diff --git a/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.md b/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b69d4e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+---
+name: Bug report
+about: Create a report to help us improve
+title: ''
+labels: bug
+assignees: ''
+
+---
+
+**Describe the bug**
+A clear and concise description of what the bug is.
+
+**To Reproduce**
+Steps to reproduce the behavior (you can also attach your script):
+1. Go to '...'
+2. Click on '....'
+3. Scroll down to '....'
+4. See error
+
+**Expected behavior**
+A clear and concise description of what you expected to happen.
+
+**Screenshots**
+If applicable, add screenshots to help explain your problem.
+
+**Desktop (please complete the following information):**
+ - OS: [e.g. iOS]
+ - CoastSat Version [e.g. 22]
+
+**Additional context**
+Add any other context about the problem here.
diff --git a/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.md b/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..11fc491
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.md
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+---
+name: Feature request
+about: Suggest an idea for this project
+title: ''
+labels: enhancement
+assignees: ''
+
+---
+
+**Is your feature request related to a problem? Please describe.**
+A clear and concise description of what the problem is. Ