|
||||||
from pylab import ginput
|
|
||||||
import pickle
|
|
||||||
import geopandas as gpd
|
|
||||||
from shapely import geometry
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# CoastSat modules
|
|
||||||
from coastsat import SDS_tools
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def create_cloud_mask(im_QA, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Creates a cloud mask using the information contained in the QA band.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_QA: np.array
|
|
||||||
Image containing the QA band
|
|
||||||
satname: string
|
|
||||||
short name for the satellite: ```'L5', 'L7', 'L8' or 'S2'```
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask_issue: boolean
|
|
||||||
True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being
|
|
||||||
erroneously masked on the images
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask : np.array
|
|
||||||
boolean array with True if a pixel is cloudy and False otherwise
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# convert QA bits (the bits allocated to cloud cover vary depending on the satellite mission)
|
|
||||||
if satname == 'L8':
|
|
||||||
cloud_values = [2800, 2804, 2808, 2812, 6896, 6900, 6904, 6908]
|
|
||||||
elif satname == 'L7' or satname == 'L5' or satname == 'L4':
|
|
||||||
cloud_values = [752, 756, 760, 764]
|
|
||||||
elif satname == 'S2':
|
|
||||||
cloud_values = [1024, 2048] # 1024 = dense cloud, 2048 = cirrus clouds
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# find which pixels have bits corresponding to cloud values
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.isin(im_QA, cloud_values)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove cloud pixels that form very thin features. These are beach or swash pixels that are
|
|
||||||
# erroneously identified as clouds by the CFMASK algorithm applied to the images by the USGS.
|
|
||||||
if sum(sum(cloud_mask)) > 0 and sum(sum(~cloud_mask)) > 0:
|
|
||||||
morphology.remove_small_objects(cloud_mask, min_size=10, connectivity=1, in_place=True)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if cloud_mask_issue:
|
|
||||||
elem = morphology.square(3) # use a square of width 3 pixels
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = morphology.binary_opening(cloud_mask,elem) # perform image opening
|
|
||||||
# remove objects with less than 25 connected pixels
|
|
||||||
morphology.remove_small_objects(cloud_mask, min_size=25, connectivity=1, in_place=True)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return cloud_mask
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def hist_match(source, template):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Adjust the pixel values of a grayscale image such that its histogram matches
|
|
||||||
that of a target image.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
source: np.array
|
|
||||||
Image to transform; the histogram is computed over the flattened
|
|
||||||
array
|
|
||||||
template: np.array
|
|
||||||
Template image; can have different dimensions to source
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
matched: np.array
|
|
||||||
The transformed output image
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
oldshape = source.shape
|
|
||||||
source = source.ravel()
|
|
||||||
template = template.ravel()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# get the set of unique pixel values and their corresponding indices and
|
|
||||||
# counts
|
|
||||||
s_values, bin_idx, s_counts = np.unique(source, return_inverse=True,
|
|
||||||
return_counts=True)
|
|
||||||
t_values, t_counts = np.unique(template, return_counts=True)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# take the cumsum of the counts and normalize by the number of pixels to
|
|
||||||
# get the empirical cumulative distribution functions for the source and
|
|
||||||
# template images (maps pixel value --> quantile)
|
|
||||||
s_quantiles = np.cumsum(s_counts).astype(np.float64)
|
|
||||||
s_quantiles /= s_quantiles[-1]
|
|
||||||
t_quantiles = np.cumsum(t_counts).astype(np.float64)
|
|
||||||
t_quantiles /= t_quantiles[-1]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# interpolate linearly to find the pixel values in the template image
|
|
||||||
# that correspond most closely to the quantiles in the source image
|
|
||||||
interp_t_values = np.interp(s_quantiles, t_quantiles, t_values)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return interp_t_values[bin_idx].reshape(oldshape)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def pansharpen(im_ms, im_pan, cloud_mask):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Pansharpens a multispectral image, using the panchromatic band and a cloud mask.
|
|
||||||
A PCA is applied to the image, then the 1st PC is replaced, after histogram
|
|
||||||
matching with the panchromatic band. Note that it is essential to match the
|
|
||||||
histrograms of the 1st PC and the panchromatic band before replacing and
|
|
||||||
inverting the PCA.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_ms: np.array
|
|
||||||
Multispectral image to pansharpen (3D)
|
|
||||||
im_pan: np.array
|
|
||||||
Panchromatic band (2D)
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_ms_ps: np.ndarray
|
|
||||||
Pansharpened multispectral image (3D)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# reshape image into vector and apply cloud mask
|
|
||||||
vec = im_ms.reshape(im_ms.shape[0] * im_ms.shape[1], im_ms.shape[2])
|
|
||||||
vec_mask = cloud_mask.reshape(im_ms.shape[0] * im_ms.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
vec = vec[~vec_mask, :]
|
|
||||||
# apply PCA to multispectral bands
|
|
||||||
pca = decomposition.PCA()
|
|
||||||
vec_pcs = pca.fit_transform(vec)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# replace 1st PC with pan band (after matching histograms)
|
|
||||||
vec_pan = im_pan.reshape(im_pan.shape[0] * im_pan.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
vec_pan = vec_pan[~vec_mask]
|
|
||||||
vec_pcs[:,0] = hist_match(vec_pan, vec_pcs[:,0])
|
|
||||||
vec_ms_ps = pca.inverse_transform(vec_pcs)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# reshape vector into image
|
|
||||||
vec_ms_ps_full = np.ones((len(vec_mask), im_ms.shape[2])) * np.nan
|
|
||||||
vec_ms_ps_full[~vec_mask,:] = vec_ms_ps
|
|
||||||
im_ms_ps = vec_ms_ps_full.reshape(im_ms.shape[0], im_ms.shape[1], im_ms.shape[2])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return im_ms_ps
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def rescale_image_intensity(im, cloud_mask, prob_high):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Rescales the intensity of an image (multispectral or single band) by applying
|
|
||||||
a cloud mask and clipping the prob_high upper percentile. This functions allows
|
|
||||||
to stretch the contrast of an image, only for visualisation purposes.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im: np.array
|
|
||||||
Image to rescale, can be 3D (multispectral) or 2D (single band)
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
prob_high: float
|
|
||||||
probability of exceedence used to calculate the upper percentile
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_adj: np.array
|
|
||||||
rescaled image
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# lower percentile is set to 0
|
|
||||||
prc_low = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# reshape the 2D cloud mask into a 1D vector
|
|
||||||
vec_mask = cloud_mask.reshape(im.shape[0] * im.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if image contains several bands, stretch the contrast for each band
|
|
||||||
if len(im.shape) > 2:
|
|
||||||
# reshape into a vector
|
|
||||||
vec = im.reshape(im.shape[0] * im.shape[1], im.shape[2])
|
|
||||||
# initiliase with NaN values
|
|
||||||
vec_adj = np.ones((len(vec_mask), im.shape[2])) * np.nan
|
|
||||||
# loop through the bands
|
|
||||||
for i in range(im.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
# find the higher percentile (based on prob)
|
|
||||||
prc_high = np.percentile(vec[~vec_mask, i], prob_high)
|
|
||||||
# clip the image around the 2 percentiles and rescale the contrast
|
|
||||||
vec_rescaled = exposure.rescale_intensity(vec[~vec_mask, i],
|
|
||||||
in_range=(prc_low, prc_high))
|
|
||||||
vec_adj[~vec_mask,i] = vec_rescaled
|
|
||||||
# reshape into image
|
|
||||||
im_adj = vec_adj.reshape(im.shape[0], im.shape[1], im.shape[2])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if image only has 1 bands (grayscale image)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
vec = im.reshape(im.shape[0] * im.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
vec_adj = np.ones(len(vec_mask)) * np.nan
|
|
||||||
prc_high = np.percentile(vec[~vec_mask], prob_high)
|
|
||||||
vec_rescaled = exposure.rescale_intensity(vec[~vec_mask], in_range=(prc_low, prc_high))
|
|
||||||
vec_adj[~vec_mask] = vec_rescaled
|
|
||||||
im_adj = vec_adj.reshape(im.shape[0], im.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return im_adj
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def preprocess_single(fn, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Reads the image and outputs the pansharpened/down-sampled multispectral bands,
|
|
||||||
the georeferencing vector of the image (coordinates of the upper left pixel),
|
|
||||||
the cloud mask, the QA band and a no_data image.
|
|
||||||
For Landsat 7-8 it also outputs the panchromatic band and for Sentinel-2 it
|
|
||||||
also outputs the 20m SWIR band.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
fn: str or list of str
|
|
||||||
filename of the .TIF file containing the image. For L7, L8 and S2 this
|
|
||||||
is a list of filenames, one filename for each band at different
|
|
||||||
resolution (30m and 15m for Landsat 7-8, 10m, 20m, 60m for Sentinel-2)
|
|
||||||
satname: str
|
|
||||||
name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask_issue: boolean
|
|
||||||
True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_ms: np.array
|
|
||||||
3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
|
|
||||||
georef: np.array
|
|
||||||
vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale] defining the
|
|
||||||
coordinates of the top-left pixel of the image
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
im_extra : np.array
|
|
||||||
2D array containing the 20m resolution SWIR band for Sentinel-2 and the 15m resolution
|
|
||||||
panchromatic band for Landsat 7 and Landsat 8. This field is empty for Landsat 5.
|
|
||||||
im_QA: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D array containing the QA band, from which the cloud_mask can be computed.
|
|
||||||
im_nodata: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D array with True where no data values (-inf) are located
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
# L5 images
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
if satname == 'L5':
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read all bands
|
|
||||||
data = gdal.Open(fn, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
|
||||||
georef = np.array(data.GetGeoTransform())
|
|
||||||
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
|
||||||
im_ms = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# down-sample to 15 m (half of the original pixel size)
|
|
||||||
nrows = im_ms.shape[0]*2
|
|
||||||
ncols = im_ms.shape[1]*2
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create cloud mask
|
|
||||||
im_QA = im_ms[:,:,5]
|
|
||||||
im_ms = im_ms[:,:,:-1]
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = create_cloud_mask(im_QA, satname, cloud_mask_issue)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# resize the image using bilinear interpolation (order 1)
|
|
||||||
im_ms = transform.resize(im_ms,(nrows, ncols), order=1, preserve_range=True,
|
|
||||||
mode='constant')
|
|
||||||
# resize the image using nearest neighbour interpolation (order 0)
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = transform.resize(cloud_mask, (nrows, ncols), order=0, preserve_range=True,
|
|
||||||
mode='constant').astype('bool_')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# adjust georeferencing vector to the new image size
|
|
||||||
# scale becomes 15m and the origin is adjusted to the center of new top left pixel
|
|
||||||
georef[1] = 15
|
|
||||||
georef[5] = -15
|
|
||||||
georef[0] = georef[0] + 7.5
|
|
||||||
georef[3] = georef[3] - 7.5
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# check if -inf or nan values on any band and add to cloud mask
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.zeros(cloud_mask.shape).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_inf = np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k], -np.inf)
|
|
||||||
im_nan = np.isnan(im_ms[:,:,k])
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(cloud_mask, im_inf), im_nan)
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(im_nodata, im_inf), im_nan)
|
|
||||||
# check if there are pixels with 0 intensity in the Green, NIR and SWIR bands and add those
|
|
||||||
# to the cloud mask as otherwise they will cause errors when calculating the NDWI and MNDWI
|
|
||||||
im_zeros = np.ones(cloud_mask.shape).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
for k in [1,3,4]: # loop through the Green, NIR and SWIR bands
|
|
||||||
im_zeros = np.logical_and(np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k],0), im_zeros)
|
|
||||||
# update cloud mask and nodata
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(im_zeros, cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.logical_or(im_zeros, im_nodata)
|
|
||||||
# no extra image for Landsat 5 (they are all 30 m bands)
|
|
||||||
im_extra = []
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
# L7 images
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
elif satname == 'L7':
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read pan image
|
|
||||||
fn_pan = fn[0]
|
|
||||||
data = gdal.Open(fn_pan, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
|
||||||
georef = np.array(data.GetGeoTransform())
|
|
||||||
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
|
||||||
im_pan = np.stack(bands, 2)[:,:,0]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# size of pan image
|
|
||||||
nrows = im_pan.shape[0]
|
|
||||||
ncols = im_pan.shape[1]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read ms image
|
|
||||||
fn_ms = fn[1]
|
|
||||||
data = gdal.Open(fn_ms, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
|
||||||
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
|
||||||
im_ms = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create cloud mask
|
|
||||||
im_QA = im_ms[:,:,5]
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = create_cloud_mask(im_QA, satname, cloud_mask_issue)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# resize the image using bilinear interpolation (order 1)
|
|
||||||
im_ms = im_ms[:,:,:5]
|
|
||||||
im_ms = transform.resize(im_ms,(nrows, ncols), order=1, preserve_range=True,
|
|
||||||
mode='constant')
|
|
||||||
# resize the image using nearest neighbour interpolation (order 0)
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = transform.resize(cloud_mask, (nrows, ncols), order=0, preserve_range=True,
|
|
||||||
mode='constant').astype('bool_')
|
|
||||||
# check if -inf or nan values on any band and eventually add those pixels to cloud mask
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.zeros(cloud_mask.shape).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_inf = np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k], -np.inf)
|
|
||||||
im_nan = np.isnan(im_ms[:,:,k])
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(cloud_mask, im_inf), im_nan)
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(im_nodata, im_inf), im_nan)
|
|
||||||
# check if there are pixels with 0 intensity in the Green, NIR and SWIR bands and add those
|
|
||||||
# to the cloud mask as otherwise they will cause errors when calculating the NDWI and MNDWI
|
|
||||||
im_zeros = np.ones(cloud_mask.shape).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
for k in [1,3,4]: # loop through the Green, NIR and SWIR bands
|
|
||||||
im_zeros = np.logical_and(np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k],0), im_zeros)
|
|
||||||
# update cloud mask and nodata
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(im_zeros, cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.logical_or(im_zeros, im_nodata)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# pansharpen Green, Red, NIR (where there is overlapping with pan band in L7)
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
im_ms_ps = pansharpen(im_ms[:,:,[1,2,3]], im_pan, cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
except: # if pansharpening fails, keep downsampled bands (for long runs)
|
|
||||||
im_ms_ps = im_ms[:,:,[1,2,3]]
|
|
||||||
# add downsampled Blue and SWIR1 bands
|
|
||||||
im_ms_ps = np.append(im_ms[:,:,[0]], im_ms_ps, axis=2)
|
|
||||||
im_ms_ps = np.append(im_ms_ps, im_ms[:,:,[4]], axis=2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
im_ms = im_ms_ps.copy()
|
|
||||||
# the extra image is the 15m panchromatic band
|
|
||||||
im_extra = im_pan
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
# L8 images
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
elif satname == 'L8':
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read pan image
|
|
||||||
fn_pan = fn[0]
|
|
||||||
data = gdal.Open(fn_pan, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
|
||||||
georef = np.array(data.GetGeoTransform())
|
|
||||||
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
|
||||||
im_pan = np.stack(bands, 2)[:,:,0]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# size of pan image
|
|
||||||
nrows = im_pan.shape[0]
|
|
||||||
ncols = im_pan.shape[1]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read ms image
|
|
||||||
fn_ms = fn[1]
|
|
||||||
data = gdal.Open(fn_ms, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
|
||||||
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
|
||||||
im_ms = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create cloud mask
|
|
||||||
im_QA = im_ms[:,:,5]
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = create_cloud_mask(im_QA, satname, cloud_mask_issue)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# resize the image using bilinear interpolation (order 1)
|
|
||||||
im_ms = im_ms[:,:,:5]
|
|
||||||
im_ms = transform.resize(im_ms,(nrows, ncols), order=1, preserve_range=True,
|
|
||||||
mode='constant')
|
|
||||||
# resize the image using nearest neighbour interpolation (order 0)
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = transform.resize(cloud_mask, (nrows, ncols), order=0, preserve_range=True,
|
|
||||||
mode='constant').astype('bool_')
|
|
||||||
# check if -inf or nan values on any band and eventually add those pixels to cloud mask
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.zeros(cloud_mask.shape).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_inf = np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k], -np.inf)
|
|
||||||
im_nan = np.isnan(im_ms[:,:,k])
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(cloud_mask, im_inf), im_nan)
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(im_nodata, im_inf), im_nan)
|
|
||||||
# check if there are pixels with 0 intensity in the Green, NIR and SWIR bands and add those
|
|
||||||
# to the cloud mask as otherwise they will cause errors when calculating the NDWI and MNDWI
|
|
||||||
im_zeros = np.ones(cloud_mask.shape).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
for k in [1,3,4]: # loop through the Green, NIR and SWIR bands
|
|
||||||
im_zeros = np.logical_and(np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k],0), im_zeros)
|
|
||||||
# update cloud mask and nodata
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(im_zeros, cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.logical_or(im_zeros, im_nodata)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# pansharpen Blue, Green, Red (where there is overlapping with pan band in L8)
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
im_ms_ps = pansharpen(im_ms[:,:,[0,1,2]], im_pan, cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
except: # if pansharpening fails, keep downsampled bands (for long runs)
|
|
||||||
im_ms_ps = im_ms[:,:,[0,1,2]]
|
|
||||||
# add downsampled NIR and SWIR1 bands
|
|
||||||
im_ms_ps = np.append(im_ms_ps, im_ms[:,:,[3,4]], axis=2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
im_ms = im_ms_ps.copy()
|
|
||||||
# the extra image is the 15m panchromatic band
|
|
||||||
im_extra = im_pan
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
# S2 images
|
|
||||||
#=============================================================================================#
|
|
||||||
if satname == 'S2':
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read 10m bands (R,G,B,NIR)
|
|
||||||
fn10 = fn[0]
|
|
||||||
data = gdal.Open(fn10, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
|
||||||
georef = np.array(data.GetGeoTransform())
|
|
||||||
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
|
||||||
im10 = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
|
||||||
im10 = im10/10000 # TOA scaled to 10000
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if image contains only zeros (can happen with S2), skip the image
|
|
||||||
if sum(sum(sum(im10))) < 1:
|
|
||||||
im_ms = []
|
|
||||||
georef = []
|
|
||||||
# skip the image by giving it a full cloud_mask
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.ones((im10.shape[0],im10.shape[1])).astype('bool')
|
|
||||||
return im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, [], [], []
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# size of 10m bands
|
|
||||||
nrows = im10.shape[0]
|
|
||||||
ncols = im10.shape[1]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read 20m band (SWIR1)
|
|
||||||
fn20 = fn[1]
|
|
||||||
data = gdal.Open(fn20, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
|
||||||
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
|
||||||
im20 = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
|
||||||
im20 = im20[:,:,0]
|
|
||||||
im20 = im20/10000 # TOA scaled to 10000
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# resize the image using bilinear interpolation (order 1)
|
|
||||||
im_swir = transform.resize(im20, (nrows, ncols), order=1, preserve_range=True,
|
|
||||||
mode='constant')
|
|
||||||
im_swir = np.expand_dims(im_swir, axis=2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# append down-sampled SWIR1 band to the other 10m bands
|
|
||||||
im_ms = np.append(im10, im_swir, axis=2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create cloud mask using 60m QA band (not as good as Landsat cloud cover)
|
|
||||||
fn60 = fn[2]
|
|
||||||
data = gdal.Open(fn60, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
|
||||||
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
|
||||||
im60 = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
|
||||||
im_QA = im60[:,:,0]
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = create_cloud_mask(im_QA, satname, cloud_mask_issue)
|
|
||||||
# resize the cloud mask using nearest neighbour interpolation (order 0)
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = transform.resize(cloud_mask,(nrows, ncols), order=0, preserve_range=True,
|
|
||||||
mode='constant')
|
|
||||||
# check if -inf or nan values on any band and add to cloud mask
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.zeros(cloud_mask.shape).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_inf = np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k], -np.inf)
|
|
||||||
im_nan = np.isnan(im_ms[:,:,k])
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(cloud_mask, im_inf), im_nan)
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(im_nodata, im_inf), im_nan)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# check if there are pixels with 0 intensity in the Green, NIR and SWIR bands and add those
|
|
||||||
# to the cloud mask as otherwise they will cause errors when calculating the NDWI and MNDWI
|
|
||||||
im_zeros = np.ones(cloud_mask.shape).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
for k in [1,3,4]: # loop through the Green, NIR and SWIR bands
|
|
||||||
im_zeros = np.logical_and(np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k],0), im_zeros)
|
|
||||||
# update cloud mask and nodata
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(im_zeros, cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
im_nodata = np.logical_or(im_zeros, im_nodata)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# the extra image is the 20m SWIR band
|
|
||||||
im_extra = im20
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def create_jpg(im_ms, cloud_mask, date, satname, filepath):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Saves a .jpg file with the RGB image as well as the NIR and SWIR1 grayscale images.
|
|
||||||
This functions can be modified to obtain different visualisations of the
|
|
||||||
multispectral images.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_ms: np.array
|
|
||||||
3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
date: str
|
|
||||||
string containing the date at which the image was acquired
|
|
||||||
satname: str
|
|
||||||
name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
Saves a .jpg image corresponding to the preprocessed satellite image
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# rescale image intensity for display purposes
|
|
||||||
im_RGB = rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
|
|
||||||
# im_NIR = rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,3], cloud_mask, 99.9)
|
|
||||||
# im_SWIR = rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,4], cloud_mask, 99.9)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# make figure (just RGB)
|
|
||||||
fig = plt.figure()
|
|
||||||
fig.set_size_inches([18,9])
|
|
||||||
fig.set_tight_layout(True)
|
|
||||||
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
|
|
||||||
ax1.axis('off')
|
|
||||||
ax1.imshow(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
ax1.set_title(date + ' ' + satname, fontsize=16)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if im_RGB.shape[1] > 2*im_RGB.shape[0]:
|
|
||||||
# ax1 = fig.add_subplot(311)
|
|
||||||
# ax2 = fig.add_subplot(312)
|
|
||||||
# ax3 = fig.add_subplot(313)
|
|
||||||
# else:
|
|
||||||
# ax1 = fig.add_subplot(131)
|
|
||||||
# ax2 = fig.add_subplot(132)
|
|
||||||
# ax3 = fig.add_subplot(133)
|
|
||||||
# # RGB
|
|
||||||
# ax1.axis('off')
|
|
||||||
# ax1.imshow(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
# ax1.set_title(date + ' ' + satname, fontsize=16)
|
|
||||||
# # NIR
|
|
||||||
# ax2.axis('off')
|
|
||||||
# ax2.imshow(im_NIR, cmap='seismic')
|
|
||||||
# ax2.set_title('Near Infrared', fontsize=16)
|
|
||||||
# # SWIR
|
|
||||||
# ax3.axis('off')
|
|
||||||
# ax3.imshow(im_SWIR, cmap='seismic')
|
|
||||||
# ax3.set_title('Short-wave Infrared', fontsize=16)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save figure
|
|
||||||
plt.rcParams['savefig.jpeg_quality'] = 100
|
|
||||||
fig.savefig(os.path.join(filepath,
|
|
||||||
date + '_' + satname + '.jpg'), dpi=150)
|
|
||||||
plt.close()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def save_jpg(metadata, settings, **kwargs):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Saves a .jpg image for all the images contained in metadata.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
metadata: dict
|
|
||||||
contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'inputs': dict
|
|
||||||
input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
|
|
||||||
'cloud_thresh': float
|
|
||||||
value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
|
|
||||||
the cropped image that is accepted
|
|
||||||
'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
|
|
||||||
True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
|
|
||||||
are erroneously being masked on the images
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
Stores the images as .jpg in a folder named /preprocessed
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
|
|
||||||
cloud_thresh = settings['cloud_thresh']
|
|
||||||
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create subfolder to store the jpg files
|
|
||||||
filepath_jpg = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'jpg_files', 'preprocessed')
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_jpg):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_jpg)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop through satellite list
|
|
||||||
for satname in metadata.keys():
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
|
|
||||||
filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop through images
|
|
||||||
for i in range(len(filenames)):
|
|
||||||
# image filename
|
|
||||||
fn = SDS_tools.get_filenames(filenames[i],filepath, satname)
|
|
||||||
# read and preprocess image
|
|
||||||
im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = preprocess_single(fn, satname, settings['cloud_mask_issue'])
|
|
||||||
# calculate cloud cover
|
|
||||||
cloud_cover = np.divide(sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int))),
|
|
||||||
(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
# skip image if cloud cover is above threshold
|
|
||||||
if cloud_cover > cloud_thresh or cloud_cover == 1:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
# save .jpg with date and satellite in the title
|
|
||||||
date = filenames[i][:19]
|
|
||||||
plt.ioff() # turning interactive plotting off
|
|
||||||
create_jpg(im_ms, cloud_mask, date, satname, filepath_jpg)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# print the location where the images have been saved
|
|
||||||
print('Satellite images saved as .jpg in ' + os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename,
|
|
||||||
'jpg_files', 'preprocessed'))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Allows the user to manually digitize a reference shoreline that is used seed
|
|
||||||
the shoreline detection algorithm. The reference shoreline helps to detect
|
|
||||||
the outliers, making the shoreline detection more robust.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
metadata: dict
|
|
||||||
contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'inputs': dict
|
|
||||||
input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
|
|
||||||
'cloud_thresh': float
|
|
||||||
value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
|
|
||||||
the cropped image that is accepted
|
|
||||||
'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
|
|
||||||
True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
|
|
||||||
are erroneously being masked on the images
|
|
||||||
'output_epsg': int
|
|
||||||
output spatial reference system as EPSG code
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
reference_shoreline: np.array
|
|
||||||
coordinates of the reference shoreline that was manually digitized.
|
|
||||||
This is also saved as a .pkl and .geojson file.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
|
|
||||||
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
|
|
||||||
pts_coords = []
|
|
||||||
# check if reference shoreline already exists in the corresponding folder
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename)
|
|
||||||
filename = sitename + '_reference_shoreline.pkl'
|
|
||||||
# if it exist, load it and return it
|
|
||||||
if filename in os.listdir(filepath):
|
|
||||||
print('Reference shoreline already exists and was loaded')
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_reference_shoreline.pkl'), 'rb') as f:
|
|
||||||
refsl = pickle.load(f)
|
|
||||||
return refsl
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# otherwise get the user to manually digitise a shoreline on S2, L8 or L5 images (no L7 because of scan line error)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# first try to use S2 images (10m res for manually digitizing the reference shoreline)
|
|
||||||
if 'S2' in metadata.keys():
|
|
||||||
satname = 'S2'
|
|
||||||
filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
|
|
||||||
filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
|
|
||||||
# if no S2 images, try L8 (15m res in the RGB with pansharpening)
|
|
||||||
elif not 'S2' in metadata.keys() and 'L8' in metadata.keys():
|
|
||||||
satname = 'L8'
|
|
||||||
filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
|
|
||||||
filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
|
|
||||||
# if no S2 images and no L8, use L5 images (L7 images have black diagonal bands making it
|
|
||||||
# hard to manually digitize a shoreline)
|
|
||||||
elif not 'S2' in metadata.keys() and not 'L8' in metadata.keys() and 'L5' in metadata.keys():
|
|
||||||
satname = 'L5'
|
|
||||||
filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
|
|
||||||
filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
raise Exception('You cannot digitize the shoreline on L7 images (because of gaps in the images), add another L8, S2 or L5 to your dataset.')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create figure
|
|
||||||
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=[18,9], tight_layout=True)
|
|
||||||
mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
|
|
||||||
mng.window.showMaximized()
|
|
||||||
# loop trhough the images
|
|
||||||
for i in range(len(filenames)):
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read image
|
|
||||||
fn = SDS_tools.get_filenames(filenames[i],filepath, satname)
|
|
||||||
im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = preprocess_single(fn, satname, settings['cloud_mask_issue'])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# calculate cloud cover
|
|
||||||
cloud_cover = np.divide(sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int))),
|
|
||||||
(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# skip image if cloud cover is above threshold
|
|
||||||
if cloud_cover > settings['cloud_thresh']:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# rescale image intensity for display purposes
|
|
||||||
im_RGB = rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# plot the image RGB on a figure
|
|
||||||
ax.axis('off')
|
|
||||||
ax.imshow(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# decide if the image if good enough for digitizing the shoreline
|
|
||||||
ax.set_title('Press <right arrow> if image is clear enough to digitize the shoreline.\n' +
|
|
||||||
'If the image is cloudy press <left arrow> to get another image', fontsize=14)
|
|
||||||
# set a key event to accept/reject the detections (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/15033071)
|
|
||||||
# this variable needs to be immuatable so we can access it after the keypress event
|
|
||||||
skip_image = False
|
|
||||||
key_event = {}
|
|
||||||
def press(event):
|
|
||||||
# store what key was pressed in the dictionary
|
|
||||||
key_event['pressed'] = event.key
|
|
||||||
# let the user press a key, right arrow to keep the image, left arrow to skip it
|
|
||||||
# to break the loop the user can press 'escape'
|
|
||||||
while True:
|
|
||||||
btn_keep = plt.text(1.1, 0.9, 'keep ⇨', size=12, ha="right", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=ax.transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
btn_skip = plt.text(-0.1, 0.9, '⇦ skip', size=12, ha="left", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=ax.transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
btn_esc = plt.text(0.5, 0, '<esc> to quit', size=12, ha="center", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=ax.transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
plt.draw()
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
|
|
||||||
plt.waitforbuttonpress()
|
|
||||||
# after button is pressed, remove the buttons
|
|
||||||
btn_skip.remove()
|
|
||||||
btn_keep.remove()
|
|
||||||
btn_esc.remove()
|
|
||||||
# keep/skip image according to the pressed key, 'escape' to break the loop
|
|
||||||
if key_event.get('pressed') == 'right':
|
|
||||||
skip_image = False
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'left':
|
|
||||||
skip_image = True
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
|
|
||||||
plt.close()
|
|
||||||
raise StopIteration('User cancelled checking shoreline detection')
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
plt.waitforbuttonpress()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if skip_image:
|
|
||||||
ax.clear()
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# create two new buttons
|
|
||||||
add_button = plt.text(0, 0.9, 'add', size=16, ha="left", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
end_button = plt.text(1, 0.9, 'end', size=16, ha="right", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
# add multiple reference shorelines (until user clicks on <end> button)
|
|
||||||
pts_sl = np.expand_dims(np.array([np.nan, np.nan]),axis=0)
|
|
||||||
geoms = []
|
|
||||||
while 1:
|
|
||||||
add_button.set_visible(False)
|
|
||||||
end_button.set_visible(False)
|
|
||||||
# update title (instructions)
|
|
||||||
ax.set_title('Click points along the shoreline (enough points to capture the beach curvature).\n' +
|
|
||||||
'Start at one end of the beach.\n' + 'When finished digitizing, click <ENTER>',
|
|
||||||
fontsize=14)
|
|
||||||
plt.draw()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# let user click on the shoreline
|
|
||||||
pts = ginput(n=50000, timeout=1e9, show_clicks=True)
|
|
||||||
pts_pix = np.array(pts)
|
|
||||||
# convert pixel coordinates to world coordinates
|
|
||||||
pts_world = SDS_tools.convert_pix2world(pts_pix[:,[1,0]], georef)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# interpolate between points clicked by the user (1m resolution)
|
|
||||||
pts_world_interp = np.expand_dims(np.array([np.nan, np.nan]),axis=0)
|
|
||||||
for k in range(len(pts_world)-1):
|
|
||||||
pt_dist = np.linalg.norm(pts_world[k,:]-pts_world[k+1,:])
|
|
||||||
xvals = np.arange(0,pt_dist)
|
|
||||||
yvals = np.zeros(len(xvals))
|
|
||||||
pt_coords = np.zeros((len(xvals),2))
|
|
||||||
pt_coords[:,0] = xvals
|
|
||||||
pt_coords[:,1] = yvals
|
|
||||||
phi = 0
|
|
||||||
deltax = pts_world[k+1,0] - pts_world[k,0]
|
|
||||||
deltay = pts_world[k+1,1] - pts_world[k,1]
|
|
||||||
phi = np.pi/2 - np.math.atan2(deltax, deltay)
|
|
||||||
tf = transform.EuclideanTransform(rotation=phi, translation=pts_world[k,:])
|
|
||||||
pts_world_interp = np.append(pts_world_interp,tf(pt_coords), axis=0)
|
|
||||||
pts_world_interp = np.delete(pts_world_interp,0,axis=0)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save as geometry (to create .geojson file later)
|
|
||||||
geoms.append(geometry.LineString(pts_world_interp))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# convert to pixel coordinates and plot
|
|
||||||
pts_pix_interp = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(pts_world_interp, georef)
|
|
||||||
pts_sl = np.append(pts_sl, pts_world_interp, axis=0)
|
|
||||||
ax.plot(pts_pix_interp[:,0], pts_pix_interp[:,1], 'r--')
|
|
||||||
ax.plot(pts_pix_interp[0,0], pts_pix_interp[0,1],'ko')
|
|
||||||
ax.plot(pts_pix_interp[-1,0], pts_pix_interp[-1,1],'ko')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# update title and buttons
|
|
||||||
add_button.set_visible(True)
|
|
||||||
end_button.set_visible(True)
|
|
||||||
ax.set_title('click on <add> to digitize another shoreline or on <end> to finish and save the shoreline(s)',
|
|
||||||
fontsize=14)
|
|
||||||
plt.draw()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# let the user click again (<add> another shoreline or <end>)
|
|
||||||
pt_input = ginput(n=1, timeout=1e9, show_clicks=False)
|
|
||||||
pt_input = np.array(pt_input)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if user clicks on <end>, save the points and break the loop
|
|
||||||
if pt_input[0][0] > im_ms.shape[1]/2:
|
|
||||||
add_button.set_visible(False)
|
|
||||||
end_button.set_visible(False)
|
|
||||||
plt.title('Reference shoreline saved as ' + sitename + '_reference_shoreline.pkl and ' + sitename + '_reference_shoreline.geojson')
|
|
||||||
plt.draw()
|
|
||||||
ginput(n=1, timeout=3, show_clicks=False)
|
|
||||||
plt.close()
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
pts_sl = np.delete(pts_sl,0,axis=0)
|
|
||||||
# convert world image coordinates to user-defined coordinate system
|
|
||||||
image_epsg = metadata[satname]['epsg'][i]
|
|
||||||
pts_coords = SDS_tools.convert_epsg(pts_sl, image_epsg, settings['output_epsg'])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save the reference shoreline as .pkl
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename)
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_reference_shoreline.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
|
|
||||||
pickle.dump(pts_coords, f)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# also store as .geojson in case user wants to drag-and-drop on GIS for verification
|
|
||||||
for k,line in enumerate(geoms):
|
|
||||||
gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame(geometry=gpd.GeoSeries(line))
|
|
||||||
gdf.index = [k]
|
|
||||||
gdf.loc[k,'name'] = 'reference shoreline ' + str(k+1)
|
|
||||||
# store into geodataframe
|
|
||||||
if k == 0:
|
|
||||||
gdf_all = gdf
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
gdf_all = gdf_all.append(gdf)
|
|
||||||
gdf_all.crs = {'init':'epsg:'+str(image_epsg)}
|
|
||||||
# convert from image_epsg to user-defined coordinate system
|
|
||||||
gdf_all = gdf_all.to_crs({'init': 'epsg:'+str(settings['output_epsg'])})
|
|
||||||
# save as geojson
|
|
||||||
gdf_all.to_file(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_reference_shoreline.geojson'),
|
|
||||||
driver='GeoJSON', encoding='utf-8')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('Reference shoreline has been saved in ' + filepath)
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# check if a shoreline was digitised
|
|
||||||
if len(pts_coords) == 0:
|
|
||||||
raise Exception('No cloud free images are available to digitise the reference shoreline,'+
|
|
||||||
'download more images and try again')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return pts_coords
|
|
||||||
@ -1,852 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
This module contains all the functions needed for extracting satellite-derived
|
|
||||||
shorelines (SDS)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# load modules
|
|
||||||
import os
|
|
||||||
import numpy as np
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
|
||||||
import pdb
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# image processing modules
|
|
||||||
import skimage.filters as filters
|
|
||||||
import skimage.measure as measure
|
|
||||||
import skimage.morphology as morphology
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# machine learning modules
|
|
||||||
from sklearn.externals import joblib
|
|
||||||
from shapely.geometry import LineString
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# other modules
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.cm as cm
|
|
||||||
from matplotlib import gridspec
|
|
||||||
from pylab import ginput
|
|
||||||
import pickle
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# CoastSat modules
|
|
||||||
from coastsat import SDS_tools, SDS_preprocess
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
# IMAGE CLASSIFICATION FUNCTIONS
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def calculate_features(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_bool):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Calculates features on the image that are used for the supervised classification.
|
|
||||||
The features include spectral normalized-difference indices and standard
|
|
||||||
deviation of the image for all the bands and indices.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_ms: np.array
|
|
||||||
RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
im_bool: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D array of boolean indicating where on the image to calculate the features
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
features: np.array
|
|
||||||
matrix containing each feature (columns) calculated for all
|
|
||||||
the pixels (rows) indicated in im_bool
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# add all the multispectral bands
|
|
||||||
features = np.expand_dims(im_ms[im_bool,0],axis=1)
|
|
||||||
for k in range(1,im_ms.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
feature = np.expand_dims(im_ms[im_bool,k],axis=1)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, feature, axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
# NIR-G
|
|
||||||
im_NIRG = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,3], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_NIRG[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
# SWIR-G
|
|
||||||
im_SWIRG = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_SWIRG[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
# NIR-R
|
|
||||||
im_NIRR = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,3], im_ms[:,:,2], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_NIRR[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
# SWIR-NIR
|
|
||||||
im_SWIRNIR = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,3], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_SWIRNIR[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
# B-R
|
|
||||||
im_BR = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,0], im_ms[:,:,2], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_BR[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
# calculate standard deviation of individual bands
|
|
||||||
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_ms[:,:,k], 1)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_std[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
# calculate standard deviation of the spectral indices
|
|
||||||
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_NIRG, 1)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_std[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_SWIRG, 1)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_std[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_NIRR, 1)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_std[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_SWIRNIR, 1)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_std[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_BR, 1)
|
|
||||||
features = np.append(features, np.expand_dims(im_std[im_bool],axis=1), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return features
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask, min_beach_area, clf):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Classifies every pixel in the image in one of 4 classes:
|
|
||||||
- sand --> label = 1
|
|
||||||
- whitewater (breaking waves and swash) --> label = 2
|
|
||||||
- water --> label = 3
|
|
||||||
- other (vegetation, buildings, rocks...) --> label = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The classifier is a Neural Network that is already trained.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_ms: np.array
|
|
||||||
Pansharpened RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
|
|
||||||
im_extra:
|
|
||||||
only used for Landsat 7 and 8 where im_extra is the panchromatic band
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
min_beach_area: int
|
|
||||||
minimum number of pixels that have to be connected to belong to the SAND class
|
|
||||||
clf: joblib object
|
|
||||||
pre-trained classifier
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_classif: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D image containing labels
|
|
||||||
im_labels: np.array of booleans
|
|
||||||
3D image containing a boolean image for each class (im_classif == label)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# calculate features
|
|
||||||
vec_features = calculate_features(im_ms, cloud_mask, np.ones(cloud_mask.shape).astype(bool))
|
|
||||||
vec_features[np.isnan(vec_features)] = 1e-9 # NaN values are create when std is too close to 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove NaNs and cloudy pixels
|
|
||||||
vec_cloud = cloud_mask.reshape(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
vec_nan = np.any(np.isnan(vec_features), axis=1)
|
|
||||||
vec_mask = np.logical_or(vec_cloud, vec_nan)
|
|
||||||
vec_features = vec_features[~vec_mask, :]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# classify pixels
|
|
||||||
labels = clf.predict(vec_features)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# recompose image
|
|
||||||
vec_classif = np.nan*np.ones((cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
vec_classif[~vec_mask] = labels
|
|
||||||
im_classif = vec_classif.reshape((cloud_mask.shape[0], cloud_mask.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create a stack of boolean images for each label
|
|
||||||
im_sand = im_classif == 1
|
|
||||||
im_swash = im_classif == 2
|
|
||||||
im_water = im_classif == 3
|
|
||||||
# remove small patches of sand or water that could be around the image (usually noise)
|
|
||||||
im_sand = morphology.remove_small_objects(im_sand, min_size=min_beach_area, connectivity=2)
|
|
||||||
im_water = morphology.remove_small_objects(im_water, min_size=min_beach_area, connectivity=2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
im_labels = np.stack((im_sand,im_swash,im_water), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return im_classif, im_labels
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
# CONTOUR MAPPING FUNCTIONS
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def find_wl_contours1(im_ndwi, cloud_mask, im_ref_buffer):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Traditional method for shoreline detection using a global threshold.
|
|
||||||
Finds the water line by thresholding the Normalized Difference Water Index
|
|
||||||
and applying the Marching Squares Algorithm to contour the iso-value
|
|
||||||
corresponding to the threshold.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_ndwi: np.ndarray
|
|
||||||
Image (2D) with the NDWI (water index)
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.ndarray
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
im_ref_buffer: np.array
|
|
||||||
Binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
contours_wl: list of np.arrays
|
|
||||||
contains the coordinates of the contour lines
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# reshape image to vector
|
|
||||||
vec_ndwi = im_ndwi.reshape(im_ndwi.shape[0] * im_ndwi.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
vec_mask = cloud_mask.reshape(cloud_mask.shape[0] * cloud_mask.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
vec = vec_ndwi[~vec_mask]
|
|
||||||
# apply otsu's threshold
|
|
||||||
vec = vec[~np.isnan(vec)]
|
|
||||||
t_otsu = filters.threshold_otsu(vec)
|
|
||||||
# use Marching Squares algorithm to detect contours on ndwi image
|
|
||||||
im_ndwi_buffer = np.copy(im_ndwi)
|
|
||||||
im_ndwi_buffer[~im_ref_buffer] = np.nan
|
|
||||||
contours = measure.find_contours(im_ndwi_buffer, t_otsu)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove contours that contain NaNs (due to cloud pixels in the contour)
|
|
||||||
contours_nonans = []
|
|
||||||
for k in range(len(contours)):
|
|
||||||
if np.any(np.isnan(contours[k])):
|
|
||||||
index_nan = np.where(np.isnan(contours[k]))[0]
|
|
||||||
contours_temp = np.delete(contours[k], index_nan, axis=0)
|
|
||||||
if len(contours_temp) > 1:
|
|
||||||
contours_nonans.append(contours_temp)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
contours_nonans.append(contours[k])
|
|
||||||
contours = contours_nonans
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return contours
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels, cloud_mask, buffer_size, im_ref_buffer):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
New robust method for extracting shorelines. Incorporates the classification
|
|
||||||
component to refine the treshold and make it specific to the sand/water interface.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_ms: np.array
|
|
||||||
RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
|
|
||||||
im_labels: np.array
|
|
||||||
3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
buffer_size: int
|
|
||||||
size of the buffer around the sandy beach over which the pixels are considered in the
|
|
||||||
thresholding algorithm.
|
|
||||||
im_ref_buffer: np.array
|
|
||||||
binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
contours_wi: list of np.arrays
|
|
||||||
contains the coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
|
|
||||||
NDWI (Normalized Difference Water Index) image
|
|
||||||
contours_mwi: list of np.arrays
|
|
||||||
contains the coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
|
|
||||||
MNDWI (Modified Normalized Difference Water Index) image
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
nrows = cloud_mask.shape[0]
|
|
||||||
ncols = cloud_mask.shape[1]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# calculate Normalized Difference Modified Water Index (SWIR - G)
|
|
||||||
im_mwi = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
# calculate Normalized Difference Modified Water Index (NIR - G)
|
|
||||||
im_wi = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,3], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
# stack indices together
|
|
||||||
im_ind = np.stack((im_wi, im_mwi), axis=-1)
|
|
||||||
vec_ind = im_ind.reshape(nrows*ncols,2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# reshape labels into vectors
|
|
||||||
vec_sand = im_labels[:,:,0].reshape(ncols*nrows)
|
|
||||||
vec_water = im_labels[:,:,2].reshape(ncols*nrows)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create a buffer around the sandy beach
|
|
||||||
se = morphology.disk(buffer_size)
|
|
||||||
im_buffer = morphology.binary_dilation(im_labels[:,:,0], se)
|
|
||||||
vec_buffer = im_buffer.reshape(nrows*ncols)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# select water/sand/swash pixels that are within the buffer
|
|
||||||
int_water = vec_ind[np.logical_and(vec_buffer,vec_water),:]
|
|
||||||
int_sand = vec_ind[np.logical_and(vec_buffer,vec_sand),:]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# make sure both classes have the same number of pixels before thresholding
|
|
||||||
if len(int_water) > 0 and len(int_sand) > 0:
|
|
||||||
if np.argmin([int_sand.shape[0],int_water.shape[0]]) == 1:
|
|
||||||
int_sand = int_sand[np.random.choice(int_sand.shape[0],int_water.shape[0], replace=False),:]
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
int_water = int_water[np.random.choice(int_water.shape[0],int_sand.shape[0], replace=False),:]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# threshold the sand/water intensities
|
|
||||||
int_all = np.append(int_water,int_sand, axis=0)
|
|
||||||
t_mwi = filters.threshold_otsu(int_all[:,0])
|
|
||||||
t_wi = filters.threshold_otsu(int_all[:,1])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# find contour with MS algorithm
|
|
||||||
im_wi_buffer = np.copy(im_wi)
|
|
||||||
im_wi_buffer[~im_ref_buffer] = np.nan
|
|
||||||
im_mwi_buffer = np.copy(im_mwi)
|
|
||||||
im_mwi_buffer[~im_ref_buffer] = np.nan
|
|
||||||
contours_wi = measure.find_contours(im_wi_buffer, t_wi)
|
|
||||||
contours_mwi = measure.find_contours(im_mwi_buffer, t_mwi)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# remove contour points that are NaNs (around clouds)
|
|
||||||
contours = contours_wi
|
|
||||||
contours_nonans = []
|
|
||||||
for k in range(len(contours)):
|
|
||||||
if np.any(np.isnan(contours[k])):
|
|
||||||
index_nan = np.where(np.isnan(contours[k]))[0]
|
|
||||||
contours_temp = np.delete(contours[k], index_nan, axis=0)
|
|
||||||
if len(contours_temp) > 1:
|
|
||||||
contours_nonans.append(contours_temp)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
contours_nonans.append(contours[k])
|
|
||||||
contours_wi = contours_nonans
|
|
||||||
# repeat for MNDWI contours
|
|
||||||
contours = contours_mwi
|
|
||||||
contours_nonans = []
|
|
||||||
for k in range(len(contours)):
|
|
||||||
if np.any(np.isnan(contours[k])):
|
|
||||||
index_nan = np.where(np.isnan(contours[k]))[0]
|
|
||||||
contours_temp = np.delete(contours[k], index_nan, axis=0)
|
|
||||||
if len(contours_temp) > 1:
|
|
||||||
contours_nonans.append(contours_temp)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
contours_nonans.append(contours[k])
|
|
||||||
contours_mwi = contours_nonans
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return contours_wi, contours_mwi
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
# SHORELINE PROCESSING FUNCTIONS
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def create_shoreline_buffer(im_shape, georef, image_epsg, pixel_size, settings):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Creates a buffer around the reference shoreline. The size of the buffer is
|
|
||||||
given by settings['max_dist_ref'].
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_shape: np.array
|
|
||||||
size of the image (rows,columns)
|
|
||||||
georef: np.array
|
|
||||||
vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
|
|
||||||
image_epsg: int
|
|
||||||
spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
|
|
||||||
pixel_size: int
|
|
||||||
size of the pixel in metres (15 for Landsat, 10 for Sentinel-2)
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'output_epsg': int
|
|
||||||
output spatial reference system
|
|
||||||
'reference_shoreline': np.array
|
|
||||||
coordinates of the reference shoreline
|
|
||||||
'max_dist_ref': int
|
|
||||||
maximum distance from the reference shoreline in metres
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_buffer: np.array
|
|
||||||
binary image, True where the buffer is, False otherwise
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
# initialise the image buffer
|
|
||||||
im_buffer = np.ones(im_shape).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if 'reference_shoreline' in settings.keys():
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# convert reference shoreline to pixel coordinates
|
|
||||||
ref_sl = settings['reference_shoreline']
|
|
||||||
ref_sl_conv = SDS_tools.convert_epsg(ref_sl, settings['output_epsg'],image_epsg)[:,:-1]
|
|
||||||
ref_sl_pix = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(ref_sl_conv, georef)
|
|
||||||
ref_sl_pix_rounded = np.round(ref_sl_pix).astype(int)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# make sure that the pixel coordinates of the reference shoreline are inside the image
|
|
||||||
idx_row = np.logical_and(ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,0] > 0, ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,0] < im_shape[1])
|
|
||||||
idx_col = np.logical_and(ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,1] > 0, ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,1] < im_shape[0])
|
|
||||||
idx_inside = np.logical_and(idx_row, idx_col)
|
|
||||||
ref_sl_pix_rounded = ref_sl_pix_rounded[idx_inside,:]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create binary image of the reference shoreline (1 where the shoreline is 0 otherwise)
|
|
||||||
im_binary = np.zeros(im_shape)
|
|
||||||
for j in range(len(ref_sl_pix_rounded)):
|
|
||||||
im_binary[ref_sl_pix_rounded[j,1], ref_sl_pix_rounded[j,0]] = 1
|
|
||||||
im_binary = im_binary.astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# dilate the binary image to create a buffer around the reference shoreline
|
|
||||||
max_dist_ref_pixels = np.ceil(settings['max_dist_ref']/pixel_size)
|
|
||||||
se = morphology.disk(max_dist_ref_pixels)
|
|
||||||
im_buffer = morphology.binary_dilation(im_binary, se)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return im_buffer
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def process_shoreline(contours, cloud_mask, georef, image_epsg, settings):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Converts the contours from image coordinates to world coordinates.
|
|
||||||
This function also removes the contours that are too small to be a shoreline
|
|
||||||
(based on the parameter settings['min_length_sl'])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
contours: np.array or list of np.array
|
|
||||||
image contours as detected by the function find_contours
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
georef: np.array
|
|
||||||
vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
|
|
||||||
image_epsg: int
|
|
||||||
spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'output_epsg': int
|
|
||||||
output spatial reference system
|
|
||||||
'min_length_sl': float
|
|
||||||
minimum length of shoreline contour to be kept (in meters)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
shoreline: np.array
|
|
||||||
array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# convert pixel coordinates to world coordinates
|
|
||||||
contours_world = SDS_tools.convert_pix2world(contours, georef)
|
|
||||||
# convert world coordinates to desired spatial reference system
|
|
||||||
contours_epsg = SDS_tools.convert_epsg(contours_world, image_epsg, settings['output_epsg'])
|
|
||||||
# remove contours that have a perimeter < min_length_sl (provided in settings dict)
|
|
||||||
# this enables to remove the very small contours that do not correspond to the shoreline
|
|
||||||
contours_long = []
|
|
||||||
for l, wl in enumerate(contours_epsg):
|
|
||||||
coords = [(wl[k,0], wl[k,1]) for k in range(len(wl))]
|
|
||||||
a = LineString(coords) # shapely LineString structure
|
|
||||||
if a.length >= settings['min_length_sl']:
|
|
||||||
contours_long.append(wl)
|
|
||||||
# format points into np.array
|
|
||||||
x_points = np.array([])
|
|
||||||
y_points = np.array([])
|
|
||||||
for k in range(len(contours_long)):
|
|
||||||
x_points = np.append(x_points,contours_long[k][:,0])
|
|
||||||
y_points = np.append(y_points,contours_long[k][:,1])
|
|
||||||
contours_array = np.transpose(np.array([x_points,y_points]))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
shoreline = contours_array
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# now remove any shoreline points that are attached to cloud pixels
|
|
||||||
if sum(sum(cloud_mask)) > 0:
|
|
||||||
# get the coordinates of the cloud pixels
|
|
||||||
idx_cloud = np.where(cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
idx_cloud = np.array([(idx_cloud[0][k], idx_cloud[1][k]) for k in range(len(idx_cloud[0]))])
|
|
||||||
# convert to world coordinates and same epsg as the shoreline points
|
|
||||||
coords_cloud = SDS_tools.convert_epsg(SDS_tools.convert_pix2world(idx_cloud, georef),
|
|
||||||
image_epsg, settings['output_epsg'])[:,:-1]
|
|
||||||
# only keep the shoreline points that are at least 30m from any cloud pixel
|
|
||||||
idx_keep = np.ones(len(shoreline)).astype(bool)
|
|
||||||
for k in range(len(shoreline)):
|
|
||||||
if np.any(np.linalg.norm(shoreline[k,:] - coords_cloud, axis=1) < 30):
|
|
||||||
idx_keep[k] = False
|
|
||||||
shoreline = shoreline[idx_keep]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return shoreline
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,image_epsg, georef,
|
|
||||||
settings, date, satname):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Shows the detected shoreline to the user for visual quality control.
|
|
||||||
The user can accept/reject the detected shorelines by using keep/skip
|
|
||||||
buttons.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_ms: np.array
|
|
||||||
RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
im_labels: np.array
|
|
||||||
3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
|
|
||||||
shoreline: np.array
|
|
||||||
array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
|
|
||||||
image_epsg: int
|
|
||||||
spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
|
|
||||||
georef: np.array
|
|
||||||
vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
|
|
||||||
date: string
|
|
||||||
date at which the image was taken
|
|
||||||
satname: string
|
|
||||||
indicates the satname (L5,L7,L8 or S2)
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'inputs': dict
|
|
||||||
input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
|
|
||||||
'output_epsg': int
|
|
||||||
output spatial reference system as EPSG code
|
|
||||||
'check_detection': bool
|
|
||||||
if True, lets user manually accept/reject the mapped shorelines
|
|
||||||
'save_figure': bool
|
|
||||||
if True, saves a -jpg file for each mapped shoreline
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
skip_image: boolean
|
|
||||||
True if the user wants to skip the image, False otherwise
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
|
|
||||||
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
|
|
||||||
# subfolder where the .jpg file is stored if the user accepts the shoreline detection
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'jpg_files', 'detection')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# compute classified image
|
|
||||||
im_class = np.copy(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
cmap = cm.get_cmap('tab20c')
|
|
||||||
colorpalette = cmap(np.arange(0,13,1))
|
|
||||||
colours = np.zeros((3,4))
|
|
||||||
colours[0,:] = colorpalette[5]
|
|
||||||
colours[1,:] = np.array([204/255,1,1,1])
|
|
||||||
colours[2,:] = np.array([0,91/255,1,1])
|
|
||||||
for k in range(0,im_labels.shape[2]):
|
|
||||||
im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],0] = colours[k,0]
|
|
||||||
im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],1] = colours[k,1]
|
|
||||||
im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],2] = colours[k,2]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# compute MNDWI grayscale image
|
|
||||||
im_mwi = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# transform world coordinates of shoreline into pixel coordinates
|
|
||||||
# use try/except in case there are no coordinates to be transformed (shoreline = [])
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
sl_pix = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(SDS_tools.convert_epsg(shoreline,
|
|
||||||
settings['output_epsg'],
|
|
||||||
image_epsg)[:,[0,1]], georef)
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
# if try fails, just add nan into the shoreline vector so the next parts can still run
|
|
||||||
sl_pix = np.array([[np.nan, np.nan],[np.nan, np.nan]])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if plt.get_fignums():
|
|
||||||
# get open figure if it exists
|
|
||||||
fig = plt.gcf()
|
|
||||||
ax1 = fig.axes[0]
|
|
||||||
ax2 = fig.axes[1]
|
|
||||||
ax3 = fig.axes[2]
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# else create a new figure
|
|
||||||
fig = plt.figure()
|
|
||||||
fig.set_size_inches([18, 9])
|
|
||||||
mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
|
|
||||||
mng.window.showMaximized()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# according to the image shape, decide whether it is better to have the images
|
|
||||||
# in vertical subplots or horizontal subplots
|
|
||||||
if im_RGB.shape[1] > 1.5*im_RGB.shape[0]:
|
|
||||||
# vertical subplots
|
|
||||||
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(3, 1)
|
|
||||||
gs.update(bottom=0.03, top=0.97, left=0.03, right=0.97)
|
|
||||||
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,0])
|
|
||||||
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1,0], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
|
|
||||||
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[2,0], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# horizontal subplots
|
|
||||||
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(1, 3)
|
|
||||||
gs.update(bottom=0.05, top=0.95, left=0.05, right=0.95)
|
|
||||||
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,0])
|
|
||||||
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,1], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
|
|
||||||
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,2], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# change the color of nans to either black (0.0) or white (1.0) or somewhere in between
|
|
||||||
nan_color = 1.0
|
|
||||||
im_RGB = np.where(np.isnan(im_RGB), nan_color, im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
im_class = np.where(np.isnan(im_class), 1.0, im_class)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create image 1 (RGB)
|
|
||||||
ax1.imshow(im_RGB)
|
|
||||||
ax1.plot(sl_pix[:,0], sl_pix[:,1], 'k.', markersize=3)
|
|
||||||
ax1.axis('off')
|
|
||||||
ax1.set_title(sitename, fontweight='bold', fontsize=16)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create image 2 (classification)
|
|
||||||
ax2.imshow(im_class)
|
|
||||||
ax2.plot(sl_pix[:,0], sl_pix[:,1], 'k.', markersize=3)
|
|
||||||
ax2.axis('off')
|
|
||||||
orange_patch = mpatches.Patch(color=colours[0,:], label='sand')
|
|
||||||
white_patch = mpatches.Patch(color=colours[1,:], label='whitewater')
|
|
||||||
blue_patch = mpatches.Patch(color=colours[2,:], label='water')
|
|
||||||
black_line = mlines.Line2D([],[],color='k',linestyle='-', label='shoreline')
|
|
||||||
ax2.legend(handles=[orange_patch,white_patch,blue_patch, black_line],
|
|
||||||
bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5), fontsize=10)
|
|
||||||
ax2.set_title(date, fontweight='bold', fontsize=16)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create image 3 (MNDWI)
|
|
||||||
ax3.imshow(im_mwi, cmap='bwr')
|
|
||||||
ax3.plot(sl_pix[:,0], sl_pix[:,1], 'k.', markersize=3)
|
|
||||||
ax3.axis('off')
|
|
||||||
ax3.set_title(satname, fontweight='bold', fontsize=16)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# additional options
|
|
||||||
# ax1.set_anchor('W')
|
|
||||||
# ax2.set_anchor('W')
|
|
||||||
# cb = plt.colorbar()
|
|
||||||
# cb.ax.tick_params(labelsize=10)
|
|
||||||
# cb.set_label('MNDWI values')
|
|
||||||
# ax3.set_anchor('W')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if check_detection is True, let user manually accept/reject the images
|
|
||||||
skip_image = False
|
|
||||||
if settings['check_detection']:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# set a key event to accept/reject the detections (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/15033071)
|
|
||||||
# this variable needs to be immuatable so we can access it after the keypress event
|
|
||||||
key_event = {}
|
|
||||||
def press(event):
|
|
||||||
# store what key was pressed in the dictionary
|
|
||||||
key_event['pressed'] = event.key
|
|
||||||
# let the user press a key, right arrow to keep the image, left arrow to skip it
|
|
||||||
# to break the loop the user can press 'escape'
|
|
||||||
while True:
|
|
||||||
btn_keep = plt.text(1.1, 0.9, 'keep ⇨', size=12, ha="right", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=ax1.transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
btn_skip = plt.text(-0.1, 0.9, '⇦ skip', size=12, ha="left", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=ax1.transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
btn_esc = plt.text(0.5, 0, '<esc> to quit', size=12, ha="center", va="top",
|
|
||||||
transform=ax1.transAxes,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
plt.draw()
|
|
||||||
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
|
|
||||||
plt.waitforbuttonpress()
|
|
||||||
# after button is pressed, remove the buttons
|
|
||||||
btn_skip.remove()
|
|
||||||
btn_keep.remove()
|
|
||||||
btn_esc.remove()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# keep/skip image according to the pressed key, 'escape' to break the loop
|
|
||||||
if key_event.get('pressed') == 'right':
|
|
||||||
skip_image = False
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'left':
|
|
||||||
skip_image = True
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
|
|
||||||
plt.close()
|
|
||||||
raise StopIteration('User cancelled checking shoreline detection')
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
plt.waitforbuttonpress()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if save_figure is True, save a .jpg under /jpg_files/detection
|
|
||||||
if settings['save_figure'] and not skip_image:
|
|
||||||
fig.savefig(os.path.join(filepath, date + '_' + satname + '.jpg'), dpi=150)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Don't close the figure window, but remove all axes and settings, ready for next plot
|
|
||||||
for ax in fig.axes:
|
|
||||||
ax.clear()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return skip_image
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Main function to extract shorelines from satellite images
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
metadata: dict
|
|
||||||
contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'inputs': dict
|
|
||||||
input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
|
|
||||||
'cloud_thresh': float
|
|
||||||
value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
|
|
||||||
the cropped image that is accepted
|
|
||||||
'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
|
|
||||||
True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
|
|
||||||
are erroneously being masked on the images
|
|
||||||
'buffer_size': int
|
|
||||||
size of the buffer (m) around the sandy pixels over which the pixels
|
|
||||||
are considered in the thresholding algorithm
|
|
||||||
'min_beach_area': int
|
|
||||||
minimum allowable object area (in metres^2) for the class 'sand',
|
|
||||||
the area is converted to number of connected pixels
|
|
||||||
'min_length_sl': int
|
|
||||||
minimum length (in metres) of shoreline contour to be valid
|
|
||||||
'sand_color': str
|
|
||||||
default', 'dark' (for grey/black sand beaches) or 'bright' (for white sand beaches)
|
|
||||||
'output_epsg': int
|
|
||||||
output spatial reference system as EPSG code
|
|
||||||
'check_detection': bool
|
|
||||||
if True, lets user manually accept/reject the mapped shorelines
|
|
||||||
'save_figure': bool
|
|
||||||
if True, saves a -jpg file for each mapped shoreline
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
output: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates + metadata
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
|
|
||||||
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
|
|
||||||
filepath_models = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classification', 'models')
|
|
||||||
# initialise output structure
|
|
||||||
output = dict([])
|
|
||||||
# create a subfolder to store the .jpg images showing the detection
|
|
||||||
filepath_jpg = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'jpg_files', 'detection')
|
|
||||||
if not os.path.exists(filepath_jpg):
|
|
||||||
os.makedirs(filepath_jpg)
|
|
||||||
# close all open figures
|
|
||||||
plt.close('all')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('Mapping shorelines:')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop through satellite list
|
|
||||||
for satname in metadata.keys():
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# get images
|
|
||||||
filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
|
|
||||||
filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# initialise the output variables
|
|
||||||
output_timestamp = [] # datetime at which the image was acquired (UTC time)
|
|
||||||
output_shoreline = [] # vector of shoreline points
|
|
||||||
output_filename = [] # filename of the images from which the shorelines where derived
|
|
||||||
output_cloudcover = [] # cloud cover of the images
|
|
||||||
output_geoaccuracy = []# georeferencing accuracy of the images
|
|
||||||
output_idxkeep = [] # index that were kept during the analysis (cloudy images are skipped)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# load classifiers and
|
|
||||||
if satname in ['L5','L7','L8']:
|
|
||||||
pixel_size = 15
|
|
||||||
if settings['sand_color'] == 'dark':
|
|
||||||
clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_dark.pkl'))
|
|
||||||
elif settings['sand_color'] == 'bright':
|
|
||||||
clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_bright.pkl'))
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat.pkl'))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif satname == 'S2':
|
|
||||||
pixel_size = 10
|
|
||||||
clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_S2.pkl'))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# convert settings['min_beach_area'] and settings['buffer_size'] from metres to pixels
|
|
||||||
buffer_size_pixels = np.ceil(settings['buffer_size']/pixel_size)
|
|
||||||
min_beach_area_pixels = np.ceil(settings['min_beach_area']/pixel_size**2)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop through the images
|
|
||||||
for i in range(len(filenames)):
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('\r%s: %d%%' % (satname,int(((i+1)/len(filenames))*100)), end='')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# get image filename
|
|
||||||
fn = SDS_tools.get_filenames(filenames[i],filepath, satname)
|
|
||||||
# preprocess image (cloud mask + pansharpening/downsampling)
|
|
||||||
im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn, satname, settings['cloud_mask_issue'])
|
|
||||||
# get image spatial reference system (epsg code) from metadata dict
|
|
||||||
image_epsg = metadata[satname]['epsg'][i]
|
|
||||||
# define an advanced cloud mask (for L7 it takes into account the fact that diagonal
|
|
||||||
# bands of no data are not clouds)
|
|
||||||
if not satname == 'L7' or sum(sum(im_nodata)) == 0 or sum(sum(im_nodata)) > 0.5*im_nodata.size:
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask_adv = cloud_mask
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask_adv = np.logical_xor(cloud_mask, im_nodata)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# calculate cloud cover
|
|
||||||
cloud_cover = np.divide(sum(sum(cloud_mask_adv.astype(int))),
|
|
||||||
(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
|
|
||||||
# skip image if cloud cover is above threshold
|
|
||||||
if cloud_cover > settings['cloud_thresh']:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# calculate a buffer around the reference shoreline (if any has been digitised)
|
|
||||||
im_ref_buffer = create_shoreline_buffer(cloud_mask.shape, georef, image_epsg,
|
|
||||||
pixel_size, settings)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
|
|
||||||
im_classif, im_labels = classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask,
|
|
||||||
min_beach_area_pixels, clf)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# there are two options to map the contours:
|
|
||||||
# if there are pixels in the 'sand' class --> use find_wl_contours2 (enhanced)
|
|
||||||
# otherwise use find_wl_contours2 (traditional)
|
|
||||||
try: # use try/except structure for long runs
|
|
||||||
if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) < 10 :
|
|
||||||
# compute MNDWI image (SWIR-G)
|
|
||||||
im_mndwi = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
|
|
||||||
# find water contours on MNDWI grayscale image
|
|
||||||
contours_mwi = find_wl_contours1(im_mndwi, cloud_mask, im_ref_buffer)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# use classification to refine threshold and extract the sand/water interface
|
|
||||||
contours_wi, contours_mwi = find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels,
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask, buffer_size_pixels, im_ref_buffer)
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
print('Could not map shoreline for this image: ' + filenames[i])
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# process the water contours into a shoreline
|
|
||||||
shoreline = process_shoreline(contours_mwi, cloud_mask, georef, image_epsg, settings)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# visualise the mapped shorelines, there are two options:
|
|
||||||
# if settings['check_detection'] = True, shows the detection to the user for accept/reject
|
|
||||||
# if settings['save_figure'] = True, saves a figure for each mapped shoreline
|
|
||||||
if settings['check_detection'] or settings['save_figure']:
|
|
||||||
date = filenames[i][:19]
|
|
||||||
if not settings['check_detection']:
|
|
||||||
plt.ioff() # turning interactive plotting off
|
|
||||||
skip_image = show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,
|
|
||||||
image_epsg, georef, settings, date, satname)
|
|
||||||
# if the user decides to skip the image, continue and do not save the mapped shoreline
|
|
||||||
if skip_image:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# append to output variables
|
|
||||||
output_timestamp.append(metadata[satname]['dates'][i])
|
|
||||||
output_shoreline.append(shoreline)
|
|
||||||
output_filename.append(filenames[i])
|
|
||||||
output_cloudcover.append(cloud_cover)
|
|
||||||
output_geoaccuracy.append(metadata[satname]['acc_georef'][i])
|
|
||||||
output_idxkeep.append(i)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# create dictionnary of output
|
|
||||||
output[satname] = {
|
|
||||||
'dates': output_timestamp,
|
|
||||||
'shorelines': output_shoreline,
|
|
||||||
'filename': output_filename,
|
|
||||||
'cloud_cover': output_cloudcover,
|
|
||||||
'geoaccuracy': output_geoaccuracy,
|
|
||||||
'idx': output_idxkeep
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
print('')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Close figure window if still open
|
|
||||||
if plt.get_fignums():
|
|
||||||
plt.close()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# change the format to have one list sorted by date with all the shorelines (easier to use)
|
|
||||||
output = SDS_tools.merge_output(output)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save outputput structure as output.pkl
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename)
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_output.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
|
|
||||||
pickle.dump(output, f)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save output into a gdb.GeoDataFrame
|
|
||||||
gdf = SDS_tools.output_to_gdf(output)
|
|
||||||
# set projection
|
|
||||||
gdf.crs = {'init':'epsg:'+str(settings['output_epsg'])}
|
|
||||||
# save as geojson
|
|
||||||
gdf.to_file(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_output.geojson'), driver='GeoJSON', encoding='utf-8')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return output
|
|
||||||
@ -1,551 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
This module contains utilities to work with satellite images
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# load modules
|
|
||||||
import os
|
|
||||||
import numpy as np
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
|
||||||
import pdb
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# other modules
|
|
||||||
from osgeo import gdal, osr
|
|
||||||
import geopandas as gpd
|
|
||||||
from shapely import geometry
|
|
||||||
import skimage.transform as transform
|
|
||||||
from astropy.convolution import convolve
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
# COORDINATES CONVERSION FUNCTIONS
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def convert_pix2world(points, georef):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Converts pixel coordinates (pixel row and column) to world projected
|
|
||||||
coordinates performing an affine transformation.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
points: np.array or list of np.array
|
|
||||||
array with 2 columns (row first and column second)
|
|
||||||
georef: np.array
|
|
||||||
vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
|
|
||||||
converted coordinates, first columns with X and second column with Y
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# make affine transformation matrix
|
|
||||||
aff_mat = np.array([[georef[1], georef[2], georef[0]],
|
|
||||||
[georef[4], georef[5], georef[3]],
|
|
||||||
[0, 0, 1]])
|
|
||||||
# create affine transformation
|
|
||||||
tform = transform.AffineTransform(aff_mat)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if list of arrays
|
|
||||||
if type(points) is list:
|
|
||||||
points_converted = []
|
|
||||||
# iterate over the list
|
|
||||||
for i, arr in enumerate(points):
|
|
||||||
tmp = arr[:,[1,0]]
|
|
||||||
points_converted.append(tform(tmp))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if single array
|
|
||||||
elif type(points) is np.ndarray:
|
|
||||||
tmp = points[:,[1,0]]
|
|
||||||
points_converted = tform(tmp)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
raise Exception('invalid input type')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return points_converted
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def convert_world2pix(points, georef):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Converts world projected coordinates (X,Y) to image coordinates
|
|
||||||
(pixel row and column) performing an affine transformation.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
points: np.array or list of np.array
|
|
||||||
array with 2 columns (X,Y)
|
|
||||||
georef: np.array
|
|
||||||
vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
|
|
||||||
converted coordinates (pixel row and column)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# make affine transformation matrix
|
|
||||||
aff_mat = np.array([[georef[1], georef[2], georef[0]],
|
|
||||||
[georef[4], georef[5], georef[3]],
|
|
||||||
[0, 0, 1]])
|
|
||||||
# create affine transformation
|
|
||||||
tform = transform.AffineTransform(aff_mat)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if list of arrays
|
|
||||||
if type(points) is list:
|
|
||||||
points_converted = []
|
|
||||||
# iterate over the list
|
|
||||||
for i, arr in enumerate(points):
|
|
||||||
points_converted.append(tform.inverse(points))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if single array
|
|
||||||
elif type(points) is np.ndarray:
|
|
||||||
points_converted = tform.inverse(points)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
print('invalid input type')
|
|
||||||
raise
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return points_converted
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def convert_epsg(points, epsg_in, epsg_out):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Converts from one spatial reference to another using the epsg codes
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
points: np.array or list of np.ndarray
|
|
||||||
array with 2 columns (rows first and columns second)
|
|
||||||
epsg_in: int
|
|
||||||
epsg code of the spatial reference in which the input is
|
|
||||||
epsg_out: int
|
|
||||||
epsg code of the spatial reference in which the output will be
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
|
|
||||||
converted coordinates from epsg_in to epsg_out
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# define input and output spatial references
|
|
||||||
inSpatialRef = osr.SpatialReference()
|
|
||||||
inSpatialRef.ImportFromEPSG(epsg_in)
|
|
||||||
outSpatialRef = osr.SpatialReference()
|
|
||||||
outSpatialRef.ImportFromEPSG(epsg_out)
|
|
||||||
# create a coordinates transform
|
|
||||||
coordTransform = osr.CoordinateTransformation(inSpatialRef, outSpatialRef)
|
|
||||||
# if list of arrays
|
|
||||||
if type(points) is list:
|
|
||||||
points_converted = []
|
|
||||||
# iterate over the list
|
|
||||||
for i, arr in enumerate(points):
|
|
||||||
points_converted.append(np.array(coordTransform.TransformPoints(arr)))
|
|
||||||
# if single array
|
|
||||||
elif type(points) is np.ndarray:
|
|
||||||
points_converted = np.array(coordTransform.TransformPoints(points))
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
raise Exception('invalid input type')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return points_converted
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
# IMAGE ANALYSIS FUNCTIONS
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def nd_index(im1, im2, cloud_mask):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Computes normalised difference index on 2 images (2D), given a cloud mask (2D).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im1: np.array
|
|
||||||
first image (2D) with which to calculate the ND index
|
|
||||||
im2: np.array
|
|
||||||
second image (2D) with which to calculate the ND index
|
|
||||||
cloud_mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
im_nd: np.array
|
|
||||||
Image (2D) containing the ND index
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# reshape the cloud mask
|
|
||||||
vec_mask = cloud_mask.reshape(im1.shape[0] * im1.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
# initialise with NaNs
|
|
||||||
vec_nd = np.ones(len(vec_mask)) * np.nan
|
|
||||||
# reshape the two images
|
|
||||||
vec1 = im1.reshape(im1.shape[0] * im1.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
vec2 = im2.reshape(im2.shape[0] * im2.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
# compute the normalised difference index
|
|
||||||
temp = np.divide(vec1[~vec_mask] - vec2[~vec_mask],
|
|
||||||
vec1[~vec_mask] + vec2[~vec_mask])
|
|
||||||
vec_nd[~vec_mask] = temp
|
|
||||||
# reshape into image
|
|
||||||
im_nd = vec_nd.reshape(im1.shape[0], im1.shape[1])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return im_nd
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def image_std(image, radius):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Calculates the standard deviation of an image, using a moving window of
|
|
||||||
specified radius. Uses astropy's convolution library'
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
image: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D array containing the pixel intensities of a single-band image
|
|
||||||
radius: int
|
|
||||||
radius defining the moving window used to calculate the standard deviation.
|
|
||||||
For example, radius = 1 will produce a 3x3 moving window.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
win_std: np.array
|
|
||||||
2D array containing the standard deviation of the image
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# convert to float
|
|
||||||
image = image.astype(float)
|
|
||||||
# first pad the image
|
|
||||||
image_padded = np.pad(image, radius, 'reflect')
|
|
||||||
# window size
|
|
||||||
win_rows, win_cols = radius*2 + 1, radius*2 + 1
|
|
||||||
# calculate std with uniform filters
|
|
||||||
win_mean = convolve(image_padded, np.ones((win_rows,win_cols)), boundary='extend',
|
|
||||||
normalize_kernel=True, nan_treatment='interpolate', preserve_nan=True)
|
|
||||||
win_sqr_mean = convolve(image_padded**2, np.ones((win_rows,win_cols)), boundary='extend',
|
|
||||||
normalize_kernel=True, nan_treatment='interpolate', preserve_nan=True)
|
|
||||||
win_var = win_sqr_mean - win_mean**2
|
|
||||||
win_std = np.sqrt(win_var)
|
|
||||||
# remove padding
|
|
||||||
win_std = win_std[radius:-radius, radius:-radius]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return win_std
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def mask_raster(fn, mask):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Masks a .tif raster using GDAL.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
fn: str
|
|
||||||
filepath + filename of the .tif raster
|
|
||||||
mask: np.array
|
|
||||||
array of boolean where True indicates the pixels that are to be masked
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
Overwrites the .tif file directly
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# open raster
|
|
||||||
raster = gdal.Open(fn, gdal.GA_Update)
|
|
||||||
# mask raster
|
|
||||||
for i in range(raster.RasterCount):
|
|
||||||
out_band = raster.GetRasterBand(i+1)
|
|
||||||
out_data = out_band.ReadAsArray()
|
|
||||||
out_band.SetNoDataValue(0)
|
|
||||||
no_data_value = out_band.GetNoDataValue()
|
|
||||||
out_data[mask] = no_data_value
|
|
||||||
out_band.WriteArray(out_data)
|
|
||||||
# close dataset and flush cache
|
|
||||||
raster = None
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
# UTILITIES
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_filepath(inputs,satname):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Create filepath to the different folders containing the satellite images.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
inputs: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'sitename': str
|
|
||||||
name of the site
|
|
||||||
'polygon': list
|
|
||||||
polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted,
|
|
||||||
longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column,
|
|
||||||
there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point:
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
polygon = [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
|
|
||||||
[151.3, -33.7]]]
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
'dates': list of str
|
|
||||||
list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in
|
|
||||||
format 'yyyy-mm-dd':
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
dates = ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
'sat_list': list of str
|
|
||||||
list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include:
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
sat_list = ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
'filepath_data': str
|
|
||||||
filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
|
|
||||||
satname: str
|
|
||||||
short name of the satellite mission ('L5','L7','L8','S2')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
filepath: str or list of str
|
|
||||||
contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
sitename = inputs['sitename']
|
|
||||||
filepath_data = inputs['filepath']
|
|
||||||
# access the images
|
|
||||||
if satname == 'L5':
|
|
||||||
# access downloaded Landsat 5 images
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, satname, '30m')
|
|
||||||
elif satname == 'L7':
|
|
||||||
# access downloaded Landsat 7 images
|
|
||||||
filepath_pan = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'L7', 'pan')
|
|
||||||
filepath_ms = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'L7', 'ms')
|
|
||||||
filepath = [filepath_pan, filepath_ms]
|
|
||||||
elif satname == 'L8':
|
|
||||||
# access downloaded Landsat 8 images
|
|
||||||
filepath_pan = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'L8', 'pan')
|
|
||||||
filepath_ms = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, 'L8', 'ms')
|
|
||||||
filepath = [filepath_pan, filepath_ms]
|
|
||||||
elif satname == 'S2':
|
|
||||||
# access downloaded Sentinel 2 images
|
|
||||||
filepath10 = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, satname, '10m')
|
|
||||||
filepath20 = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, satname, '20m')
|
|
||||||
filepath60 = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename, satname, '60m')
|
|
||||||
filepath = [filepath10, filepath20, filepath60]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return filepath
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_filenames(filename, filepath, satname):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Creates filepath + filename for all the bands belonging to the same image.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
filename: str
|
|
||||||
name of the downloaded satellite image as found in the metadata
|
|
||||||
filepath: str or list of str
|
|
||||||
contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
|
|
||||||
satname: str
|
|
||||||
short name of the satellite mission
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
fn: str or list of str
|
|
||||||
contains the filepath + filenames to access the satellite image
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if satname == 'L5':
|
|
||||||
fn = os.path.join(filepath, filename)
|
|
||||||
if satname == 'L7' or satname == 'L8':
|
|
||||||
filename_ms = filename.replace('pan','ms')
|
|
||||||
fn = [os.path.join(filepath[0], filename),
|
|
||||||
os.path.join(filepath[1], filename_ms)]
|
|
||||||
if satname == 'S2':
|
|
||||||
filename20 = filename.replace('10m','20m')
|
|
||||||
filename60 = filename.replace('10m','60m')
|
|
||||||
fn = [os.path.join(filepath[0], filename),
|
|
||||||
os.path.join(filepath[1], filename20),
|
|
||||||
os.path.join(filepath[2], filename60)]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return fn
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def merge_output(output):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Function to merge the output dictionnary, which has one key per satellite mission
|
|
||||||
into a dictionnary containing all the shorelines and dates ordered chronologically.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
output: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates, organised by
|
|
||||||
satellite mission
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
output_all: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the extracted shorelines in a single list sorted by date
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# initialize output dict
|
|
||||||
output_all = dict([])
|
|
||||||
satnames = list(output.keys())
|
|
||||||
for key in output[satnames[0]].keys():
|
|
||||||
output_all[key] = []
|
|
||||||
# create extra key for the satellite name
|
|
||||||
output_all['satname'] = []
|
|
||||||
# fill the output dict
|
|
||||||
for satname in list(output.keys()):
|
|
||||||
for key in output[satnames[0]].keys():
|
|
||||||
output_all[key] = output_all[key] + output[satname][key]
|
|
||||||
output_all['satname'] = output_all['satname'] + [_ for _ in np.tile(satname,
|
|
||||||
len(output[satname]['dates']))]
|
|
||||||
# sort chronologically
|
|
||||||
idx_sorted = sorted(range(len(output_all['dates'])), key=output_all['dates'].__getitem__)
|
|
||||||
for key in output_all.keys():
|
|
||||||
output_all[key] = [output_all[key][i] for i in idx_sorted]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return output_all
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
# CONVERSIONS FROM DICT TO GEODATAFRAME AND READ/WRITE GEOJSON
|
|
||||||
###################################################################################################
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def polygon_from_kml(fn):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Extracts coordinates from a .kml file.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
fn: str
|
|
||||||
filepath + filename of the kml file to be read
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
polygon: list
|
|
||||||
coordinates extracted from the .kml file
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# read .kml file
|
|
||||||
with open(fn) as kmlFile:
|
|
||||||
doc = kmlFile.read()
|
|
||||||
# parse to find coordinates field
|
|
||||||
str1 = '<coordinates>'
|
|
||||||
str2 = '</coordinates>'
|
|
||||||
subdoc = doc[doc.find(str1)+len(str1):doc.find(str2)]
|
|
||||||
coordlist = subdoc.split('\n')
|
|
||||||
# read coordinates
|
|
||||||
polygon = []
|
|
||||||
for i in range(1,len(coordlist)-1):
|
|
||||||
polygon.append([float(coordlist[i].split(',')[0]), float(coordlist[i].split(',')[1])])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return [polygon]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def transects_from_geojson(filename):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Reads transect coordinates from a .geojson file.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
filename: str
|
|
||||||
contains the path and filename of the geojson file to be loaded
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
transects: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the X and Y coordinates of each transect
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
gdf = gpd.read_file(filename)
|
|
||||||
transects = dict([])
|
|
||||||
for i in gdf.index:
|
|
||||||
transects[gdf.loc[i,'name']] = np.array(gdf.loc[i,'geometry'].coords)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print('%d transects have been loaded' % len(transects.keys()))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return transects
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def output_to_gdf(output):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Saves the mapped shorelines as a gpd.GeoDataFrame
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
output: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the coordinates of the mapped shorelines + attributes
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
|
|
||||||
contains the shorelines + attirbutes
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop through the mapped shorelines
|
|
||||||
counter = 0
|
|
||||||
for i in range(len(output['shorelines'])):
|
|
||||||
# skip if there shoreline is empty
|
|
||||||
if len(output['shorelines'][i]) == 0:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# save the geometry + attributes
|
|
||||||
geom = geometry.LineString(output['shorelines'][i])
|
|
||||||
gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame(geometry=gpd.GeoSeries(geom))
|
|
||||||
gdf.index = [i]
|
|
||||||
gdf.loc[i,'date'] = output['dates'][i].strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
|
|
||||||
gdf.loc[i,'satname'] = output['satname'][i]
|
|
||||||
gdf.loc[i,'geoaccuracy'] = output['geoaccuracy'][i]
|
|
||||||
gdf.loc[i,'cloud_cover'] = output['cloud_cover'][i]
|
|
||||||
# store into geodataframe
|
|
||||||
if counter == 0:
|
|
||||||
gdf_all = gdf
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
gdf_all = gdf_all.append(gdf)
|
|
||||||
counter = counter + 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return gdf_all
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def transects_to_gdf(transects):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Saves the shore-normal transects as a gpd.GeoDataFrame
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
transects: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the coordinates of the transects
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# loop through the mapped shorelines
|
|
||||||
for i,key in enumerate(list(transects.keys())):
|
|
||||||
# save the geometry + attributes
|
|
||||||
geom = geometry.LineString(transects[key])
|
|
||||||
gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame(geometry=gpd.GeoSeries(geom))
|
|
||||||
gdf.index = [i]
|
|
||||||
gdf.loc[i,'name'] = key
|
|
||||||
# store into geodataframe
|
|
||||||
if i == 0:
|
|
||||||
gdf_all = gdf
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
gdf_all = gdf_all.append(gdf)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return gdf_all
|
|
||||||
@ -1,257 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
This module contains functions to analyze the 2D shorelines along shore-normal
|
|
||||||
transects
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# load modules
|
|
||||||
import os
|
|
||||||
import numpy as np
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
|
||||||
import pdb
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# other modules
|
|
||||||
import skimage.transform as transform
|
|
||||||
from pylab import ginput
|
|
||||||
import geopandas as gpd
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# CoastSat modules
|
|
||||||
from coastsat import SDS_tools
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def create_transect(origin, orientation, length):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Create a transect given an origin, orientation and length.
|
|
||||||
Points are spaced at 1m intervals.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
KV WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
origin: np.array
|
|
||||||
contains the X and Y coordinates of the origin of the transect
|
|
||||||
orientation: int
|
|
||||||
angle of the transect (anti-clockwise from North) in degrees
|
|
||||||
length: int
|
|
||||||
length of the transect in metres
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
transect: np.array
|
|
||||||
contains the X and Y coordinates of the transect
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# origin of the transect
|
|
||||||
x0 = origin[0]
|
|
||||||
y0 = origin[1]
|
|
||||||
# orientation of the transect
|
|
||||||
phi = (90 - orientation)*np.pi/180
|
|
||||||
# create a vector with points at 1 m intervals
|
|
||||||
x = np.linspace(0,length,length+1)
|
|
||||||
y = np.zeros(len(x))
|
|
||||||
coords = np.zeros((len(x),2))
|
|
||||||
coords[:,0] = x
|
|
||||||
coords[:,1] = y
|
|
||||||
# translate and rotate the vector using the origin and orientation
|
|
||||||
tf = transform.EuclideanTransform(rotation=phi, translation=(x0,y0))
|
|
||||||
transect = tf(coords)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return transect
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def draw_transects(output, settings):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Draw shore-normal transects interactively on top of the mapped shorelines
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
output: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding metadata
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'inputs': dict
|
|
||||||
input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
transects: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the X and Y coordinates of all the transects drawn.
|
|
||||||
Also saves the coordinates as a .geojson as well as a .jpg figure
|
|
||||||
showing the location of the transects.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(settings['inputs']['filepath'], sitename)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# plot the mapped shorelines
|
|
||||||
fig1 = plt.figure()
|
|
||||||
ax1 = fig1.add_subplot(111)
|
|
||||||
ax1.axis('equal')
|
|
||||||
ax1.set_xlabel('Eastings [m]')
|
|
||||||
ax1.set_ylabel('Northings [m]')
|
|
||||||
ax1.grid(linestyle=':', color='0.5')
|
|
||||||
for i in range(len(output['shorelines'])):
|
|
||||||
sl = output['shorelines'][i]
|
|
||||||
date = output['dates'][i]
|
|
||||||
ax1.plot(sl[:, 0], sl[:, 1], '.', markersize=3, label=date.strftime('%d-%m-%Y'))
|
|
||||||
# ax1.legend()
|
|
||||||
fig1.set_tight_layout(True)
|
|
||||||
mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
|
|
||||||
mng.window.showMaximized()
|
|
||||||
ax1.set_title('Click two points to define each transect (first point is the origin of the transect).\n'+
|
|
||||||
'When all transects have been defined, click on <ENTER>', fontsize=16)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# initialise transects dict
|
|
||||||
transects = dict([])
|
|
||||||
counter = 0
|
|
||||||
# loop until user breaks it by click <enter>
|
|
||||||
while 1:
|
|
||||||
# let user click two points
|
|
||||||
pts = ginput(n=2, timeout=1e9)
|
|
||||||
if len(pts) > 0:
|
|
||||||
origin = pts[0]
|
|
||||||
# if user presses <enter>, no points are selected
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# save figure as .jpg
|
|
||||||
fig1.gca().set_title('Transect locations', fontsize=16)
|
|
||||||
fig1.savefig(os.path.join(filepath, 'jpg_files', sitename + '_transect_locations.jpg'), dpi=200)
|
|
||||||
plt.title('Transect coordinates saved as ' + sitename + '_transects.geojson')
|
|
||||||
plt.draw()
|
|
||||||
# wait 3 seconds for user to visualise the transects that are saved
|
|
||||||
ginput(n=1, timeout=3, show_clicks=True)
|
|
||||||
plt.close(fig1)
|
|
||||||
# break the loop
|
|
||||||
break
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# add selectect points to the transect dict
|
|
||||||
counter = counter + 1
|
|
||||||
transect = np.array([pts[0], pts[1]])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# alternative of making the transect the origin, orientation and length
|
|
||||||
# temp = np.array(pts[1]) - np.array(origin)
|
|
||||||
# phi = np.arctan2(temp[1], temp[0])
|
|
||||||
# orientation = -(phi*180/np.pi - 90)
|
|
||||||
# length = np.linalg.norm(temp)
|
|
||||||
# transect = create_transect(origin, orientation, length)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
transects[str(counter)] = transect
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# plot the transects on the figure
|
|
||||||
ax1.plot(transect[:,0], transect[:,1], 'b-', lw=2.5)
|
|
||||||
ax1.plot(transect[0,0], transect[0,1], 'rx', markersize=10)
|
|
||||||
ax1.text(transect[-1,0], transect[-1,1], str(counter), size=16,
|
|
||||||
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
|
|
||||||
plt.draw()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# save transects.geojson
|
|
||||||
gdf = SDS_tools.transects_to_gdf(transects)
|
|
||||||
# set projection
|
|
||||||
gdf.crs = {'init':'epsg:'+str(settings['output_epsg'])}
|
|
||||||
# save as geojson
|
|
||||||
gdf.to_file(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_transects.geojson'), driver='GeoJSON', encoding='utf-8')
|
|
||||||
# print the location of the files
|
|
||||||
print('Transect locations saved in ' + filepath)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return transects
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def compute_intersection(output, transects, settings):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Computes the intersection between the 2D shorelines and the shore-normal.
|
|
||||||
transects. It returns time-series of cross-shore distance along each transect.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Arguments:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
output: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding metadata
|
|
||||||
transects: dict
|
|
||||||
contains the X and Y coordinates of each transect
|
|
||||||
settings: dict with the following keys
|
|
||||||
'along_dist': int
|
|
||||||
alongshore distance considered caluclate the intersection
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns:
|
|
||||||
-----------
|
|
||||||
cross_dist: dict
|
|
||||||
time-series of cross-shore distance along each of the transects.
|
|
||||||
Not tidally corrected.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
shorelines = output['shorelines']
|
|
||||||
along_dist = settings['along_dist']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# initialise variables
|
|
||||||
chainage_mtx = np.zeros((len(shorelines),len(transects),6))
|
|
||||||
idx_points = []
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for i in range(len(shorelines)):
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
sl = shorelines[i]
|
|
||||||
idx_points_all = []
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for j,key in enumerate(list(transects.keys())):
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# compute rotation matrix
|
|
||||||
X0 = transects[key][0,0]
|
|
||||||
Y0 = transects[key][0,1]
|
|
||||||
temp = np.array(transects[key][-1,:]) - np.array(transects[key][0,:])
|
|
||||||
phi = np.arctan2(temp[1], temp[0])
|
|
||||||
Mrot = np.array([[np.cos(phi), np.sin(phi)],[-np.sin(phi), np.cos(phi)]])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# calculate point to line distance between shoreline points and the transect
|
|
||||||
p1 = np.array([X0,Y0])
|
|
||||||
p2 = transects[key][-1,:]
|
|
||||||
d_line = np.abs(np.cross(p2-p1,sl-p1)/np.linalg.norm(p2-p1))
|
|
||||||
# calculate the distance between shoreline points and the origin of the transect
|
|
||||||
d_origin = np.array([np.linalg.norm(sl[k,:] - p1) for k in range(len(sl))])
|
|
||||||
# find the shoreline points that are close to the transects and to the origin
|
|
||||||
# the distance to the origin is hard-coded here to 1 km
|
|
||||||
idx_dist = np.logical_and(d_line <= along_dist, d_origin <= 1000)
|
|
||||||
# find the shoreline points that are in the direction of the transect (within 90 degrees)
|
|
||||||
temp_sl = sl - np.array(transects[key][0,:])
|
|
||||||
phi_sl = np.array([np.arctan2(temp_sl[k,1], temp_sl[k,0]) for k in range(len(temp_sl))])
|
|
||||||
diff_angle = (phi - phi_sl)
|
|
||||||
idx_angle = np.abs(diff_angle) < np.pi/2
|
|
||||||
# combine the transects that are close in distance and close in orientation
|
|
||||||
idx_close = np.where(np.logical_and(idx_dist,idx_angle))[0]
|
|
||||||
idx_points_all.append(idx_close)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# in case there are no shoreline points close to the transect
|
|
||||||
if len(idx_close) == 0:
|
|
||||||
chainage_mtx[i,j,:] = np.tile(np.nan,(1,6))
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
# change of base to shore-normal coordinate system
|
|
||||||
xy_close = np.array([sl[idx_close,0],sl[idx_close,1]]) - np.tile(np.array([[X0],
|
|
||||||
[Y0]]), (1,len(sl[idx_close])))
|
|
||||||
xy_rot = np.matmul(Mrot, xy_close)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# compute mean, median, max, min and std of chainage position
|
|
||||||
n_points = len(xy_rot[0,:])
|
|
||||||
mean_cross = np.nanmean(xy_rot[0,:])
|
|
||||||
median_cross = np.nanmedian(xy_rot[0,:])
|
|
||||||
max_cross = np.nanmax(xy_rot[0,:])
|
|
||||||
min_cross = np.nanmin(xy_rot[0,:])
|
|
||||||
std_cross = np.nanstd(xy_rot[0,:])
|
|
||||||
# store all statistics
|
|
||||||
chainage_mtx[i,j,:] = np.array([mean_cross, median_cross, max_cross,
|
|
||||||
min_cross, n_points, std_cross])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# store the indices of the shoreline points that were used
|
|
||||||
idx_points.append(idx_points_all)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# format into dictionnary
|
|
||||||
chainage = dict([])
|
|
||||||
chainage['mean'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,0]
|
|
||||||
chainage['median'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,1]
|
|
||||||
chainage['max'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,2]
|
|
||||||
chainage['min'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,3]
|
|
||||||
chainage['npoints'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,4]
|
|
||||||
chainage['std'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,5]
|
|
||||||
chainage['idx_points'] = idx_points
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# only return the median
|
|
||||||
cross_dist = dict([])
|
|
||||||
for j,key in enumerate(list(transects.keys())):
|
|
||||||
cross_dist[key] = chainage['median'][:,j]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return cross_dist
|
|
||||||
@ -1,540 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
|
||||||
###############################################################################
|
|
||||||
# $Id$
|
|
||||||
#
|
|
||||||
# Project: InSAR Peppers
|
|
||||||
# Purpose: Module to extract data from many rasters into one output.
|
|
||||||
# Author: Frank Warmerdam, warmerdam@pobox.com
|
|
||||||
#
|
|
||||||
###############################################################################
|
|
||||||
# Copyright (c) 2000, Atlantis Scientific Inc. (www.atlsci.com)
|
|
||||||
# Copyright (c) 2009-2011, Even Rouault <even dot rouault at mines-paris dot org>
|
|
||||||
#
|
|
||||||
# This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
|
||||||
# modify it under the terms of the GNU Library General Public
|
|
||||||
# License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
|
||||||
# version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
|
||||||
#
|
|
||||||
# This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
|
||||||
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
|
||||||
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
|
||||||
# Library General Public License for more details.
|
|
||||||
#
|
|
||||||
# You should have received a copy of the GNU Library General Public
|
|
||||||
# License along with this library; if not, write to the
|
|
||||||
# Free Software Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place - Suite 330,
|
|
||||||
# Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA.
|
|
||||||
###############################################################################
|
|
||||||
# changes 29Apr2011
|
|
||||||
# If the input image is a multi-band one, use all the channels in
|
|
||||||
# building the stack.
|
|
||||||
# anssi.pekkarinen@fao.org
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
import math
|
|
||||||
import sys
|
|
||||||
import time
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from osgeo import gdal
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
progress = gdal.TermProgress_nocb
|
|
||||||
except:
|
|
||||||
progress = gdal.TermProgress
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
__version__ = '$id$'[5:-1]
|
|
||||||
verbose = 0
|
|
||||||
quiet = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# =============================================================================
|
|
||||||
def raster_copy( s_fh, s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize, s_band_n,
|
|
||||||
t_fh, t_xoff, t_yoff, t_xsize, t_ysize, t_band_n,
|
|
||||||
nodata=None ):
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if verbose != 0:
|
|
||||||
print('Copy %d,%d,%d,%d to %d,%d,%d,%d.'
|
|
||||||
% (s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize,
|
|
||||||
t_xoff, t_yoff, t_xsize, t_ysize ))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if nodata is not None:
|
|
||||||
return raster_copy_with_nodata(
|
|
||||||
s_fh, s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize, s_band_n,
|
|
||||||
t_fh, t_xoff, t_yoff, t_xsize, t_ysize, t_band_n,
|
|
||||||
nodata )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
s_band = s_fh.GetRasterBand( s_band_n )
|
|
||||||
m_band = None
|
|
||||||
# Works only in binary mode and doesn't take into account
|
|
||||||
# intermediate transparency values for compositing.
|
|
||||||
if s_band.GetMaskFlags() != gdal.GMF_ALL_VALID:
|
|
||||||
m_band = s_band.GetMaskBand()
|
|
||||||
elif s_band.GetColorInterpretation() == gdal.GCI_AlphaBand:
|
|
||||||
m_band = s_band
|
|
||||||
if m_band is not None:
|
|
||||||
return raster_copy_with_mask(
|
|
||||||
s_fh, s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize, s_band_n,
|
|
||||||
t_fh, t_xoff, t_yoff, t_xsize, t_ysize, t_band_n,
|
|
||||||
m_band )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
s_band = s_fh.GetRasterBand( s_band_n )
|
|
||||||
t_band = t_fh.GetRasterBand( t_band_n )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
data = s_band.ReadRaster( s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize,
|
|
||||||
t_xsize, t_ysize, t_band.DataType )
|
|
||||||
t_band.WriteRaster( t_xoff, t_yoff, t_xsize, t_ysize,
|
|
||||||
data, t_xsize, t_ysize, t_band.DataType )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# =============================================================================
|
|
||||||
def raster_copy_with_nodata( s_fh, s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize, s_band_n,
|
|
||||||
t_fh, t_xoff, t_yoff, t_xsize, t_ysize, t_band_n,
|
|
||||||
nodata ):
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
import numpy as Numeric
|
|
||||||
except ImportError:
|
|
||||||
import Numeric
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
s_band = s_fh.GetRasterBand( s_band_n )
|
|
||||||
t_band = t_fh.GetRasterBand( t_band_n )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
data_src = s_band.ReadAsArray( s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize,
|
|
||||||
t_xsize, t_ysize )
|
|
||||||
data_dst = t_band.ReadAsArray( t_xoff, t_yoff, t_xsize, t_ysize )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
nodata_test = Numeric.equal(data_src,nodata)
|
|
||||||
to_write = Numeric.choose( nodata_test, (data_src, data_dst) )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
t_band.WriteArray( to_write, t_xoff, t_yoff )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# =============================================================================
|
|
||||||
def raster_copy_with_mask( s_fh, s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize, s_band_n,
|
|
||||||
t_fh, t_xoff, t_yoff, t_xsize, t_ysize, t_band_n,
|
|
||||||
m_band ):
|
|
||||||
try:
|
|
||||||
import numpy as Numeric
|
|
||||||
except ImportError:
|
|
||||||
import Numeric
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
s_band = s_fh.GetRasterBand( s_band_n )
|
|
||||||
t_band = t_fh.GetRasterBand( t_band_n )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
data_src = s_band.ReadAsArray( s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize,
|
|
||||||
t_xsize, t_ysize )
|
|
||||||
data_mask = m_band.ReadAsArray( s_xoff, s_yoff, s_xsize, s_ysize,
|
|
||||||
t_xsize, t_ysize )
|
|
||||||
data_dst = t_band.ReadAsArray( t_xoff, t_yoff, t_xsize, t_ysize )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
mask_test = Numeric.equal(data_mask, 0)
|
|
||||||
to_write = Numeric.choose( mask_test, (data_src, data_dst) )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
t_band.WriteArray( to_write, t_xoff, t_yoff )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# =============================================================================
|
|
||||||
def names_to_fileinfos( names ):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Translate a list of GDAL filenames, into file_info objects.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
names -- list of valid GDAL dataset names.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns a list of file_info objects. There may be less file_info objects
|
|
||||||
than names if some of the names could not be opened as GDAL files.
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
file_infos = []
|
|
||||||
for name in names:
|
|
||||||
fi = file_info()
|
|
||||||
if fi.init_from_name( name ) == 1:
|
|
||||||
file_infos.append( fi )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return file_infos
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# *****************************************************************************
|
|
||||||
class file_info:
|
|
||||||
"""A class holding information about a GDAL file."""
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def init_from_name(self, filename):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Initialize file_info from filename
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
filename -- Name of file to read.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns 1 on success or 0 if the file can't be opened.
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
fh = gdal.Open( filename )
|
|
||||||
if fh is None:
|
|
||||||
return 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
self.filename = filename
|
|
||||||
self.bands = fh.RasterCount
|
|
||||||
self.xsize = fh.RasterXSize
|
|
||||||
self.ysize = fh.RasterYSize
|
|
||||||
self.band_type = fh.GetRasterBand(1).DataType
|
|
||||||
self.projection = fh.GetProjection()
|
|
||||||
self.geotransform = fh.GetGeoTransform()
|
|
||||||
self.ulx = self.geotransform[0]
|
|
||||||
self.uly = self.geotransform[3]
|
|
||||||
self.lrx = self.ulx + self.geotransform[1] * self.xsize
|
|
||||||
self.lry = self.uly + self.geotransform[5] * self.ysize
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
ct = fh.GetRasterBand(1).GetRasterColorTable()
|
|
||||||
if ct is not None:
|
|
||||||
self.ct = ct.Clone()
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
self.ct = None
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def report( self ):
|
|
||||||
print('Filename: '+ self.filename)
|
|
||||||
print('File Size: %dx%dx%d'
|
|
||||||
% (self.xsize, self.ysize, self.bands))
|
|
||||||
print('Pixel Size: %f x %f'
|
|
||||||
% (self.geotransform[1],self.geotransform[5]))
|
|
||||||
print('UL:(%f,%f) LR:(%f,%f)'
|
|
||||||
% (self.ulx,self.uly,self.lrx,self.lry))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def copy_into( self, t_fh, s_band = 1, t_band = 1, nodata_arg=None ):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Copy this files image into target file.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This method will compute the overlap area of the file_info objects
|
|
||||||
file, and the target gdal.Dataset object, and copy the image data
|
|
||||||
for the common window area. It is assumed that the files are in
|
|
||||||
a compatible projection ... no checking or warping is done. However,
|
|
||||||
if the destination file is a different resolution, or different
|
|
||||||
image pixel type, the appropriate resampling and conversions will
|
|
||||||
be done (using normal GDAL promotion/demotion rules).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
t_fh -- gdal.Dataset object for the file into which some or all
|
|
||||||
of this file may be copied.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Returns 1 on success (or if nothing needs to be copied), and zero one
|
|
||||||
failure.
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
t_geotransform = t_fh.GetGeoTransform()
|
|
||||||
t_ulx = t_geotransform[0]
|
|
||||||
t_uly = t_geotransform[3]
|
|
||||||
t_lrx = t_geotransform[0] + t_fh.RasterXSize * t_geotransform[1]
|
|
||||||
t_lry = t_geotransform[3] + t_fh.RasterYSize * t_geotransform[5]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# figure out intersection region
|
|
||||||
tgw_ulx = max(t_ulx,self.ulx)
|
|
||||||
tgw_lrx = min(t_lrx,self.lrx)
|
|
||||||
if t_geotransform[5] < 0:
|
|
||||||
tgw_uly = min(t_uly,self.uly)
|
|
||||||
tgw_lry = max(t_lry,self.lry)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
tgw_uly = max(t_uly,self.uly)
|
|
||||||
tgw_lry = min(t_lry,self.lry)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# do they even intersect?
|
|
||||||
if tgw_ulx >= tgw_lrx:
|
|
||||||
return 1
|
|
||||||
if t_geotransform[5] < 0 and tgw_uly <= tgw_lry:
|
|
||||||
return 1
|
|
||||||
if t_geotransform[5] > 0 and tgw_uly >= tgw_lry:
|
|
||||||
return 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# compute target window in pixel coordinates.
|
|
||||||
tw_xoff = int((tgw_ulx - t_geotransform[0]) / t_geotransform[1] + 0.1)
|
|
||||||
tw_yoff = int((tgw_uly - t_geotransform[3]) / t_geotransform[5] + 0.1)
|
|
||||||
tw_xsize = int((tgw_lrx - t_geotransform[0])/t_geotransform[1] + 0.5) \
|
|
||||||
- tw_xoff
|
|
||||||
tw_ysize = int((tgw_lry - t_geotransform[3])/t_geotransform[5] + 0.5) \
|
|
||||||
- tw_yoff
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if tw_xsize < 1 or tw_ysize < 1:
|
|
||||||
return 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Compute source window in pixel coordinates.
|
|
||||||
sw_xoff = int((tgw_ulx - self.geotransform[0]) / self.geotransform[1])
|
|
||||||
sw_yoff = int((tgw_uly - self.geotransform[3]) / self.geotransform[5])
|
|
||||||
sw_xsize = int((tgw_lrx - self.geotransform[0]) \
|
|
||||||
/ self.geotransform[1] + 0.5) - sw_xoff
|
|
||||||
sw_ysize = int((tgw_lry - self.geotransform[3]) \
|
|
||||||
/ self.geotransform[5] + 0.5) - sw_yoff
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if sw_xsize < 1 or sw_ysize < 1:
|
|
||||||
return 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Open the source file, and copy the selected region.
|
|
||||||
s_fh = gdal.Open( self.filename )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return raster_copy( s_fh, sw_xoff, sw_yoff, sw_xsize, sw_ysize, s_band,
|
|
||||||
t_fh, tw_xoff, tw_yoff, tw_xsize, tw_ysize, t_band,
|
|
||||||
nodata_arg )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# =============================================================================
|
|
||||||
def Usage():
|
|
||||||
print('Usage: gdal_merge.py [-o out_filename] [-of out_format] [-co NAME=VALUE]*')
|
|
||||||
print(' [-ps pixelsize_x pixelsize_y] [-tap] [-separate] [-q] [-v] [-pct]')
|
|
||||||
print(' [-ul_lr ulx uly lrx lry] [-init "value [value...]"]')
|
|
||||||
print(' [-n nodata_value] [-a_nodata output_nodata_value]')
|
|
||||||
print(' [-ot datatype] [-createonly] input_files')
|
|
||||||
print(' [--help-general]')
|
|
||||||
print('')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# =============================================================================
|
|
||||||
#
|
|
||||||
# Program mainline.
|
|
||||||
#
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def main( argv=None ):
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
global verbose, quiet
|
|
||||||
verbose = 0
|
|
||||||
quiet = 0
|
|
||||||
names = []
|
|
||||||
format = 'GTiff'
|
|
||||||
out_file = 'out.tif'
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
ulx = None
|
|
||||||
psize_x = None
|
|
||||||
separate = 0
|
|
||||||
copy_pct = 0
|
|
||||||
nodata = None
|
|
||||||
a_nodata = None
|
|
||||||
create_options = []
|
|
||||||
pre_init = []
|
|
||||||
band_type = None
|
|
||||||
createonly = 0
|
|
||||||
bTargetAlignedPixels = False
|
|
||||||
start_time = time.time()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
gdal.AllRegister()
|
|
||||||
if argv is None:
|
|
||||||
argv = sys.argv
|
|
||||||
argv = gdal.GeneralCmdLineProcessor( argv )
|
|
||||||
if argv is None:
|
|
||||||
sys.exit( 0 )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Parse command line arguments.
|
|
||||||
i = 1
|
|
||||||
while i < len(argv):
|
|
||||||
arg = argv[i]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if arg == '-o':
|
|
||||||
i = i + 1
|
|
||||||
out_file = argv[i]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-v':
|
|
||||||
verbose = 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-q' or arg == '-quiet':
|
|
||||||
quiet = 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-createonly':
|
|
||||||
createonly = 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-separate':
|
|
||||||
separate = 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-seperate':
|
|
||||||
separate = 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-pct':
|
|
||||||
copy_pct = 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-ot':
|
|
||||||
i = i + 1
|
|
||||||
band_type = gdal.GetDataTypeByName( argv[i] )
|
|
||||||
if band_type == gdal.GDT_Unknown:
|
|
||||||
print('Unknown GDAL data type: %s' % argv[i])
|
|
||||||
sys.exit( 1 )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-init':
|
|
||||||
i = i + 1
|
|
||||||
str_pre_init = argv[i].split()
|
|
||||||
for x in str_pre_init:
|
|
||||||
pre_init.append(float(x))
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-n':
|
|
||||||
i = i + 1
|
|
||||||
nodata = float(argv[i])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-a_nodata':
|
|
||||||
i = i + 1
|
|
||||||
a_nodata = float(argv[i])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-f':
|
|
||||||
# for backward compatibility.
|
|
||||||
i = i + 1
|
|
||||||
format = argv[i]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-of':
|
|
||||||
i = i + 1
|
|
||||||
format = argv[i]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-co':
|
|
||||||
i = i + 1
|
|
||||||
create_options.append( argv[i] )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-ps':
|
|
||||||
psize_x = float(argv[i+1])
|
|
||||||
psize_y = -1 * abs(float(argv[i+2]))
|
|
||||||
i = i + 2
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-tap':
|
|
||||||
bTargetAlignedPixels = True
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg == '-ul_lr':
|
|
||||||
ulx = float(argv[i+1])
|
|
||||||
uly = float(argv[i+2])
|
|
||||||
lrx = float(argv[i+3])
|
|
||||||
lry = float(argv[i+4])
|
|
||||||
i = i + 4
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
elif arg[:1] == '-':
|
|
||||||
print('Unrecognized command option: %s' % arg)
|
|
||||||
Usage()
|
|
||||||
sys.exit( 1 )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
names.append(arg)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
i = i + 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if len(names) == 0:
|
|
||||||
print('No input files selected.')
|
|
||||||
Usage()
|
|
||||||
sys.exit( 1 )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Driver = gdal.GetDriverByName(format)
|
|
||||||
if Driver is None:
|
|
||||||
print('Format driver %s not found, pick a supported driver.' % format)
|
|
||||||
sys.exit( 1 )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
DriverMD = Driver.GetMetadata()
|
|
||||||
if 'DCAP_CREATE' not in DriverMD:
|
|
||||||
print('Format driver %s does not support creation and piecewise writing.\nPlease select a format that does, such as GTiff (the default) or HFA (Erdas Imagine).' % format)
|
|
||||||
sys.exit( 1 )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Collect information on all the source files.
|
|
||||||
file_infos = names_to_fileinfos( names )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if ulx is None:
|
|
||||||
ulx = file_infos[0].ulx
|
|
||||||
uly = file_infos[0].uly
|
|
||||||
lrx = file_infos[0].lrx
|
|
||||||
lry = file_infos[0].lry
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for fi in file_infos:
|
|
||||||
ulx = min(ulx, fi.ulx)
|
|
||||||
uly = max(uly, fi.uly)
|
|
||||||
lrx = max(lrx, fi.lrx)
|
|
||||||
lry = min(lry, fi.lry)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if psize_x is None:
|
|
||||||
psize_x = file_infos[0].geotransform[1]
|
|
||||||
psize_y = file_infos[0].geotransform[5]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if band_type is None:
|
|
||||||
band_type = file_infos[0].band_type
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Try opening as an existing file.
|
|
||||||
gdal.PushErrorHandler( 'CPLQuietErrorHandler' )
|
|
||||||
t_fh = gdal.Open( out_file, gdal.GA_Update )
|
|
||||||
gdal.PopErrorHandler()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Create output file if it does not already exist.
|
|
||||||
if t_fh is None:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if bTargetAlignedPixels:
|
|
||||||
ulx = math.floor(ulx / psize_x) * psize_x
|
|
||||||
lrx = math.ceil(lrx / psize_x) * psize_x
|
|
||||||
lry = math.floor(lry / -psize_y) * -psize_y
|
|
||||||
uly = math.ceil(uly / -psize_y) * -psize_y
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
geotransform = [ulx, psize_x, 0, uly, 0, psize_y]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
xsize = int((lrx - ulx) / geotransform[1] + 0.5)
|
|
||||||
ysize = int((lry - uly) / geotransform[5] + 0.5)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if separate != 0:
|
|
||||||
bands=0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for fi in file_infos:
|
|
||||||
bands=bands + fi.bands
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
bands = file_infos[0].bands
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
t_fh = Driver.Create( out_file, xsize, ysize, bands,
|
|
||||||
band_type, create_options )
|
|
||||||
if t_fh is None:
|
|
||||||
print('Creation failed, terminating gdal_merge.')
|
|
||||||
sys.exit( 1 )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
t_fh.SetGeoTransform( geotransform )
|
|
||||||
t_fh.SetProjection( file_infos[0].projection )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if copy_pct:
|
|
||||||
t_fh.GetRasterBand(1).SetRasterColorTable(file_infos[0].ct)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
if separate != 0:
|
|
||||||
bands=0
|
|
||||||
for fi in file_infos:
|
|
||||||
bands=bands + fi.bands
|
|
||||||
if t_fh.RasterCount < bands :
|
|
||||||
print('Existing output file has less bands than the input files. You should delete it before. Terminating gdal_merge.')
|
|
||||||
sys.exit( 1 )
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
bands = min(file_infos[0].bands,t_fh.RasterCount)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Do we need to set nodata value ?
|
|
||||||
if a_nodata is not None:
|
|
||||||
for i in range(t_fh.RasterCount):
|
|
||||||
t_fh.GetRasterBand(i+1).SetNoDataValue(a_nodata)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Do we need to pre-initialize the whole mosaic file to some value?
|
|
||||||
if pre_init is not None:
|
|
||||||
if t_fh.RasterCount <= len(pre_init):
|
|
||||||
for i in range(t_fh.RasterCount):
|
|
||||||
t_fh.GetRasterBand(i+1).Fill( pre_init[i] )
|
|
||||||
elif len(pre_init) == 1:
|
|
||||||
for i in range(t_fh.RasterCount):
|
|
||||||
t_fh.GetRasterBand(i+1).Fill( pre_init[0] )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Copy data from source files into output file.
|
|
||||||
t_band = 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if quiet == 0 and verbose == 0:
|
|
||||||
progress( 0.0 )
|
|
||||||
fi_processed = 0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for fi in file_infos:
|
|
||||||
if createonly != 0:
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if verbose != 0:
|
|
||||||
print("")
|
|
||||||
print("Processing file %5d of %5d, %6.3f%% completed in %d minutes."
|
|
||||||
% (fi_processed+1,len(file_infos),
|
|
||||||
fi_processed * 100.0 / len(file_infos),
|
|
||||||
int(round((time.time() - start_time)/60.0)) ))
|
|
||||||
fi.report()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if separate == 0 :
|
|
||||||
for band in range(1, bands+1):
|
|
||||||
fi.copy_into( t_fh, band, band, nodata )
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
for band in range(1, fi.bands+1):
|
|
||||||
fi.copy_into( t_fh, band, t_band, nodata )
|
|
||||||
t_band = t_band+1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
fi_processed = fi_processed+1
|
|
||||||
if quiet == 0 and verbose == 0:
|
|
||||||
progress( fi_processed / float(len(file_infos)) )
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Force file to be closed.
|
|
||||||
t_fh = None
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
|
||||||
sys.exit(main())
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,390 @@
|
|||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Download L5, L7, L8, S2 images of a given area
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Initial settings
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
import os
|
||||||
|
import numpy as np
|
||||||
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||||
|
import pdb
|
||||||
|
import ee
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# other modules
|
||||||
|
from osgeo import gdal, ogr, osr
|
||||||
|
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
|
||||||
|
import zipfile
|
||||||
|
from datetime import datetime
|
||||||
|
import pytz
|
||||||
|
import pickle
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# import own modules
|
||||||
|
import functions.utils as utils
|
||||||
|
import functions.sds as sds
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
|
||||||
|
ee.Initialize()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Location
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## location (Narrabeen-Collaroy beach)
|
||||||
|
#polygon = [[[151.301454, -33.700754],
|
||||||
|
# [151.311453, -33.702075],
|
||||||
|
# [151.307237, -33.739761],
|
||||||
|
# [151.294220, -33.736329],
|
||||||
|
# [151.301454, -33.700754]]];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# location (Tairua beach)
|
||||||
|
sitename = 'TAIRUA'
|
||||||
|
polygon = [[[175.835574, -36.982022],
|
||||||
|
[175.888220, -36.980680],
|
||||||
|
[175.893527, -37.029610],
|
||||||
|
[175.833444, -37.031767],
|
||||||
|
[175.835574, -36.982022]]];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# initialise metadata dictionnary (stores timestamps and georefencing accuracy of each image)
|
||||||
|
metadata = dict([])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# create directories
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
os.makedirs(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data',sitename))
|
||||||
|
except:
|
||||||
|
print('directory already exists')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#%%
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# L5
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# define filenames for images
|
||||||
|
suffix = '.tif'
|
||||||
|
filepath = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename, 'L5', '30m')
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
os.makedirs(filepath)
|
||||||
|
except:
|
||||||
|
print('directory already exists')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Select L5 collection
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
satname = 'L5'
|
||||||
|
input_col = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LT05/C01/T1_TOA')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# filter by location
|
||||||
|
flt_col = input_col.filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Polygon(polygon))
|
||||||
|
n_img = flt_col.size().getInfo()
|
||||||
|
print('Number of images covering ' + sitename, n_img)
|
||||||
|
im_all = flt_col.getInfo().get('features')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Main loop trough images
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
timestamps = []
|
||||||
|
acc_georef = []
|
||||||
|
all_names = []
|
||||||
|
for i in range(n_img):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# find each image in ee database
|
||||||
|
im = ee.Image(im_all[i].get('id'))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
im_dic = im.getInfo()
|
||||||
|
im_bands = im_dic.get('bands')
|
||||||
|
t = im_dic['properties']['system:time_start']
|
||||||
|
im_timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(t/1000, tz=pytz.utc)
|
||||||
|
timestamps.append(im_timestamp)
|
||||||
|
im_date = im_timestamp.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S')
|
||||||
|
im_epsg = int(im_dic['bands'][0]['crs'][5:])
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
acc_georef.append(im_dic['properties']['GEOMETRIC_RMSE_MODEL'])
|
||||||
|
except:
|
||||||
|
acc_georef.append(12)
|
||||||
|
print('No geometric rmse model property')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# delete dimensions key from dictionnary, otherwise the entire image is extracted
|
||||||
|
for j in range(len(im_bands)): del im_bands[j]['dimensions']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# bands for L5
|
||||||
|
ms_bands = [im_bands[0], im_bands[1], im_bands[2], im_bands[3], im_bands[4], im_bands[7]]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# filenames
|
||||||
|
filename = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + suffix
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
print(i)
|
||||||
|
if any(filename in _ for _ in all_names):
|
||||||
|
filename = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_dup' + suffix
|
||||||
|
all_names.append(filename)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
local_data = sds.download_tif(im, polygon, ms_bands, filepath)
|
||||||
|
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, filename))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# sort timestamps and georef accuracy (dowloaded images are sorted by date in directory)
|
||||||
|
timestamps_sorted = sorted(timestamps)
|
||||||
|
idx_sorted = sorted(range(len(timestamps)), key=timestamps.__getitem__)
|
||||||
|
acc_georef_sorted = [acc_georef[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
metadata[satname] = {'dates':timestamps_sorted, 'acc_georef':acc_georef_sorted, 'epsg':im_epsg}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#%%
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# L7&L8
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# define filenames for images
|
||||||
|
suffix = '.tif'
|
||||||
|
filepath = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename, 'L7&L8')
|
||||||
|
filepath_pan = os.path.join(filepath, 'pan')
|
||||||
|
filepath_ms = os.path.join(filepath, 'ms')
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
os.makedirs(filepath_pan)
|
||||||
|
os.makedirs(filepath_ms)
|
||||||
|
except:
|
||||||
|
print('directory already exists')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Select L7 collection
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
satname = 'L7'
|
||||||
|
input_col = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LE07/C01/T1_RT_TOA')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# filter by location
|
||||||
|
flt_col = input_col.filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Polygon(polygon))
|
||||||
|
n_img = flt_col.size().getInfo()
|
||||||
|
print('Number of images covering ' + sitename, n_img)
|
||||||
|
im_all = flt_col.getInfo().get('features')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Main loop trough images
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
timestamps = []
|
||||||
|
acc_georef = []
|
||||||
|
all_names = []
|
||||||
|
for i in range(n_img):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# find each image in ee database
|
||||||
|
im = ee.Image(im_all[i].get('id'))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
im_dic = im.getInfo()
|
||||||
|
im_bands = im_dic.get('bands')
|
||||||
|
t = im_dic['properties']['system:time_start']
|
||||||
|
im_timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(t/1000, tz=pytz.utc)
|
||||||
|
timestamps.append(im_timestamp)
|
||||||
|
im_date = im_timestamp.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S')
|
||||||
|
im_epsg = int(im_dic['bands'][0]['crs'][5:])
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
acc_georef.append(im_dic['properties']['GEOMETRIC_RMSE_MODEL'])
|
||||||
|
except:
|
||||||
|
acc_georef.append(12)
|
||||||
|
print('No geometric rmse model property')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# delete dimensions key from dictionnary, otherwise the entire image is extracted
|
||||||
|
for j in range(len(im_bands)): del im_bands[j]['dimensions']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# bands for L7
|
||||||
|
pan_band = [im_bands[8]]
|
||||||
|
ms_bands = [im_bands[0], im_bands[1], im_bands[2], im_bands[3], im_bands[4], im_bands[9]]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# filenames
|
||||||
|
filename_pan = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_pan' + suffix
|
||||||
|
filename_ms = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_ms' + suffix
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
print(i)
|
||||||
|
if any(filename_pan in _ for _ in all_names):
|
||||||
|
filename_pan = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_pan' + '_dup' + suffix
|
||||||
|
filename_ms = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_ms' + '_dup' + suffix
|
||||||
|
all_names.append(filename_pan)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
local_data_pan = sds.download_tif(im, polygon, pan_band, filepath_pan)
|
||||||
|
os.rename(local_data_pan, os.path.join(filepath_pan, filename_pan))
|
||||||
|
local_data_ms = sds.download_tif(im, polygon, ms_bands, filepath_ms)
|
||||||
|
os.rename(local_data_ms, os.path.join(filepath_ms, filename_ms))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Select L8 collection
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
satname = 'L8'
|
||||||
|
input_col = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LC08/C01/T1_RT_TOA')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# filter by location
|
||||||
|
flt_col = input_col.filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Polygon(polygon))
|
||||||
|
n_img = flt_col.size().getInfo()
|
||||||
|
print('Number of images covering Narrabeen:', n_img)
|
||||||
|
im_all = flt_col.getInfo().get('features')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Main loop trough images
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for i in range(n_img):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# find each image in ee database
|
||||||
|
im = ee.Image(im_all[i].get('id'))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
im_dic = im.getInfo()
|
||||||
|
im_bands = im_dic.get('bands')
|
||||||
|
t = im_dic['properties']['system:time_start']
|
||||||
|
im_timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(t/1000, tz=pytz.utc)
|
||||||
|
timestamps.append(im_timestamp)
|
||||||
|
im_date = im_timestamp.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S')
|
||||||
|
im_epsg = int(im_dic['bands'][0]['crs'][5:])
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
acc_georef.append(im_dic['properties']['GEOMETRIC_RMSE_MODEL'])
|
||||||
|
except:
|
||||||
|
acc_georef.append(12)
|
||||||
|
print('No geometric rmse model property')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# delete dimensions key from dictionnary, otherwise the entire image is extracted
|
||||||
|
for j in range(len(im_bands)): del im_bands[j]['dimensions']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# bands for L8
|
||||||
|
pan_band = [im_bands[7]]
|
||||||
|
ms_bands = [im_bands[1], im_bands[2], im_bands[3], im_bands[4], im_bands[5], im_bands[11]]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# filenames
|
||||||
|
filename_pan = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_pan' + suffix
|
||||||
|
filename_ms = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_ms' + suffix
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
print(i)
|
||||||
|
if any(filename_pan in _ for _ in all_names):
|
||||||
|
filename_pan = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_pan' + '_dup' + suffix
|
||||||
|
filename_ms = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_ms' + '_dup' + suffix
|
||||||
|
all_names.append(filename_pan)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
local_data_pan = sds.download_tif(im, polygon, pan_band, filepath_pan)
|
||||||
|
os.rename(local_data_pan, os.path.join(filepath_pan, filename_pan))
|
||||||
|
local_data_ms = sds.download_tif(im, polygon, ms_bands, filepath_ms)
|
||||||
|
os.rename(local_data_ms, os.path.join(filepath_ms, filename_ms))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# sort timestamps and georef accuracy (dowloaded images are sorted by date in directory)
|
||||||
|
timestamps_sorted = sorted(timestamps)
|
||||||
|
idx_sorted = sorted(range(len(timestamps)), key=timestamps.__getitem__)
|
||||||
|
acc_georef_sorted = [acc_georef[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
metadata[satname] = {'dates':timestamps_sorted, 'acc_georef':acc_georef_sorted, 'epsg':im_epsg}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#%%
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# S2
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# define filenames for images
|
||||||
|
suffix = '.tif'
|
||||||
|
filepath = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename, 'S2')
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
os.makedirs(os.path.join(filepath, '10m'))
|
||||||
|
os.makedirs(os.path.join(filepath, '20m'))
|
||||||
|
os.makedirs(os.path.join(filepath, '60m'))
|
||||||
|
except:
|
||||||
|
print('directory already exists')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Select L2 collection
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
satname = 'S2'
|
||||||
|
input_col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# filter by location
|
||||||
|
flt_col = input_col.filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Polygon(polygon))
|
||||||
|
n_img = flt_col.size().getInfo()
|
||||||
|
print('Number of images covering ' + sitename, n_img)
|
||||||
|
im_all = flt_col.getInfo().get('features')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Main loop trough images
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
timestamps = []
|
||||||
|
acc_georef = []
|
||||||
|
all_names = []
|
||||||
|
for i in range(n_img):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# find each image in ee database
|
||||||
|
im = ee.Image(im_all[i].get('id'))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
im_dic = im.getInfo()
|
||||||
|
im_bands = im_dic.get('bands')
|
||||||
|
t = im_dic['properties']['system:time_start']
|
||||||
|
im_timestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(t/1000, tz=pytz.utc)
|
||||||
|
im_date = im_timestamp.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S')
|
||||||
|
timestamps.append(im_timestamp)
|
||||||
|
im_epsg = int(im_dic['bands'][0]['crs'][5:])
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
if im_dic['properties']['GEOMETRIC_QUALITY_FLAG'] == 'PASSED':
|
||||||
|
acc_georef.append(1)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
acc_georef.append(0)
|
||||||
|
except:
|
||||||
|
acc_georef.append(0)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# delete dimensions key from dictionnary, otherwise the entire image is extracted
|
||||||
|
for j in range(len(im_bands)): del im_bands[j]['dimensions']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# bands for S2
|
||||||
|
bands10 = [im_bands[1], im_bands[2], im_bands[3], im_bands[7]]
|
||||||
|
bands20 = [im_bands[11]]
|
||||||
|
bands60 = [im_bands[15]]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# filenames
|
||||||
|
filename10 = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_' + '10m' + suffix
|
||||||
|
filename20 = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_' + '20m' + suffix
|
||||||
|
filename60 = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_' + '60m' + suffix
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
print(i)
|
||||||
|
if any(filename10 in _ for _ in all_names):
|
||||||
|
filename10 = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_' + '10m' + '_dup' + suffix
|
||||||
|
filename20 = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_' + '20m' + '_dup' + suffix
|
||||||
|
filename60 = im_date + '_' + satname + '_' + sitename + '_' + '60m' + '_dup' + suffix
|
||||||
|
all_names.append(filename10)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
local_data = sds.download_tif(im, polygon, bands10, filepath)
|
||||||
|
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, '10m', filename10))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
local_data = sds.download_tif(im, polygon, bands20, filepath)
|
||||||
|
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, '20m', filename20))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
local_data = sds.download_tif(im, polygon, bands60, filepath)
|
||||||
|
os.rename(local_data, os.path.join(filepath, '60m', filename60))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# sort timestamps and georef accuracy (dowloaded images are sorted by date in directory)
|
||||||
|
timestamps_sorted = sorted(timestamps)
|
||||||
|
idx_sorted = sorted(range(len(timestamps)), key=timestamps.__getitem__)
|
||||||
|
acc_georef_sorted = [acc_georef[j] for j in idx_sorted]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
metadata[satname] = {'dates':timestamps_sorted, 'acc_georef':acc_georef_sorted, 'epsg':im_epsg}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#%% save metadata
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
filepath = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename)
|
||||||
|
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_metadata' + '.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
|
||||||
|
pickle.dump(metadata, f)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
channels:
|
|
||||||
- defaults
|
|
||||||
- conda-forge
|
|
||||||
dependencies:
|
|
||||||
- python=3.7
|
|
||||||
- numpy=1.16.3
|
|
||||||
- matplotlib=3.0.3
|
|
||||||
- earthengine-api=0.1.173
|
|
||||||
- gdal=2.3.3
|
|
||||||
- pandas=0.24.2
|
|
||||||
- geopandas=0.4.1
|
|
||||||
- pytz=2019.1
|
|
||||||
- scikit-image=0.15.0
|
|
||||||
- scikit-learn=0.20.3
|
|
||||||
- shapely=1.6.4
|
|
||||||
- scipy=1.2.1
|
|
||||||
- spyder=3.3.4
|
|
||||||
- notebook=5.7.8
|
|
||||||
- astropy
|
|
||||||
@ -1,152 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
#==========================================================#
|
|
||||||
# Shoreline extraction from satellite images
|
|
||||||
#==========================================================#
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Kilian Vos WRL 2018
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#%% 1. Initial settings
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# load modules
|
|
||||||
import os
|
|
||||||
import numpy as np
|
|
||||||
import pickle
|
|
||||||
import warnings
|
|
||||||
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
|
|
||||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
|
||||||
from coastsat import SDS_download, SDS_preprocess, SDS_shoreline, SDS_tools, SDS_transects
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# region of interest (longitude, latitude in WGS84)
|
|
||||||
polygon = [[[151.301454, -33.700754],
|
|
||||||
[151.311453, -33.702075],
|
|
||||||
[151.307237, -33.739761],
|
|
||||||
[151.294220, -33.736329],
|
|
||||||
[151.301454, -33.700754]]]
|
|
||||||
# can also be loaded from a .kml polygon
|
|
||||||
#kml_polygon = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'examples', 'NARRA_polygon.kml')
|
|
||||||
#polygon = SDS_tools.polygon_from_kml(kml_polygon)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# date range
|
|
||||||
dates = ['2017-12-01', '2018-01-01']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# satellite missions
|
|
||||||
sat_list = ['S2']
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# name of the site
|
|
||||||
sitename = 'NARRA'
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# filepath where data will be stored
|
|
||||||
filepath_data = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# put all the inputs into a dictionnary
|
|
||||||
inputs = {
|
|
||||||
'polygon': polygon,
|
|
||||||
'dates': dates,
|
|
||||||
'sat_list': sat_list,
|
|
||||||
'sitename': sitename,
|
|
||||||
'filepath': filepath_data
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#%% 2. Retrieve images
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# retrieve satellite images from GEE
|
|
||||||
metadata = SDS_download.retrieve_images(inputs)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if you have already downloaded the images, just load the metadata file
|
|
||||||
metadata = SDS_download.get_metadata(inputs)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#%% 3. Batch shoreline detection
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# settings for the shoreline extraction
|
|
||||||
settings = {
|
|
||||||
# general parameters:
|
|
||||||
'cloud_thresh': 0.5, # threshold on maximum cloud cover
|
|
||||||
'output_epsg': 28356, # epsg code of spatial reference system desired for the output
|
|
||||||
# quality control:
|
|
||||||
'check_detection': True, # if True, shows each shoreline detection to the user for validation
|
|
||||||
'save_figure': True, # if True, saves a figure showing the mapped shoreline for each image
|
|
||||||
# add the inputs defined previously
|
|
||||||
'inputs': inputs,
|
|
||||||
# [ONLY FOR ADVANCED USERS] shoreline detection parameters:
|
|
||||||
'min_beach_area': 4500, # minimum area (in metres^2) for an object to be labelled as a beach
|
|
||||||
'buffer_size': 150, # radius (in metres) of the buffer around sandy pixels considered in the shoreline detection
|
|
||||||
'min_length_sl': 200, # minimum length (in metres) of shoreline perimeter to be valid
|
|
||||||
'cloud_mask_issue': False, # switch this parameter to True if sand pixels are masked (in black) on many images
|
|
||||||
'sand_color': 'default', # 'default', 'dark' (for grey/black sand beaches) or 'bright' (for white sand beaches)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# [OPTIONAL] preprocess images (cloud masking, pansharpening/down-sampling)
|
|
||||||
SDS_preprocess.save_jpg(metadata, settings)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# [OPTIONAL] create a reference shoreline (helps to identify outliers and false detections)
|
|
||||||
settings['reference_shoreline'] = SDS_preprocess.get_reference_sl(metadata, settings)
|
|
||||||
# set the max distance (in meters) allowed from the reference shoreline for a detected shoreline to be valid
|
|
||||||
settings['max_dist_ref'] = 100
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# extract shorelines from all images (also saves output.pkl and shorelines.kml)
|
|
||||||
output = SDS_shoreline.extract_shorelines(metadata, settings)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# plot the mapped shorelines
|
|
||||||
fig = plt.figure()
|
|
||||||
plt.axis('equal')
|
|
||||||
plt.xlabel('Eastings')
|
|
||||||
plt.ylabel('Northings')
|
|
||||||
plt.grid(linestyle=':', color='0.5')
|
|
||||||
for i in range(len(output['shorelines'])):
|
|
||||||
sl = output['shorelines'][i]
|
|
||||||
date = output['dates'][i]
|
|
||||||
plt.plot(sl[:,0], sl[:,1], '.', label=date.strftime('%d-%m-%Y'))
|
|
||||||
plt.legend()
|
|
||||||
mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
|
|
||||||
mng.window.showMaximized()
|
|
||||||
fig.set_size_inches([15.76, 8.52])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#%% 4. Shoreline analysis
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# if you have already mapped the shorelines, load the output.pkl file
|
|
||||||
filepath = os.path.join(inputs['filepath'], sitename)
|
|
||||||
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_output' + '.pkl'), 'rb') as f:
|
|
||||||
output = pickle.load(f)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# now we have to define cross-shore transects over which to quantify the shoreline changes
|
|
||||||
# each transect is defined by two points, its origin and a second point that defines its orientation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# there are 3 options to create the transects:
|
|
||||||
# - option 1: draw the shore-normal transects along the beach
|
|
||||||
# - option 2: load the transect coordinates from a .kml file
|
|
||||||
# - option 3: create the transects manually by providing the coordinates
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# option 1: draw origin of transect first and then a second point to define the orientation
|
|
||||||
transects = SDS_transects.draw_transects(output, settings)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# option 2: load the transects from a .geojson file
|
|
||||||
#geojson_file = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'examples', 'NARRA_transects.geojson')
|
|
||||||
#transects = SDS_tools.transects_from_geojson(geojson_file)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# option 3: create the transects by manually providing the coordinates of two points
|
|
||||||
#transects = dict([])
|
|
||||||
#transects['Transect 1'] = np.array([[342836, 6269215], [343315, 6269071]])
|
|
||||||
#transects['Transect 2'] = np.array([[342482, 6268466], [342958, 6268310]])
|
|
||||||
#transects['Transect 3'] = np.array([[342185, 6267650], [342685, 6267641]])
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# intersect the transects with the 2D shorelines to obtain time-series of cross-shore distance
|
|
||||||
settings['along_dist'] = 25
|
|
||||||
cross_distance = SDS_transects.compute_intersection(output, transects, settings)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# plot the time-series
|
|
||||||
from matplotlib import gridspec
|
|
||||||
fig = plt.figure()
|
|
||||||
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(len(cross_distance),1)
|
|
||||||
gs.update(left=0.05, right=0.95, bottom=0.05, top=0.95, hspace=0.05)
|
|
||||||
for i,key in enumerate(cross_distance.keys()):
|
|
||||||
if np.all(np.isnan(cross_distance[key])):
|
|
||||||
continue
|
|
||||||
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[i,0])
|
|
||||||
ax.grid(linestyle=':', color='0.5')
|
|
||||||
ax.set_ylim([-50,50])
|
|
||||||
ax.plot(output['dates'], cross_distance[key]- np.nanmedian(cross_distance[key]), '-^', markersize=6)
|
|
||||||
ax.set_ylabel('distance [m]', fontsize=12)
|
|
||||||
ax.text(0.5,0.95,'Transect ' + key, bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'), ha='center',
|
|
||||||
va='top', transform=ax.transAxes, fontsize=14)
|
|
||||||
mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
|
|
||||||
mng.window.showMaximized()
|
|
||||||
fig.set_size_inches([15.76, 8.52])
|
|
||||||
@ -1,412 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cells": [
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# *CoastSat*: example at Narrabeen-Collaroy, Australia\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"This software is described in details in:\n",
|
|
||||||
"* Vos K., Splinter K.D., Harley M.D., Simmons J.A., Turner I.L. (2019). CoastSat: a Google Earth Engine-enabled Python toolkit to extract shorelines from publicly available satellite imagery. Environmental Modelling and Software. 122, 104528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2019.104528\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"It enables the users to extract time-series of shoreline change over the last 30+ years at their site of interest.\n",
|
|
||||||
"There are three main steps:\n",
|
|
||||||
"1. Retrieval of the satellite images of the region of interest from Google Earth Engine\n",
|
|
||||||
"2. Shoreline extraction at sub-pixel resolution\n",
|
|
||||||
"3. Intersection of the shorelines with cross-shore transects\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"## Initial settings\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"Refer to the **Installation** section of the README for instructions on how to install the Python packages necessary to run the software, including Google Earth Engine Python API. If that step has been completed correctly, the following packages should be imported without any problem."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"import os\n",
|
|
||||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
|
||||||
"import pickle\n",
|
|
||||||
"import warnings\n",
|
|
||||||
"warnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\n",
|
|
||||||
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
|
|
||||||
"from coastsat import SDS_download, SDS_preprocess, SDS_shoreline, SDS_tools, SDS_transects"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"## 1. Retrieval of the images from GEE\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"Define the region of interest (`polygon`), the date range (`dates`) and the satellite missions (`sat_list`) from which you wish to retrieve the satellite images. The images will be cropped on the Google Earth Engine server and only the region of interest will be downloaded as a .tif file. The files will stored in the directory defined in `filepath`.\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"Make sure the area of your ROI is smaller than 100 km2 (if larger split it into smaller ROIs)."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# region of interest (longitude, latitude)\n",
|
|
||||||
"polygon = [[[151.2957545, -33.7012561],\n",
|
|
||||||
" [151.297557, -33.7388075],\n",
|
|
||||||
" [151.312234, -33.7390216],\n",
|
|
||||||
" [151.311204, -33.701399],\n",
|
|
||||||
" [151.2957545, -33.7012561]]] \n",
|
|
||||||
"# date range\n",
|
|
||||||
"dates = ['2017-12-01', '2018-01-01']\n",
|
|
||||||
"# satellite missions\n",
|
|
||||||
"sat_list = ['S2']\n",
|
|
||||||
"# name of the site\n",
|
|
||||||
"sitename = 'NARRA'\n",
|
|
||||||
"# directory where the data will be stored\n",
|
|
||||||
"filepath = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data')\n",
|
|
||||||
"# put all the inputs into a dictionnary\n",
|
|
||||||
"inputs = {'polygon': polygon, 'dates': dates, 'sat_list': sat_list, 'sitename': sitename, 'filepath':filepath}"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"Retrieve satellite images from GEE"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"metadata = SDS_download.retrieve_images(inputs)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"**If you have already retrieved the images**, just load the metadata file by only running the section below"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"metadata = SDS_download.get_metadata(inputs) "
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"## 2. Shoreline extraction\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"This section maps the position of the shoreline on the satellite images. The user can define the cloud threhold (`cloud_thresh`) and select the spatial reference system in which to output the coordinates of the mapped shorelines (`output_epsg`). See http://spatialreference.org/ to find the EPSG number corresponding to your local coordinate system. Make sure that your are using cartesian coordinates and not spherical coordinates (lat,lon) like WGS84. \n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"To quality control each shoreline detection and manually validate the mapped shorelines, the user has the option to set the parameter `check_detection` to **True**. To save a figure for each mapped shoreline set `save_figure` to **True**. \n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"The other parameters are for advanced users only and are described in the README."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"settings = { \n",
|
|
||||||
" # general parameters:\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'cloud_thresh': 0.5, # threshold on maximum cloud cover\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'output_epsg': 28356, # epsg code of spatial reference system desired for the output \n",
|
|
||||||
" # quality control:\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'check_detection': True, # if True, shows each shoreline detection to the user for validation\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'save_figure': True, # if True, saves a figure showing the mapped shoreline for each image\n",
|
|
||||||
" # add the inputs defined previously\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'inputs': inputs,\n",
|
|
||||||
" # [ONLY FOR ADVANCED USERS] shoreline detection parameters:\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'min_beach_area': 4500, # minimum area (in metres^2) for an object to be labelled as a beach\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'buffer_size': 150, # radius (in metres) of the buffer around sandy pixels considered in the shoreline detection\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'min_length_sl': 200, # minimum length (in metres) of shoreline perimeter to be valid\n",
|
|
||||||
" 'cloud_mask_issue': False, # switch this parameter to True if sand pixels are masked (in black) on many images \n",
|
|
||||||
" 'sand_color': 'default', # 'default', 'dark' (for grey/black sand beaches) or 'bright' (for white sand beaches)\n",
|
|
||||||
"}"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"### [OPTIONAL] Save .jpg of the satellite images \n",
|
|
||||||
"Saves .jpg files of the preprocessed satellite images (cloud masking + pansharpening/down-sampling) under *./data/sitename/jpeg_files\\preprocessed*"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"SDS_preprocess.save_jpg(metadata, settings)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"### [OPTIONAL] Digitize a reference shoreline\n",
|
|
||||||
"Creates a reference shoreline which helps to identify outliers and false detections. The reference shoreline is manually digitised by the user on one of the images. The parameter `max_dist_ref` defines the maximum distance from the reference shoreline (in metres) at which a valid detected shoreline can be. If you think that the default value of 100 m will not capture the full shoreline variability of your site, increase this value to an appropriate distance."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"%matplotlib qt\n",
|
|
||||||
"settings['reference_shoreline'] = SDS_preprocess.get_reference_sl(metadata, settings)\n",
|
|
||||||
"settings['max_dist_ref'] = 100 # max distance (in meters) allowed from the reference shoreline"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"### Batch shoreline detection\n",
|
|
||||||
"Extracts the 2D shorelines from the images in the spatial reference system specified by the user in `'output_epsg'`. The mapped shorelines are saved into `output.pkl` (under *./data/sitename*) and `output.geojson` (to be used in a GIS software).\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"If you see that the sand pixels on the images are not being identified, change the parameter `sand_color` from `default` to `dark` or `bright` depending on the color of your beach. "
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"scrolled": true
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"%matplotlib qt\n",
|
|
||||||
"output = SDS_shoreline.extract_shorelines(metadata, settings)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"Simple plot of the mapped shorelines. The coordinates are stored in the output dictionnary together with the exact dates in UTC time, the georeferencing accuracy and the cloud cover."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"fig = plt.figure()\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.axis('equal')\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.xlabel('Eastings')\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.ylabel('Northings')\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.grid(linestyle=':', color='0.5')\n",
|
|
||||||
"for i in range(len(output['shorelines'])):\n",
|
|
||||||
" sl = output['shorelines'][i]\n",
|
|
||||||
" date = output['dates'][i]\n",
|
|
||||||
" plt.plot(sl[:,0], sl[:,1], '.', label=date.strftime('%d-%m-%Y'))\n",
|
|
||||||
"plt.legend()\n",
|
|
||||||
"mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager() \n",
|
|
||||||
"mng.window.showMaximized() \n",
|
|
||||||
"fig.set_size_inches([15.76, 8.52])"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"## 3. Shoreline analysis\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"In this section we show how to compute time-series of cross-shore distance along user-defined shore-normal transects."
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"**If you have already mapped the shorelines**, just load the output file (`output.pkl`) by running the section below"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"filepath = os.path.join(inputs['filepath'], sitename)\n",
|
|
||||||
"with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_output' + '.pkl'), 'rb') as f:\n",
|
|
||||||
" output = pickle.load(f) "
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"There are 3 options to define the coordinates of the shore-normal transects:\n",
|
|
||||||
"\n",
|
|
||||||
"**Option 1**: the user can interactively draw the shore-normal transects along the beach by calling:"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"%matplotlib qt\n",
|
|
||||||
"transects = SDS_transects.draw_transects(output, settings)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"**Option 2**: the user can load the transect coordinates (make sure the spatial reference system is the same as defined previously by the parameter *output_epsg*) from a .geojson file by calling:"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"geojson_file = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'examples', 'NARRA_transects.geojson')\n",
|
|
||||||
"transects = SDS_tools.transects_from_geojson(geojson_file)"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"**Option 3**: manually provide the coordinates of the transects as shown in the example below:"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"transects = dict([])\n",
|
|
||||||
"transects['Transect 1'] = np.array([[342836, 6269215], [343315, 6269071]])\n",
|
|
||||||
"transects['Transect 2'] = np.array([[342482, 6268466], [342958, 6268310]])\n",
|
|
||||||
"transects['Transect 3'] = np.array([[342185, 6267650], [342685, 6267641]])"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"Now, intersect the transects with the 2D shorelines to obtain time-series of cross-shore distance"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"# defines the along-shore distance over which to consider shoreline points to compute the median intersection (robust to outliers)\n",
|
|
||||||
"settings['along_dist'] = 25 \n",
|
|
||||||
"cross_distance = SDS_transects.compute_intersection(output, transects, settings) "
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"Plot the time-series of shoreline change along each transect"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
|
||||||
"execution_count": null,
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {},
|
|
||||||
"outputs": [],
|
|
||||||
"source": [
|
|
||||||
"from matplotlib import gridspec\n",
|
|
||||||
"import numpy as np\n",
|
|
||||||
"fig = plt.figure()\n",
|
|
||||||
"gs = gridspec.GridSpec(len(cross_distance),1)\n",
|
|
||||||
"gs.update(left=0.05, right=0.95, bottom=0.05, top=0.95, hspace=0.05)\n",
|
|
||||||
"for i,key in enumerate(cross_distance.keys()):\n",
|
|
||||||
" if np.all(np.isnan(cross_distance[key])):\n",
|
|
||||||
" continue\n",
|
|
||||||
" ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[i,0])\n",
|
|
||||||
" ax.grid(linestyle=':', color='0.5')\n",
|
|
||||||
" ax.set_ylim([-50,50])\n",
|
|
||||||
" ax.plot(output['dates'], cross_distance[key]- np.nanmedian(cross_distance[key]), '-^', markersize=6)\n",
|
|
||||||
" ax.set_ylabel('distance [m]', fontsize=12)\n",
|
|
||||||
" ax.text(0.5,0.95, key, bbox=dict(boxstyle=\"square\", ec='k',fc='w'), ha='center',\n",
|
|
||||||
" va='top', transform=ax.transAxes, fontsize=14)\n",
|
|
||||||
"mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager() \n",
|
|
||||||
"mng.window.showMaximized() \n",
|
|
||||||
"fig.set_size_inches([15.76, 8.52])"
|
|
||||||
]
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
],
|
|
||||||
"metadata": {
|
|
||||||
"kernelspec": {
|
|
||||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
|
||||||
"language": "python",
|
|
||||||
"name": "python3"
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"language_info": {
|
|
||||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
|
||||||
"name": "ipython",
|
|
||||||
"version": 3
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
|
||||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
|
||||||
"name": "python",
|
|
||||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
|
||||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
|
||||||
"version": "3.6.7"
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"varInspector": {
|
|
||||||
"cols": {
|
|
||||||
"lenName": 16,
|
|
||||||
"lenType": 16,
|
|
||||||
"lenVar": 40
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"kernels_config": {
|
|
||||||
"python": {
|
|
||||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": "",
|
|
||||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "del ",
|
|
||||||
"library": "var_list.py",
|
|
||||||
"varRefreshCmd": "print(var_dic_list())"
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"r": {
|
|
||||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": ") ",
|
|
||||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "rm(",
|
|
||||||
"library": "var_list.r",
|
|
||||||
"varRefreshCmd": "cat(var_dic_list()) "
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"types_to_exclude": [
|
|
||||||
"module",
|
|
||||||
"function",
|
|
||||||
"builtin_function_or_method",
|
|
||||||
"instance",
|
|
||||||
"_Feature"
|
|
||||||
],
|
|
||||||
"window_display": false
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
},
|
|
||||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
|
||||||
"nbformat_minor": 2
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
|
||||||
<kml xmlns="http://www.opengis.net/kml/2.2">
|
|
||||||
<Document>
|
|
||||||
<name>NARRA</name>
|
|
||||||
<Style id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal">
|
|
||||||
<LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>ff000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<width>1.2</width>
|
|
||||||
</LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>4d000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<fill>1</fill>
|
|
||||||
<outline>1</outline>
|
|
||||||
</PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
<text><![CDATA[<h3>$[name]</h3>]]></text>
|
|
||||||
</BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
</Style>
|
|
||||||
<Style id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight">
|
|
||||||
<LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>ff000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<width>1.8</width>
|
|
||||||
</LineStyle>
|
|
||||||
<PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<color>4d000000</color>
|
|
||||||
<fill>1</fill>
|
|
||||||
<outline>1</outline>
|
|
||||||
</PolyStyle>
|
|
||||||
<BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
<text><![CDATA[<h3>$[name]</h3>]]></text>
|
|
||||||
</BalloonStyle>
|
|
||||||
</Style>
|
|
||||||
<StyleMap id="poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc">
|
|
||||||
<Pair>
|
|
||||||
<key>normal</key>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
</Pair>
|
|
||||||
<Pair>
|
|
||||||
<key>highlight</key>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
</Pair>
|
|
||||||
</StyleMap>
|
|
||||||
<Placemark>
|
|
||||||
<name>Polygon 1</name>
|
|
||||||
<styleUrl>#poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc</styleUrl>
|
|
||||||
<Polygon>
|
|
||||||
<outerBoundaryIs>
|
|
||||||
<LinearRing>
|
|
||||||
<tessellate>1</tessellate>
|
|
||||||
<coordinates>
|
|
||||||
151.2957545,-33.7012561,0
|
|
||||||
151.297557,-33.7388075,0
|
|
||||||
151.312234,-33.7390216,0
|
|
||||||
151.311204,-33.701399,0
|
|
||||||
151.2957545,-33.7012561,0
|
|
||||||
</coordinates>
|
|
||||||
</LinearRing>
|
|
||||||
</outerBoundaryIs>
|
|
||||||
</Polygon>
|
|
||||||
</Placemark>
|
|
||||||
</Document>
|
|
||||||
</kml>
|
|
||||||
Binary file not shown.
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 18 MiB |
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
@ -0,0 +1,432 @@
|
|||||||
|
"""This module contains all the functions needed for data analysis """
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Initial settings
|
||||||
|
import numpy as np
|
||||||
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||||
|
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
|
||||||
|
from matplotlib import gridspec
|
||||||
|
import pdb
|
||||||
|
import ee
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# other modules
|
||||||
|
from osgeo import gdal, ogr, osr
|
||||||
|
import scipy.interpolate as interpolate
|
||||||
|
import scipy.stats as sstats
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# image processing modules
|
||||||
|
import skimage.filters as filters
|
||||||
|
import skimage.exposure as exposure
|
||||||
|
import skimage.transform as transform
|
||||||
|
import sklearn.decomposition as decomposition
|
||||||
|
import skimage.measure as measure
|
||||||
|
import skimage.morphology as morphology
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# machine learning modules
|
||||||
|
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
|
||||||
|
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
|
||||||
|
from sklearn.externals import joblib
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import time
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# import own modules
|
||||||
|
import functions.utils as utils
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def get_tide(dates_sds, dates_tide, tide_level):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
tide = []
|
||||||
|
for i in range(len(dates_sds)):
|
||||||
|
dates_diff = np.abs(np.array([ (dates_sds[i] - _).total_seconds() for _ in dates_tide]))
|
||||||
|
if np.min(dates_diff) <= 1800: # half-an-hour
|
||||||
|
idx_closest = np.argmin(dates_diff)
|
||||||
|
tide.append(tide_level[idx_closest])
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
tide.append(np.nan)
|
||||||
|
tide = np.array(tide)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return tide
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def remove_duplicates(output, satname):
|
||||||
|
" removes duplicates from output structure, keep the one with less cloud cover or best georeferencing "
|
||||||
|
dates = output['dates']
|
||||||
|
dates_str = [_.strftime('%Y%m%d') for _ in dates]
|
||||||
|
dupl = utils.duplicates_dict(dates_str)
|
||||||
|
if dupl:
|
||||||
|
output_nodup = dict([])
|
||||||
|
idx_remove = []
|
||||||
|
if satname == 'L8' or satname == 'L5':
|
||||||
|
for k,v in dupl.items():
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
idx1 = v[0]
|
||||||
|
idx2 = v[1]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
c1 = output['metadata']['cloud_cover'][idx1]
|
||||||
|
c2 = output['metadata']['cloud_cover'][idx2]
|
||||||
|
g1 = output['metadata']['acc_georef'][idx1]
|
||||||
|
g2 = output['metadata']['acc_georef'][idx2]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if c1 < c2 - 0.01:
|
||||||
|
idx_remove.append(idx2)
|
||||||
|
elif g1 < g2 - 0.1:
|
||||||
|
idx_remove.append(idx2)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
idx_remove.append(idx1)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
for k,v in dupl.items():
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
idx1 = v[0]
|
||||||
|
idx2 = v[1]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
c1 = output['metadata']['cloud_cover'][idx1]
|
||||||
|
c2 = output['metadata']['cloud_cover'][idx2]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if c1 < c2 - 0.01:
|
||||||
|
idx_remove.append(idx2)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
idx_remove.append(idx1)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
idx_remove = sorted(idx_remove)
|
||||||
|
idx_all = np.linspace(0, len(dates_str)-1, len(dates_str))
|
||||||
|
idx_keep = list(np.where(~np.isin(idx_all,idx_remove))[0])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
output_nodup['dates'] = [output['dates'][k] for k in idx_keep]
|
||||||
|
output_nodup['shorelines'] = [output['shorelines'][k] for k in idx_keep]
|
||||||
|
output_nodup['metadata'] = dict([])
|
||||||
|
for key in list(output['metadata'].keys()):
|
||||||
|
output_nodup['metadata'][key] = [output['metadata'][key][k] for k in idx_keep]
|
||||||
|
print(satname + ' : ' + str(len(idx_remove)) + ' duplicates')
|
||||||
|
return output_nodup
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
print(satname + ' : ' + 'no duplicates')
|
||||||
|
return output
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def merge(output):
|
||||||
|
" merges data from the different satellites "
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# stack all list together under one key
|
||||||
|
output_all = {'dates':[], 'shorelines':[],
|
||||||
|
'metadata':{'filenames':[], 'satname':[], 'cloud_cover':[], 'acc_georef':[]}}
|
||||||
|
for satname in list(output.keys()):
|
||||||
|
output_all['dates'] = output_all['dates'] + output[satname]['dates']
|
||||||
|
output_all['shorelines'] = output_all['shorelines'] + output[satname]['shorelines']
|
||||||
|
for key in list(output[satname]['metadata'].keys()):
|
||||||
|
output_all['metadata'][key] = output_all['metadata'][key] + output[satname]['metadata'][key]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
output_all_sorted = {'dates':[], 'shorelines':[],
|
||||||
|
'metadata':{'filenames':[], 'satname':[], 'cloud_cover':[], 'acc_georef':[]}}
|
||||||
|
# sort the dates
|
||||||
|
idx_sorted = sorted(range(len(output_all['dates'])), key=output_all['dates'].__getitem__)
|
||||||
|
output_all_sorted['dates'] = [output_all['dates'][i] for i in idx_sorted]
|
||||||
|
output_all_sorted['shorelines'] = [output_all['shorelines'][i] for i in idx_sorted]
|
||||||
|
for key in list(output_all['metadata'].keys()):
|
||||||
|
output_all_sorted['metadata'][key] = [output_all['metadata'][key][i] for i in idx_sorted]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return output_all_sorted
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def create_transects(x0, y0, orientation, chainage_length):
|
||||||
|
" creates shore-normal transects "
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
transects = []
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for k in range(len(x0)):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# orientation of cross-shore profile
|
||||||
|
phi = (90 - orientation[k])*np.pi/180
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# create a vector using the chainage length
|
||||||
|
x = np.linspace(0,chainage_length,chainage_length+1)
|
||||||
|
y = np.zeros(len(x))
|
||||||
|
coords = np.zeros((len(x),2))
|
||||||
|
coords[:,0] = x
|
||||||
|
coords[:,1] = y
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# translate and rotate the vector using the origin and orientation
|
||||||
|
tf = transform.EuclideanTransform(rotation=phi, translation=(x0[k],y0[k]))
|
||||||
|
coords_tf = tf(coords)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
transects.append(coords_tf)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return transects
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def calculate_chainage(sds, transects, orientation, along_dist):
|
||||||
|
" intersect SDS with transect and compute chainage position "
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
chainage_mtx = np.zeros((len(sds),len(transects),6))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for i in range(len(sds)):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sl = sds[i]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for j in range(len(transects)):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# compute rotation matrix
|
||||||
|
X0 = transects[j][0,0]
|
||||||
|
Y0 = transects[j][0,1]
|
||||||
|
phi = (90 - orientation[j])*np.pi/180
|
||||||
|
Mrot = np.array([[np.cos(phi), np.sin(phi)],[-np.sin(phi), np.cos(phi)]])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# calculate point to line distance between shoreline points and profile
|
||||||
|
p1 = np.array([X0,Y0])
|
||||||
|
p2 = transects[j][-1,:]
|
||||||
|
p3 = sl
|
||||||
|
d = np.abs(np.cross(p2-p1,p3-p1)/np.linalg.norm(p2-p1))
|
||||||
|
idx_close = utils.find_indices(d, lambda e: e <= along_dist)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# check if there are SDS points around the profile or not
|
||||||
|
if not idx_close:
|
||||||
|
chainage_mtx[i,j,:] = np.tile(np.nan,(1,6))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
# change of base to shore-normal coordinate system
|
||||||
|
xy_close = np.array([sl[idx_close,0],sl[idx_close,1]]) - np.tile(np.array([[X0],[Y0]]), (1,len(sl[idx_close])))
|
||||||
|
xy_rot = np.matmul(Mrot, xy_close)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# put nan values if the chainage is negative (MAKE SURE TO PICK ORIGIN CORRECTLY)
|
||||||
|
if np.any(xy_rot[0,:] < 0):
|
||||||
|
xy_rot[0,np.where(xy_rot[0,:] < 0)] = np.nan
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# compute mean, median max and std of chainage position
|
||||||
|
n_points = len(xy_rot[0,:])
|
||||||
|
mean_cross = np.nanmean(xy_rot[0,:])
|
||||||
|
median_cross = np.nanmedian(xy_rot[0,:])
|
||||||
|
max_cross = np.nanmax(xy_rot[0,:])
|
||||||
|
min_cross = np.nanmin(xy_rot[0,:])
|
||||||
|
std_cross = np.nanstd(xy_rot[0,:])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if std_cross > 10: # if large std, take the most seaward point
|
||||||
|
mean_cross = max_cross
|
||||||
|
median_cross = max_cross
|
||||||
|
min_cross = max_cross
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# store the statistics
|
||||||
|
chainage_mtx[i,j,:] = np.array([mean_cross, median_cross, max_cross,
|
||||||
|
min_cross, n_points, std_cross])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# format into dictionnary
|
||||||
|
chainage = dict([])
|
||||||
|
chainage['mean'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,0]
|
||||||
|
chainage['median'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,1]
|
||||||
|
chainage['max'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,2]
|
||||||
|
chainage['min'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,3]
|
||||||
|
chainage['npoints'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,4]
|
||||||
|
chainage['std'] = chainage_mtx[:,:,5]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return chainage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def compare_sds(dates_sds, chain_sds, topo_profiles, mod=0, mindays=5):
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
Compare sds with groundtruth data from topographic surveys / argus shorelines
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
KV WRL 2018
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Arguments:
|
||||||
|
-----------
|
||||||
|
dates_sds: list
|
||||||
|
list of dates corresponding to each row in chain_sds
|
||||||
|
chain_sds: np.ndarray
|
||||||
|
array with time series of chainage for each transect (each transect is one column)
|
||||||
|
topo_profiles: dict
|
||||||
|
dict containing the dates and chainage of the groundtruth
|
||||||
|
mod: 0 or 1
|
||||||
|
0 for linear interpolation between 2 closest surveys, 1 for only nearest neighbour
|
||||||
|
min_days: int
|
||||||
|
minimum number of days for which the data can be compared
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Returns: -----------
|
||||||
|
stats: dict
|
||||||
|
contains all the statistics of the comparison
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# create 3 figures
|
||||||
|
fig1 = plt.figure()
|
||||||
|
gs1 = gridspec.GridSpec(chain_sds.shape[1], 1)
|
||||||
|
fig2 = plt.figure()
|
||||||
|
gs2 = gridspec.GridSpec(2, chain_sds.shape[1])
|
||||||
|
fig3 = plt.figure()
|
||||||
|
gs3 = gridspec.GridSpec(2,1)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dates_sds_num = np.array([_.toordinal() for _ in dates_sds])
|
||||||
|
stats = dict([])
|
||||||
|
data_fin = dict([])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# for each transect compare and plot the data
|
||||||
|
for i in range(chain_sds.shape[1]):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
pfname = list(topo_profiles.keys())[i]
|
||||||
|
stats[pfname] = dict([])
|
||||||
|
data_fin[pfname] = dict([])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dates_sur = topo_profiles[pfname]['dates']
|
||||||
|
chain_sur = topo_profiles[pfname]['chainage']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# convert to datenum
|
||||||
|
dates_sur_num = np.array([_.toordinal() for _ in dates_sur])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
chain_sur_interp = []
|
||||||
|
diff_days = []
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for j, satdate in enumerate(dates_sds_num):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
temp_diff = satdate - dates_sur_num
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if mod==0:
|
||||||
|
# select measurement before and after sat image date and interpolate
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ind_before = np.where(temp_diff == temp_diff[temp_diff > 0][-1])[0]
|
||||||
|
if ind_before == len(temp_diff)-1:
|
||||||
|
chain_sur_interp.append(np.nan)
|
||||||
|
diff_days.append(np.abs(satdate-dates_sur_num[ind_before])[0])
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
ind_after = np.where(temp_diff == temp_diff[temp_diff < 0][0])[0]
|
||||||
|
tempx = np.zeros(2)
|
||||||
|
tempx[0] = dates_sur_num[ind_before]
|
||||||
|
tempx[1] = dates_sur_num[ind_after]
|
||||||
|
tempy = np.zeros(2)
|
||||||
|
tempy[0] = chain_sur[ind_before]
|
||||||
|
tempy[1] = chain_sur[ind_after]
|
||||||
|
diff_days.append(np.abs(np.max([satdate-tempx[0], satdate-tempx[1]])))
|
||||||
|
# interpolate
|
||||||
|
f = interpolate.interp1d(tempx, tempy)
|
||||||
|
chain_sur_interp.append(f(satdate))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
elif mod==1:
|
||||||
|
# select the closest measurement
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
idx_closest = utils.find_indices(np.abs(temp_diff), lambda e: e == np.min(np.abs(temp_diff)))[0]
|
||||||
|
diff_days.append(np.abs(satdate-dates_sur_num[idx_closest]))
|
||||||
|
if diff_days[j] > mindays:
|
||||||
|
chain_sur_interp.append(np.nan)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
chain_sur_interp.append(chain_sur[idx_closest])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
chain_sur_interp = np.array(chain_sur_interp)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# remove nan values
|
||||||
|
idx_sur_nan = ~np.isnan(chain_sur_interp)
|
||||||
|
idx_sat_nan = ~np.isnan(chain_sds[:,i])
|
||||||
|
idx_nan = np.logical_and(idx_sur_nan, idx_sat_nan)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# groundtruth and sds
|
||||||
|
chain_sur_fin = chain_sur_interp[idx_nan]
|
||||||
|
chain_sds_fin = chain_sds[idx_nan,i]
|
||||||
|
dates_fin = [k for (k, v) in zip(dates_sds, idx_nan) if v]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# calculate statistics
|
||||||
|
slope, intercept, rvalue, pvalue, std_err = sstats.linregress(chain_sur_fin, chain_sds_fin)
|
||||||
|
R2 = rvalue**2
|
||||||
|
correlation = np.corrcoef(chain_sur_fin, chain_sds_fin)[0,1]
|
||||||
|
diff_chain = chain_sur_fin - chain_sds_fin
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
rmse = np.sqrt(np.nanmean((diff_chain)**2))
|
||||||
|
mean = np.nanmean(diff_chain)
|
||||||
|
std = np.nanstd(diff_chain)
|
||||||
|
q90 = np.percentile(np.abs(diff_chain), 90)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# store data
|
||||||
|
stats[pfname]['rmse'] = rmse
|
||||||
|
stats[pfname]['mean'] = mean
|
||||||
|
stats[pfname]['std'] = std
|
||||||
|
stats[pfname]['q90'] = q90
|
||||||
|
stats[pfname]['diffdays'] = diff_days
|
||||||
|
stats[pfname]['corr'] = correlation
|
||||||
|
stats[pfname]['linfit'] = {'slope':slope, 'intercept':intercept, 'R2':R2, 'pvalue':pvalue}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
data_fin[pfname]['dates'] = dates_fin
|
||||||
|
data_fin[pfname]['sds'] = chain_sds_fin
|
||||||
|
data_fin[pfname]['survey'] = chain_sur_fin
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# make time-series plot
|
||||||
|
plt.figure(fig1.number)
|
||||||
|
fig1.add_subplot(gs1[i,0])
|
||||||
|
plt.plot(dates_sur, chain_sur, 'o-', color='C1', markersize=4, label='survey all')
|
||||||
|
plt.plot(dates_fin, chain_sur_fin, 'o', color=[0.3, 0.3, 0.3], markersize=2, label='survey interp')
|
||||||
|
plt.plot(dates_fin, chain_sds_fin, 'o--', color='b', markersize=4, label='SDS')
|
||||||
|
plt.title(pfname, fontweight='bold')
|
||||||
|
# plt.xlim([dates_sds[0], dates_sds[-1]])
|
||||||
|
plt.ylabel('chainage [m]')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# make scatter plot
|
||||||
|
plt.figure(fig2.number)
|
||||||
|
fig2.add_subplot(gs2[0,i])
|
||||||
|
plt.axis('equal')
|
||||||
|
plt.plot(chain_sur_fin, chain_sds_fin, 'ko', markersize=4, markerfacecolor='w', alpha=0.7)
|
||||||
|
xmax = np.max([np.nanmax(chain_sds_fin),np.nanmax(chain_sur_fin)])
|
||||||
|
xmin = np.min([np.nanmin(chain_sds_fin),np.nanmin(chain_sur_fin)])
|
||||||
|
ymax = np.max([np.nanmax(chain_sds_fin),np.nanmax(chain_sur_fin)])
|
||||||
|
ymin = np.min([np.nanmin(chain_sds_fin),np.nanmin(chain_sur_fin)])
|
||||||
|
plt.plot([xmin, xmax], [ymin, ymax], 'k--')
|
||||||
|
plt.plot([xmin, xmax], [xmin*slope + intercept, xmax*slope + intercept], 'b:')
|
||||||
|
str_corr = ' y = %.2f x + %.2f\n R2 = %.2f' % (slope, intercept, R2)
|
||||||
|
plt.text(xmin, ymax-5, str_corr, bbox=dict(facecolor=[0.7,0.7,0.7], alpha=0.5), horizontalalignment='left')
|
||||||
|
plt.xlabel('chainage survey [m]')
|
||||||
|
plt.ylabel('chainage satellite [m]')
|
||||||
|
plt.title(pfname, fontweight='bold')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
fig2.add_subplot(gs2[1,i])
|
||||||
|
binwidth = 3
|
||||||
|
bins = np.arange(min(diff_chain), max(diff_chain) + binwidth, binwidth)
|
||||||
|
density = plt.hist(diff_chain, bins=bins, density=True, color=[0.8, 0.8, 0.8], edgecolor='k')
|
||||||
|
plt.xlim([-50, 50])
|
||||||
|
plt.xlabel('error [m]')
|
||||||
|
str_stats = ' rmse = %.1f\n mean = %.1f\n std = %.1f\n q90 = %.1f' % (rmse, mean, std, q90)
|
||||||
|
plt.text(15, np.max(density[0])-0.015, str_stats, bbox=dict(facecolor=[0.8,0.8,0.8], alpha=0.3), horizontalalignment='left', fontsize=10)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
fig1.set_size_inches(19.2, 9.28)
|
||||||
|
fig1.set_tight_layout(True)
|
||||||
|
fig2.set_size_inches(19.2, 9.28)
|
||||||
|
fig2.set_tight_layout(True)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# all transects together
|
||||||
|
chain_sds_all = []
|
||||||
|
chain_sur_all = []
|
||||||
|
for i in range(chain_sds.shape[1]):
|
||||||
|
pfname = list(topo_profiles.keys())[i]
|
||||||
|
chain_sds_all = np.append(chain_sds_all,data_fin[pfname]['sds'])
|
||||||
|
chain_sur_all = np.append(chain_sur_all,data_fin[pfname]['survey'])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# calculate statistics
|
||||||
|
slope, intercept, rvalue, pvalue, std_err = sstats.linregress(chain_sur_all, chain_sds_all)
|
||||||
|
R2 = rvalue**2
|
||||||
|
correlation = np.corrcoef(chain_sur_all, chain_sds_all)[0,1]
|
||||||
|
diff_chain_all = chain_sur_all - chain_sds_all
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
rmse = np.sqrt(np.nanmean((diff_chain_all)**2))
|
||||||
|
mean = np.nanmean(diff_chain_all)
|
||||||
|
std = np.nanstd(diff_chain_all)
|
||||||
|
q90 = np.percentile(np.abs(diff_chain_all), 90)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
stats['all'] = {'rmse':rmse,'mean':mean,'std':std,'q90':q90, 'corr':correlation,
|
||||||
|
'linfit':{'slope':slope, 'intercept':intercept, 'R2':R2, 'pvalue':pvalue}}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# make plot
|
||||||
|
plt.figure(fig3.number)
|
||||||
|
fig3.add_subplot(gs3[0,0])
|
||||||
|
plt.axis('equal')
|
||||||
|
plt.plot(chain_sur_all, chain_sds_all, 'ko', markersize=4, markerfacecolor='w', alpha=0.7)
|
||||||
|
xmax = np.max([np.nanmax(chain_sds_all),np.nanmax(chain_sur_all)])
|
||||||
|
xmin = np.min([np.nanmin(chain_sds_all),np.nanmin(chain_sur_all)])
|
||||||
|
ymax = np.max([np.nanmax(chain_sds_all),np.nanmax(chain_sur_all)])
|
||||||
|
ymin = np.min([np.nanmin(chain_sds_all),np.nanmin(chain_sur_all)])
|
||||||
|
plt.plot([xmin, xmax], [ymin, ymax], 'k--')
|
||||||
|
plt.plot([xmin, xmax], [xmin*slope + intercept, xmax*slope + intercept], 'b:')
|
||||||
|
str_corr = ' y = %.2f x + %.2f\n R2 = %.2f' % (slope, intercept, R2)
|
||||||
|
plt.text(xmin, ymax-5, str_corr, bbox=dict(facecolor=[0.7,0.7,0.7], alpha=0.5), horizontalalignment='left')
|
||||||
|
plt.xlabel('chainage survey [m]')
|
||||||
|
plt.ylabel('chainage satellite [m]')
|
||||||
|
plt.title(pfname, fontweight='bold')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
fig3.add_subplot(gs3[1,0])
|
||||||
|
binwidth = 3
|
||||||
|
bins = np.arange(min(diff_chain_all), max(diff_chain_all) + binwidth, binwidth)
|
||||||
|
density = plt.hist(diff_chain_all, bins=bins, density=True, color=[0.8, 0.8, 0.8], edgecolor='k')
|
||||||
|
plt.xlim([-50, 50])
|
||||||
|
plt.xlabel('error [m]')
|
||||||
|
str_stats = ' rmse = %.1f\n mean = %.1f\n std = %.1f\n q90 = %.1f' % (rmse, mean, std, q90)
|
||||||
|
plt.text(15, np.max(density[0])-0.015, str_stats, bbox=dict(facecolor=[0.8,0.8,0.8], alpha=0.3), horizontalalignment='left', fontsize=10)
|
||||||
|
fig3.set_size_inches(9.2, 9.28)
|
||||||
|
fig3.set_tight_layout(True)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return stats
|
||||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
|
|||||||
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
Created on Thu Mar 1 11:30:31 2018
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@author: z5030440
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Contains all the utilities, convenience functions and small functions that do simple things
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||||
|
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
|
||||||
|
import numpy as np
|
||||||
|
import scipy.io as sio
|
||||||
|
import pdb
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def ecdf(x):
|
||||||
|
"""convenience function for computing the empirical CDF"""
|
||||||
|
vals, counts = np.unique(x, return_counts=True)
|
||||||
|
ecdf = np.cumsum(counts).astype(np.float64)
|
||||||
|
ecdf /= ecdf[-1]
|
||||||
|
return vals, ecdf
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def intensity_histogram(image):
|
||||||
|
"""plots histogram and cumulative distribution of the pixel intensities in an image"""
|
||||||
|
imSize = image.shape
|
||||||
|
if len(imSize) == 2:
|
||||||
|
im = image[:,:].reshape(imSize[0] * imSize[1])
|
||||||
|
im = im[~np.isnan(im)]
|
||||||
|
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2,1, sharex=True, figsize = (8,6))
|
||||||
|
ax1.hist(im, bins=300)
|
||||||
|
ax1.set_title('Probability density function')
|
||||||
|
ax2.hist(im, bins=300, cumulative=True, histtype='step')
|
||||||
|
ax2.set_title('Cumulative distribution')
|
||||||
|
plt.show()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
for i in range(imSize[2]):
|
||||||
|
im = image[:,:,i].reshape(imSize[0] * imSize[1])
|
||||||
|
im = im[~np.isnan(im)]
|
||||||
|
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2,1, sharex=True, figsize = (8,6))
|
||||||
|
ax1.hist(im, bins=300)
|
||||||
|
ax1.set_title('Probability density function')
|
||||||
|
ax2.hist(im, bins=300, cumulative=True, histtype='step')
|
||||||
|
ax2.set_title('Cumulative distribution')
|
||||||
|
plt.show()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def compare_images(im1, im2):
|
||||||
|
"""plots 2 images next to each other, sharing the axis"""
|
||||||
|
plt.figure()
|
||||||
|
ax1 = plt.subplot(121)
|
||||||
|
plt.imshow(im1, cmap='gray')
|
||||||
|
ax2 = plt.subplot(122, sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
|
||||||
|
plt.imshow(im2, cmap='gray')
|
||||||
|
plt.show()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def find_indices(lst, condition):
|
||||||
|
"imitation of MATLAB find function"
|
||||||
|
return [i for i, elem in enumerate(lst) if condition(elem)]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def reject_outliers(data, m=2):
|
||||||
|
"rejects outliers in a numpy array"
|
||||||
|
return data[abs(data - np.mean(data)) < m * np.std(data)]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def duplicates_dict(lst):
|
||||||
|
"return duplicates and indices"
|
||||||
|
# nested function
|
||||||
|
def duplicates(lst, item):
|
||||||
|
return [i for i, x in enumerate(lst) if x == item]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return dict((x, duplicates(lst, x)) for x in set(lst) if lst.count(x) > 1)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def datenum2datetime(datenum):
|
||||||
|
"convert datenum to datetime"
|
||||||
|
#takes in datenum and outputs python datetime
|
||||||
|
time = [datetime.fromordinal(int(dn)) + timedelta(days=float(dn)%1) - timedelta(days = 366) for dn in datenum]
|
||||||
|
return time
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def loadmat(filename):
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
this function should be called instead of direct spio.loadmat
|
||||||
|
as it cures the problem of not properly recovering python dictionaries
|
||||||
|
from mat files. It calls the function check keys to cure all entries
|
||||||
|
which are still mat-objects
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
data = sio.loadmat(filename, struct_as_record=False, squeeze_me=True)
|
||||||
|
return _check_keys(data)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def _check_keys(dict):
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
checks if entries in dictionary are mat-objects. If yes
|
||||||
|
todict is called to change them to nested dictionaries
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
for key in dict:
|
||||||
|
if isinstance(dict[key], sio.matlab.mio5_params.mat_struct):
|
||||||
|
dict[key] = _todict(dict[key])
|
||||||
|
return dict
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def _todict(matobj):
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
A recursive function which constructs from matobjects nested dictionaries
|
||||||
|
'''
|
||||||
|
dict = {}
|
||||||
|
for strg in matobj._fieldnames:
|
||||||
|
elem = matobj.__dict__[strg]
|
||||||
|
if isinstance(elem, sio.matlab.mio5_params.mat_struct):
|
||||||
|
dict[strg] = _todict(elem)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
dict[strg] = elem
|
||||||
|
return dict
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
|
|||||||
|
# This file may be used to create an environment using:
|
||||||
|
# $ conda create --name <env> --file <this file>
|
||||||
|
# platform: win-64
|
||||||
|
@EXPLICIT
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/alabaster-0.7.10-py36hcd07829_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/asn1crypto-0.24.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/astroid-1.6.1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/babel-2.5.3-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/backports-1.0-py36h81696a8_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/free/win-64/backports.weakref-1.0rc1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/free/win-64/bleach-1.5.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/bokeh-0.12.14-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/ca-certificates-2017.08.26-h94faf87_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/certifi-2018.1.18-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/cffi-1.11.4-py36hfa6e2cd_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/chardet-3.0.4-py36h420ce6e_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/click-6.7-py36hec8c647_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/cloudpickle-0.5.2-py36_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/colorama-0.3.9-py36h029ae33_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/cryptography-2.1.4-py36he1d7878_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/curl-7.58.0-h7602738_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/cycler-0.10.0-py36h009560c_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/dask-0.17.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/dask-core-0.17.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/decorator-4.2.1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/distributed-1.21.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/docutils-0.14-py36h6012d8f_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/entrypoints-0.2.3-py36hfd66bb0_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/expat-2.2.5-hcc4222d_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/freetype-2.8.1-vc14_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/freexl-1.0.4-h342dbcb_5.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/geos-3.6.2-h9ef7328_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/hdf4-4.2.13-h712560f_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/hdf5-1.10.1-h98b8871_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/heapdict-1.0.0-py36_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/free/win-64/html5lib-0.9999999-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/icc_rt-2017.0.4-h97af966_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/icu-58.2-vc14_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/idna-2.6-py36h148d497_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/imageio-2.3.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/imagesize-0.7.1-py36he29f638_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/intel-openmp-2018.0.0-hd92c6cd_8.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/ipykernel-4.8.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/ipython-6.2.1-py36h9cf0123_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/ipython_genutils-0.2.0-py36h3c5d0ee_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/ipywidgets-7.1.1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/isort-4.2.15-py36h6198cc5_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/jedi-0.11.1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/jinja2-2.10-py36h292fed1_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/jpeg-9b-vc14_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/jsonschema-2.6.0-py36h7636477_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/jupyter-1.0.0-py36_4.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/jupyter_client-5.2.2-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/jupyter_console-5.2.0-py36h6d89b47_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/jupyter_contrib_core-0.3.3-py36_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/jupyter_contrib_nbextensions-0.4.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/jupyter_core-4.4.0-py36h56e9d50_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/jupyter_highlight_selected_word-0.1.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/jupyter_latex_envs-1.3.8.2-py36_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/jupyter_nbextensions_configurator-0.4.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/jupyterlab-0.31.5-py36_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/jupyterlab_launcher-0.10.3-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/kealib-1.4.7-ha5b336b_5.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/krb5-1.14.2-h63dfc2a_6.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/lazy-object-proxy-1.3.1-py36hd1c21d2_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libboost-1.65.1-he51fdeb_4.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libcurl-7.58.0-h7602738_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libgdal-2.2.2-h2727f2b_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libiconv-1.15-h1df5818_7.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libkml-1.3.0-hc65d273_3.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libnetcdf-4.4.1.1-h825a56a_8.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/libpng-1.6.34-vc14_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libpq-9.6.6-hfe3f2bf_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libprotobuf-3.4.1-h3dba5dd_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libspatialite-4.3.0a-h383548d_18.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/libssh2-1.8.0-hd619d38_4.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/libtiff-4.0.9-vc14_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/libxml2-2.9.5-vc14_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/libxslt-1.1.32-vc14_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/locket-0.2.0-py36hfed976d_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/lxml-4.1.1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/free/win-64/markdown-2.6.9-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/markupsafe-1.0-py36h0e26971_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/matplotlib-2.1.2-py36h016c42a_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/mccabe-0.6.1-py36hb41005a_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/mistune-0.8.3-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/mkl-2018.0.1-h2108138_4.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/msgpack-python-0.5.1-py36he980bc4_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/nbconvert-5.3.1-py36h8dc0fde_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/nbformat-4.4.0-py36h3a5bc1b_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/networkx-2.1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/nodejs-8.9.3-hd6b2f15_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/notebook-5.4.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/numpy-1.14.1-py36hb69e940_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/numpydoc-0.7.0-py36ha25429e_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/olefile-0.45.1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/openjpeg-2.2.0-h29c51c3_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/openssl-1.0.2n-vc14_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/packaging-16.8-py36ha0986f6_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pandas-0.22.0-py36h6538335_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pandoc-1.19.2.1-hb2460c7_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pandocfilters-1.4.2-py36h3ef6317_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/parso-0.1.1-py36hae3edee_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/partd-0.3.8-py36hc8e763b_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/patsy-0.5.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pickleshare-0.7.4-py36h9de030f_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pillow-5.0.0-py36h0738816_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pip-9.0.1-py36h226ae91_4.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/proj4-4.9.3-hcf24537_7.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/prompt_toolkit-1.0.15-py36h60b8f86_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/protobuf-3.4.1-py36h07fa351_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/psutil-5.4.3-py36hfa6e2cd_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pycodestyle-2.3.1-py36h7cc55cd_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pycparser-2.18-py36hd053e01_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pyflakes-1.6.0-py36h0b975d6_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pygments-2.2.0-py36hb010967_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pylint-1.8.2-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pyopenssl-17.5.0-py36h5b7d817_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pyparsing-2.2.0-py36h785a196_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pyqt-5.6.0-py36hb5ed885_5.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pysocks-1.6.7-py36h698d350_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/python-3.6.4-h6538335_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/python-dateutil-2.6.1-py36h509ddcb_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pytz-2018.3-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pywavelets-0.5.2-py36hc649158_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pywinpty-0.5-py36h6538335_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/pyyaml-3.12-py36_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/pyzmq-16.0.3-py36he714bf5_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/qt-5.6.2-vc14_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/qtawesome-0.4.4-py36h5aa48f6_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/qtconsole-4.3.1-py36h99a29a9_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/qtpy-1.3.1-py36hb8717c5_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/requests-2.18.4-py36h4371aae_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/rope-0.10.7-py36had63a69_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/scikit-image-0.13.1-py36hfa6e2cd_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/scikit-learn-0.19.1-py36h53aea1b_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/scipy-1.0.0-py36h1260518_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/send2trash-1.4.2-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/setuptools-38.4.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/shapely-1.6.4-py36h2a969d5_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/simplegeneric-0.8.1-py36_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/sip-4.18.1-py36h9c25514_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/six-1.11.0-py36h4db2310_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/snowballstemmer-1.2.1-py36h763602f_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/sortedcontainers-1.5.9-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/sphinx-1.6.6-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/sphinxcontrib-1.0-py36hbbac3d2_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/sphinxcontrib-websupport-1.0.1-py36hb5e5916_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/spyder-3.2.8-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/sqlite-3.20.1-vc14_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/statsmodels-0.8.0-py36h6189b4c_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/tblib-1.3.2-py36h30f5020_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/free/win-64/tensorflow-1.2.1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/terminado-0.8.1-py36_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/testpath-0.3.1-py36h2698cfe_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/tk-8.6.7-vc14_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/toolz-0.9.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/tornado-4.5.3-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/traitlets-4.3.2-py36h096827d_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/typing-3.6.2-py36hb035bda_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/urllib3-1.22-py36h276f60a_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/vc-14-h0510ff6_3.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/free/win-64/vs2015_runtime-14.0.25420-0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/wcwidth-0.1.7-py36h3d5aa90_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/webencodings-0.5.1-py36h67c50ae_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/werkzeug-0.14.1-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/wheel-0.30.0-py36h6c3ec14_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/widgetsnbextension-3.1.0-py36_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/win_inet_pton-1.0.1-py36he67d7fd_1.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/wincertstore-0.2-py36h7fe50ca_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/winpty-0.4.3-vc14_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/wrapt-1.10.11-py36he5f5981_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/xerces-c-3.2.0-h44c76bb_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/xz-5.2.3-h7c615d8_2.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/yaml-0.1.7-vc14_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://repo.continuum.io/pkgs/main/win-64/zict-0.1.3-py36h2d8e73e_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
|
https://conda.anaconda.org/conda-forge/win-64/zlib-1.2.11-vc14_0.tar.bz2
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,589 @@
|
|||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Extract shorelines from Landsat images
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Initial settings
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import os
|
||||||
|
import numpy as np
|
||||||
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||||
|
import ee
|
||||||
|
import pdb
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# other modules
|
||||||
|
from osgeo import gdal, ogr, osr
|
||||||
|
import pickle
|
||||||
|
import matplotlib.cm as cm
|
||||||
|
from pylab import ginput
|
||||||
|
from shapely.geometry import LineString
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# image processing modules
|
||||||
|
import skimage.filters as filters
|
||||||
|
import skimage.exposure as exposure
|
||||||
|
import skimage.transform as transform
|
||||||
|
import sklearn.decomposition as decomposition
|
||||||
|
import skimage.measure as measure
|
||||||
|
import skimage.morphology as morphology
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# machine learning modules
|
||||||
|
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
|
||||||
|
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
|
||||||
|
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, Normalizer
|
||||||
|
from sklearn.externals import joblib
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# import own modules
|
||||||
|
import functions.utils as utils
|
||||||
|
import functions.sds as sds
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# some other settings
|
||||||
|
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
|
||||||
|
plt.rcParams['axes.grid'] = True
|
||||||
|
plt.rcParams['figure.max_open_warning'] = 100
|
||||||
|
ee.Initialize()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Parameters
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sitename = 'NARRA'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
cloud_thresh = 0.7 # threshold for cloud cover
|
||||||
|
plot_bool = False # if you want the plots
|
||||||
|
output_epsg = 28356 # GDA94 / MGA Zone 56
|
||||||
|
buffer_size = 7 # radius (in pixels) of disk for buffer (pixel classification)
|
||||||
|
min_beach_size = 20 # number of pixels in a beach (pixel classification)
|
||||||
|
dist_ref = 100 # maximum distance from reference point
|
||||||
|
min_length_wl = 200 # minimum length of shoreline LineString to be kept
|
||||||
|
manual_bool = True # to manually check images
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
output = dict([])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Metadata
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
filepath = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename)
|
||||||
|
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_metadata' + '.pkl'), 'rb') as f:
|
||||||
|
metadata = pickle.load(f)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#%%
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Read S2 images
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
satname = 'S2'
|
||||||
|
dates = metadata[satname]['dates']
|
||||||
|
input_epsg = 32756 # metadata[satname]['epsg']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# path to images
|
||||||
|
filepath10 = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename, satname, '10m')
|
||||||
|
filenames10 = os.listdir(filepath10)
|
||||||
|
filepath20 = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename, satname, '20m')
|
||||||
|
filenames20 = os.listdir(filepath20)
|
||||||
|
filepath60 = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename, satname, '60m')
|
||||||
|
filenames60 = os.listdir(filepath60)
|
||||||
|
if (not len(filenames10) == len(filenames20)) or (not len(filenames20) == len(filenames60)):
|
||||||
|
raise 'error: not the same amount of files for 10, 20 and 60 m'
|
||||||
|
N = len(filenames10)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# initialise variables
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover_ts = []
|
||||||
|
acc_georef_ts = []
|
||||||
|
date_acquired_ts = []
|
||||||
|
filename_ts = []
|
||||||
|
satname_ts = []
|
||||||
|
timestamp = []
|
||||||
|
shorelines = []
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped = []
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
spacing = '=========================================================='
|
||||||
|
msg = ' %s\n %s\n %s' % (spacing, satname, spacing)
|
||||||
|
print(msg)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for i in range(N):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# read 10m bands
|
||||||
|
fn = os.path.join(filepath10, filenames10[i])
|
||||||
|
data = gdal.Open(fn, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
||||||
|
georef = np.array(data.GetGeoTransform())
|
||||||
|
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
||||||
|
im10 = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
||||||
|
im10 = im10/10000 # TOA scaled to 10000
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if image is only zeros, skip it
|
||||||
|
if sum(sum(sum(im10))) < 1:
|
||||||
|
print('skip ' + str(i) + ' - no data')
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped.append(i)
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
nrows = im10.shape[0]
|
||||||
|
ncols = im10.shape[1]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# read 20m band (SWIR1)
|
||||||
|
fn = os.path.join(filepath20, filenames20[i])
|
||||||
|
data = gdal.Open(fn, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
||||||
|
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
||||||
|
im20 = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
||||||
|
im20 = im20[:,:,0]
|
||||||
|
im20 = im20/10000 # TOA scaled to 10000
|
||||||
|
im_swir = transform.resize(im20, (nrows, ncols), order=1, preserve_range=True, mode='constant')
|
||||||
|
im_swir = np.expand_dims(im_swir, axis=2)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# append down-sampled swir band to the 10m bands
|
||||||
|
im_ms = np.append(im10, im_swir, axis=2)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# read 60m band (QA)
|
||||||
|
fn = os.path.join(filepath60, filenames60[i])
|
||||||
|
data = gdal.Open(fn, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
||||||
|
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
||||||
|
im60 = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
||||||
|
im_qa = im60[:,:,0]
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = sds.create_cloud_mask(im_qa, satname, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = transform.resize(cloud_mask,(nrows, ncols), order=0, preserve_range=True, mode='constant')
|
||||||
|
# check if -inf or nan values on any band and add to cloud mask
|
||||||
|
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
|
||||||
|
im_inf = np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k], -np.inf)
|
||||||
|
im_nan = np.isnan(im_ms[:,:,k])
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(cloud_mask, im_inf), im_nan)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# calculate cloud cover and if above threshold, skip it
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover = sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int)))/(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1])
|
||||||
|
if cloud_cover > cloud_thresh:
|
||||||
|
print('skip ' + str(i) + ' - cloudy (' + str(np.round(cloud_cover*100).astype(int)) + '%)')
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped.append(i)
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# rescale image intensity for display purposes
|
||||||
|
im_display = sds.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9, False)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
|
||||||
|
im_classif, im_labels = sds.classify_image_NN_nopan(im_ms, cloud_mask, min_beach_size, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if there aren't any sandy pixels
|
||||||
|
if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) == 0 :
|
||||||
|
# use global threshold
|
||||||
|
im_ndwi = sds.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
contours = sds.find_wl_contours(im_ndwi, cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
# use specific threhsold
|
||||||
|
contours_wi, contours_mwi = sds.find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels, cloud_mask, buffer_size, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# convert from pixels to world coordinates
|
||||||
|
wl_coords = sds.convert_pix2world(contours_mwi, georef)
|
||||||
|
# convert to output epsg spatial reference
|
||||||
|
wl = sds.convert_epsg(wl_coords, input_epsg, output_epsg)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# remove contour lines that have a perimeter < min_length_wl
|
||||||
|
wl_good = []
|
||||||
|
for l, wls in enumerate(wl):
|
||||||
|
coords = [(wls[k,0], wls[k,1]) for k in range(len(wls))]
|
||||||
|
a = LineString(coords) # shapely LineString structure
|
||||||
|
if a.length >= min_length_wl:
|
||||||
|
wl_good.append(wls)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# format points and only select the ones close to the refpoints
|
||||||
|
x_points = np.array([])
|
||||||
|
y_points = np.array([])
|
||||||
|
for k in range(len(wl_good)):
|
||||||
|
x_points = np.append(x_points,wl_good[k][:,0])
|
||||||
|
y_points = np.append(y_points,wl_good[k][:,1])
|
||||||
|
wl_good = np.transpose(np.array([x_points,y_points]))
|
||||||
|
temp = np.zeros((len(wl_good))).astype(bool)
|
||||||
|
for k in range(len(refpoints)):
|
||||||
|
temp = np.logical_or(np.linalg.norm(wl_good - refpoints[k,[0,1]], axis=1) < dist_ref, temp)
|
||||||
|
wl_final = wl_good[temp]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# plot output
|
||||||
|
plt.figure()
|
||||||
|
im = np.copy(im_display)
|
||||||
|
colours = np.array([[1,128/255,0/255],[204/255,1,1],[0,0,204/255]])
|
||||||
|
for k in range(0,im_labels.shape[2]):
|
||||||
|
im[im_labels[:,:,k],0] = colours[k,0]
|
||||||
|
im[im_labels[:,:,k],1] = colours[k,1]
|
||||||
|
im[im_labels[:,:,k],2] = colours[k,2]
|
||||||
|
plt.imshow(im)
|
||||||
|
for k,contour in enumerate(contours_mwi): plt.plot(contour[:, 1], contour[:, 0], linewidth=2, color='k', linestyle='--')
|
||||||
|
plt.title(satname + ' ' + metadata[satname]['dates'][i].strftime('%Y-%m-%d') + ' acc : ' + str(metadata[satname]['acc_georef'][i]) + ' m' )
|
||||||
|
plt.draw()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
pt_in = np.array(ginput(n=1, timeout=1000))
|
||||||
|
plt.close()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if image is rejected, skip it
|
||||||
|
if pt_in[0][1] > nrows/2:
|
||||||
|
print('skip ' + str(i) + ' - rejected')
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped.append(i)
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if accepted, store the data
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover_ts.append(cloud_cover)
|
||||||
|
acc_georef_ts.append(metadata[satname]['acc_georef'][i])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
filename_ts.append(filenames10[i])
|
||||||
|
satname_ts.append(satname)
|
||||||
|
date_acquired_ts.append(filenames10[i][:10])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
timestamp.append(metadata[satname]['dates'][i])
|
||||||
|
shorelines.append(wl_final)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# store in output structure
|
||||||
|
output[satname] = {'dates':timestamp, 'shorelines':shorelines, 'idx_skipped':idx_skipped,
|
||||||
|
'metadata':{'filenames':filename_ts, 'satname':satname_ts, 'cloud_cover':cloud_cover_ts,
|
||||||
|
'acc_georef':acc_georef_ts}}
|
||||||
|
del idx_skipped
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#%%
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Read L7&L8 images
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
satname = 'L8'
|
||||||
|
dates = metadata[satname]['dates']
|
||||||
|
input_epsg = 32656 # metadata[satname]['epsg']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# path to images
|
||||||
|
filepath_pan = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename, 'L7&L8', 'pan')
|
||||||
|
filepath_ms = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename, 'L7&L8', 'ms')
|
||||||
|
filenames_pan = os.listdir(filepath_pan)
|
||||||
|
filenames_ms = os.listdir(filepath_ms)
|
||||||
|
if (not len(filenames_pan) == len(filenames_ms)):
|
||||||
|
raise 'error: not the same amount of files for pan and ms'
|
||||||
|
N = len(filenames_pan)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# initialise variables
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover_ts = []
|
||||||
|
acc_georef_ts = []
|
||||||
|
date_acquired_ts = []
|
||||||
|
filename_ts = []
|
||||||
|
satname_ts = []
|
||||||
|
timestamp = []
|
||||||
|
shorelines = []
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped = []
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
spacing = '=========================================================='
|
||||||
|
msg = ' %s\n %s\n %s' % (spacing, satname, spacing)
|
||||||
|
print(msg)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for i in range(N):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# get satellite name
|
||||||
|
sat = filenames_pan[i][20:22]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# read pan image
|
||||||
|
fn_pan = os.path.join(filepath_pan, filenames_pan[i])
|
||||||
|
data = gdal.Open(fn_pan, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
||||||
|
georef = np.array(data.GetGeoTransform())
|
||||||
|
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
||||||
|
im_pan = np.stack(bands, 2)[:,:,0]
|
||||||
|
nrows = im_pan.shape[0]
|
||||||
|
ncols = im_pan.shape[1]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# read ms image
|
||||||
|
fn_ms = os.path.join(filepath_ms, filenames_ms[i])
|
||||||
|
data = gdal.Open(fn_ms, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
||||||
|
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
||||||
|
im_ms = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# cloud mask
|
||||||
|
im_qa = im_ms[:,:,5]
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = sds.create_cloud_mask(im_qa, sat, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = transform.resize(cloud_mask, (nrows, ncols), order=0, preserve_range=True, mode='constant').astype('bool_')
|
||||||
|
# resize the image using bilinear interpolation (order 1)
|
||||||
|
im_ms = im_ms[:,:,:5]
|
||||||
|
im_ms = transform.resize(im_ms,(nrows, ncols), order=1, preserve_range=True, mode='constant')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# check if -inf or nan values on any band and add to cloud mask
|
||||||
|
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]+1):
|
||||||
|
if k == 5:
|
||||||
|
im_inf = np.isin(im_pan, -np.inf)
|
||||||
|
im_nan = np.isnan(im_pan)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
im_inf = np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k], -np.inf)
|
||||||
|
im_nan = np.isnan(im_ms[:,:,k])
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(cloud_mask, im_inf), im_nan)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# calculate cloud cover and skip image if above threshold
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover = sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int)))/(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1])
|
||||||
|
if cloud_cover > cloud_thresh:
|
||||||
|
print('skip ' + str(i) + ' - cloudy (' + str(np.round(cloud_cover*100).astype(int)) + '%)')
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped.append(i)
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Pansharpen image (different for L8 and L7)
|
||||||
|
if sat == 'L7':
|
||||||
|
# pansharpen (Green, Red, NIR) and downsample Blue and SWIR1
|
||||||
|
im_ms_ps = sds.pansharpen(im_ms[:,:,[1,2,3]], im_pan, cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
im_ms_ps = np.append(im_ms[:,:,[0]], im_ms_ps, axis=2)
|
||||||
|
im_ms_ps = np.append(im_ms_ps, im_ms[:,:,[4]], axis=2)
|
||||||
|
im_display = sds.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9, False)
|
||||||
|
elif sat == 'L8':
|
||||||
|
# pansharpen RGB image and downsample NIR and SWIR1
|
||||||
|
im_ms_ps = sds.pansharpen(im_ms[:,:,[0,1,2]], im_pan, cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
im_ms_ps = np.append(im_ms_ps, im_ms[:,:,[3,4]], axis=2)
|
||||||
|
im_display = sds.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms_ps[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9, False)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
|
||||||
|
im_classif, im_labels = sds.classify_image_NN(im_ms_ps, im_pan, cloud_mask, min_beach_size, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if there aren't any sandy pixels
|
||||||
|
if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) == 0 :
|
||||||
|
# use global threshold
|
||||||
|
im_ndwi = sds.nd_index(im_ms_ps[:,:,4], im_ms_ps[:,:,1], cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
contours = sds.find_wl_contours(im_ndwi, cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
# use specific threhsold
|
||||||
|
contours_wi, contours_mwi = sds.find_wl_contours2(im_ms_ps, im_labels, cloud_mask, buffer_size, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# convert from pixels to world coordinates
|
||||||
|
wl_coords = sds.convert_pix2world(contours_mwi, georef)
|
||||||
|
# convert to output epsg spatial reference
|
||||||
|
wl = sds.convert_epsg(wl_coords, input_epsg, output_epsg)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# remove contour lines that have a perimeter < min_length_wl
|
||||||
|
wl_good = []
|
||||||
|
for l, wls in enumerate(wl):
|
||||||
|
coords = [(wls[k,0], wls[k,1]) for k in range(len(wls))]
|
||||||
|
a = LineString(coords) # shapely LineString structure
|
||||||
|
if a.length >= min_length_wl:
|
||||||
|
wl_good.append(wls)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# format points and only select the ones close to the refpoints
|
||||||
|
x_points = np.array([])
|
||||||
|
y_points = np.array([])
|
||||||
|
for k in range(len(wl_good)):
|
||||||
|
x_points = np.append(x_points,wl_good[k][:,0])
|
||||||
|
y_points = np.append(y_points,wl_good[k][:,1])
|
||||||
|
wl_good = np.transpose(np.array([x_points,y_points]))
|
||||||
|
temp = np.zeros((len(wl_good))).astype(bool)
|
||||||
|
for k in range(len(refpoints)):
|
||||||
|
temp = np.logical_or(np.linalg.norm(wl_good - refpoints[k,[0,1]], axis=1) < dist_ref, temp)
|
||||||
|
wl_final = wl_good[temp]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# plot output
|
||||||
|
plt.figure()
|
||||||
|
plt.subplot(121)
|
||||||
|
im = np.copy(im_display)
|
||||||
|
colours = np.array([[1,128/255,0/255],[204/255,1,1],[0,0,204/255]])
|
||||||
|
for k in range(0,im_labels.shape[2]):
|
||||||
|
im[im_labels[:,:,k],0] = colours[k,0]
|
||||||
|
im[im_labels[:,:,k],1] = colours[k,1]
|
||||||
|
im[im_labels[:,:,k],2] = colours[k,2]
|
||||||
|
plt.imshow(im)
|
||||||
|
for k,contour in enumerate(contours_mwi): plt.plot(contour[:, 1], contour[:, 0], linewidth=2, color='k', linestyle='--')
|
||||||
|
plt.title(sat + ' ' + metadata[satname]['dates'][i].strftime('%Y-%m-%d') + ' acc : ' + str(metadata[satname]['acc_georef'][i]) + ' m' )
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
pt_in = np.array(ginput(n=1, timeout=1000))
|
||||||
|
plt.close()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if image is rejected, skip it
|
||||||
|
if pt_in[0][1] > nrows/2:
|
||||||
|
print('skip ' + str(i) + ' - rejected')
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped.append(i)
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if accepted, store the data
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover_ts.append(cloud_cover)
|
||||||
|
acc_georef_ts.append(metadata[satname]['acc_georef'][i])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
filename_ts.append(filenames_pan[i])
|
||||||
|
satname_ts.append(sat)
|
||||||
|
date_acquired_ts.append(filenames_pan[i][:10])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
timestamp.append(metadata[satname]['dates'][i])
|
||||||
|
shorelines.append(wl_final)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# store in output structure
|
||||||
|
output[satname] = {'dates':timestamp, 'shorelines':shorelines, 'idx_skipped':idx_skipped,
|
||||||
|
'metadata':{'filenames':filename_ts, 'satname':satname_ts, 'cloud_cover':cloud_cover_ts,
|
||||||
|
'acc_georef':acc_georef_ts}}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
del idx_skipped
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#%%
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Read L5 images
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
satname = 'L5'
|
||||||
|
dates = metadata[satname]['dates']
|
||||||
|
input_epsg = 32656 # metadata[satname]['epsg']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# path to images
|
||||||
|
filepath_img = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', sitename, satname, '30m')
|
||||||
|
filenames = os.listdir(filepath_img)
|
||||||
|
N = len(filenames)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# initialise variables
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover_ts = []
|
||||||
|
acc_georef_ts = []
|
||||||
|
date_acquired_ts = []
|
||||||
|
filename_ts = []
|
||||||
|
satname_ts = []
|
||||||
|
timestamp = []
|
||||||
|
shorelines = []
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped = []
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
spacing = '=========================================================='
|
||||||
|
msg = ' %s\n %s\n %s' % (spacing, satname, spacing)
|
||||||
|
print(msg)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for i in range(N):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# read ms image
|
||||||
|
fn = os.path.join(filepath_img, filenames[i])
|
||||||
|
data = gdal.Open(fn, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
|
||||||
|
georef = np.array(data.GetGeoTransform())
|
||||||
|
bands = [data.GetRasterBand(k + 1).ReadAsArray() for k in range(data.RasterCount)]
|
||||||
|
im_ms = np.stack(bands, 2)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# down-sample to half hte original pixel size
|
||||||
|
nrows = im_ms.shape[0]*2
|
||||||
|
ncols = im_ms.shape[1]*2
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# cloud mask
|
||||||
|
im_qa = im_ms[:,:,5]
|
||||||
|
im_ms = im_ms[:,:,:-1]
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = sds.create_cloud_mask(im_qa, satname, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = transform.resize(cloud_mask, (nrows, ncols), order=0, preserve_range=True, mode='constant').astype('bool_')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# resize the image using bilinear interpolation (order 1)
|
||||||
|
im_ms = transform.resize(im_ms,(nrows, ncols), order=1, preserve_range=True, mode='constant')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# adjust georef vector (scale becomes 15m and origin is adjusted to the center of new corner pixel)
|
||||||
|
georef[1] = 15
|
||||||
|
georef[5] = -15
|
||||||
|
georef[0] = georef[0] + 7.5
|
||||||
|
georef[3] = georef[3] - 7.5
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# check if -inf or nan values on any band and add to cloud mask
|
||||||
|
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
|
||||||
|
im_inf = np.isin(im_ms[:,:,k], -np.inf)
|
||||||
|
im_nan = np.isnan(im_ms[:,:,k])
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(cloud_mask, im_inf), im_nan)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# calculate cloud cover and skip image if above threshold
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover = sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int)))/(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1])
|
||||||
|
if cloud_cover > cloud_thresh:
|
||||||
|
print('skip ' + str(i) + ' - cloudy (' + str(np.round(cloud_cover*100).astype(int)) + '%)')
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped.append(i)
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# rescale image intensity for display purposes
|
||||||
|
im_display = sds.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9, False)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
|
||||||
|
im_classif, im_labels = sds.classify_image_NN_nopan(im_ms, cloud_mask, min_beach_size, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if there aren't any sandy pixels
|
||||||
|
if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) == 0 :
|
||||||
|
# use global threshold
|
||||||
|
im_ndwi = sds.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
contours = sds.find_wl_contours(im_ndwi, cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
# use specific threhsold
|
||||||
|
contours_wi, contours_mwi = sds.find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels, cloud_mask, buffer_size, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# convert from pixels to world coordinates
|
||||||
|
wl_coords = sds.convert_pix2world(contours_mwi, georef)
|
||||||
|
# convert to output epsg spatial reference
|
||||||
|
wl = sds.convert_epsg(wl_coords, input_epsg, output_epsg)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# remove contour lines that have a perimeter < min_length_wl
|
||||||
|
wl_good = []
|
||||||
|
for l, wls in enumerate(wl):
|
||||||
|
coords = [(wls[k,0], wls[k,1]) for k in range(len(wls))]
|
||||||
|
a = LineString(coords) # shapely LineString structure
|
||||||
|
if a.length >= min_length_wl:
|
||||||
|
wl_good.append(wls)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# format points and only select the ones close to the refpoints
|
||||||
|
x_points = np.array([])
|
||||||
|
y_points = np.array([])
|
||||||
|
for k in range(len(wl_good)):
|
||||||
|
x_points = np.append(x_points,wl_good[k][:,0])
|
||||||
|
y_points = np.append(y_points,wl_good[k][:,1])
|
||||||
|
wl_good = np.transpose(np.array([x_points,y_points]))
|
||||||
|
temp = np.zeros((len(wl_good))).astype(bool)
|
||||||
|
for k in range(len(refpoints)):
|
||||||
|
temp = np.logical_or(np.linalg.norm(wl_good - refpoints[k,[0,1]], axis=1) < dist_ref, temp)
|
||||||
|
wl_final = wl_good[temp]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# plot output
|
||||||
|
plt.figure()
|
||||||
|
plt.subplot(121)
|
||||||
|
im = np.copy(im_display)
|
||||||
|
colours = np.array([[1,128/255,0/255],[204/255,1,1],[0,0,204/255]])
|
||||||
|
for k in range(0,im_labels.shape[2]):
|
||||||
|
im[im_labels[:,:,k],0] = colours[k,0]
|
||||||
|
im[im_labels[:,:,k],1] = colours[k,1]
|
||||||
|
im[im_labels[:,:,k],2] = colours[k,2]
|
||||||
|
plt.imshow(im)
|
||||||
|
for k,contour in enumerate(contours_mwi): plt.plot(contour[:, 1], contour[:, 0], linewidth=2, color='k', linestyle='--')
|
||||||
|
plt.title(satname + ' ' + metadata[satname]['dates'][i].strftime('%Y-%m-%d') + ' acc : ' + str(metadata[satname]['acc_georef'][i]) + ' m' )
|
||||||
|
plt.subplot(122)
|
||||||
|
plt.axis('equal')
|
||||||
|
plt.axis('off')
|
||||||
|
plt.plot(refpoints[:,0], refpoints[:,1], 'k.')
|
||||||
|
plt.plot(wl_final[:,0], wl_final[:,1], 'r.')
|
||||||
|
mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
|
||||||
|
mng.window.showMaximized()
|
||||||
|
plt.tight_layout()
|
||||||
|
plt.draw()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
pt_in = np.array(ginput(n=1, timeout=1000))
|
||||||
|
plt.close()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if image is rejected, skip it
|
||||||
|
if pt_in[0][1] > nrows/2:
|
||||||
|
print('skip ' + str(i) + ' - rejected')
|
||||||
|
idx_skipped.append(i)
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# if accepted, store the data
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover_ts.append(cloud_cover)
|
||||||
|
acc_georef_ts.append(metadata[satname]['acc_georef'][i])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
filename_ts.append(filenames[i])
|
||||||
|
satname_ts.append(satname)
|
||||||
|
date_acquired_ts.append(filenames[i][:10])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
timestamp.append(metadata[satname]['dates'][i])
|
||||||
|
shorelines.append(wl_final)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# store in output structure
|
||||||
|
output[satname] = {'dates':timestamp, 'shorelines':shorelines, 'idx_skipped':idx_skipped,
|
||||||
|
'metadata':{'filenames':filename_ts, 'satname':satname_ts, 'cloud_cover':cloud_cover_ts,
|
||||||
|
'acc_georef':acc_georef_ts}}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
del idx_skipped
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#%%
|
||||||
|
# save output
|
||||||
|
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_output' + '.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
|
||||||
|
pickle.dump(output, f)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# save idx_skipped
|
||||||
|
#idx_skipped = dict([])
|
||||||
|
#for satname in list(output.keys()):
|
||||||
|
# idx_skipped[satname] = output[satname]['idx_skipped']
|
||||||
|
#with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_idxskipped' + '.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
|
||||||
|
# pickle.dump(idx_skipped, f)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
|||||||
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
# Extract shorelines from Landsat images
|
||||||
|
#==========================================================#
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Initial settings
|
||||||
|
import ee
|
||||||
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||||
|
import matplotlib.cm as cm
|
||||||
|
import numpy as np
|
||||||
|
import pandas as pd
|
||||||
|
from datetime import datetime
|
||||||
|
import pickle
|
||||||
|
import pdb
|
||||||
|
import pytz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# image processing modules
|
||||||
|
import skimage.filters as filters
|
||||||
|
import skimage.exposure as exposure
|
||||||
|
import skimage.transform as transform
|
||||||
|
import sklearn.decomposition as decomposition
|
||||||
|
import skimage.morphology as morphology
|
||||||
|
import skimage.measure as measure
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# my modules
|
||||||
|
import functions.utils as utils
|
||||||
|
import functions.sds as sds
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# some settings
|
||||||
|
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
|
||||||
|
plt.rcParams['axes.grid'] = False
|
||||||
|
plt.rcParams['figure.max_open_warning'] = 100
|
||||||
|
ee.Initialize()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# parameters
|
||||||
|
cloud_thresh = 0.5 # threshold for cloud cover
|
||||||
|
plot_bool = True # if you want the plots
|
||||||
|
min_contour_points = 100# minimum number of points contained in each water line
|
||||||
|
output_epsg = 28356 # GDA94 / MGA Zone 56
|
||||||
|
buffer_size = 10 # radius of disk for buffer (sand classif parameter)
|
||||||
|
min_beach_size = 50 # number of pixels in a beach (sand classif parameter)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# select collection
|
||||||
|
satname = 'L8'
|
||||||
|
input_col = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LC08/C01/T1_RT_TOA') # Landsat 8 Tier 1 TOA
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# location (Narrabeen-Collaroy beach)
|
||||||
|
polygon = [[[151.3473129272461,-33.69035274454718],
|
||||||
|
[151.2820816040039,-33.68206818063878],
|
||||||
|
[151.27281188964844,-33.74775138989556],
|
||||||
|
[151.3425064086914,-33.75231878701767],
|
||||||
|
[151.3473129272461,-33.69035274454718]]];
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# dates
|
||||||
|
start_date = '2013-01-01'
|
||||||
|
end_date = '2018-12-31'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# filter by location and date
|
||||||
|
flt_col = input_col.filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Polygon(polygon)).filterDate(start_date, end_date)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
n_img = flt_col.size().getInfo()
|
||||||
|
print('Number of images covering the polygon:', n_img)
|
||||||
|
im_all = flt_col.getInfo().get('features')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
i = 0 # first image
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# find image in ee database
|
||||||
|
im = ee.Image(im_all[i].get('id'))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# load image as np.array
|
||||||
|
im_pan, im_ms, cloud_mask, crs, meta = sds.read_eeimage(im, polygon, satname, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# mask -inf or nan values on the image and add to cloud_mask
|
||||||
|
im_inf = np.isin(im_ms[:,:,0], -np.inf)
|
||||||
|
im_nan = np.isnan(im_ms[:,:,0])
|
||||||
|
cloud_mask = np.logical_or(np.logical_or(cloud_mask, im_inf), im_nan)
|
||||||
|
cloud_cover = sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int)))/(cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1])
|
||||||
|
print('Cloud cover : ' + str(int(round(100*cloud_cover))) + ' %')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# pansharpen rgb image
|
||||||
|
im_ms_ps = sds.pansharpen(im_ms[:,:,[0,1,2]], im_pan, cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# add down-sized bands for NIR and SWIR (since pansharpening is not possible)
|
||||||
|
im_ms_ps = np.append(im_ms_ps, im_ms[:,:,[3,4]], axis=2)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# calculate NDWI
|
||||||
|
im_ndwi = sds.nd_index(im_ms_ps[:,:,3], im_ms_ps[:,:,1], cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# edge detection
|
||||||
|
wl_pix = sds.find_wl_contours(im_ndwi, cloud_mask, min_contour_points, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
plt.figure()
|
||||||
|
plt.imshow(im_ms_ps[:,:,[2,1,0]])
|
||||||
|
for i,contour in enumerate(wl_pix): plt.plot(contour[:, 1], contour[:, 0], linewidth=2)
|
||||||
|
plt.axis('image')
|
||||||
|
plt.title('Detected water lines')
|
||||||
|
plt.show()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# convert from pixels to world coordinates
|
||||||
|
wl_coords = sds.convert_pix2world(wl_pix, crs['crs_15m'])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# convert to output epsg spatial reference
|
||||||
|
wl = sds.convert_epsg(wl_coords, crs['epsg_code'], output_epsg)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# classify sand pixels with Kmeans
|
||||||
|
#im_sand = sds.classify_sand_unsupervised(im_ms_ps, im_pan, cloud_mask, wl_pix, buffer_size, min_beach_size, plot_bool)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
|
||||||
|
im_classif = sds.classify_image_NN(im_ms_ps, im_pan, cloud_mask, plot_bool)
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue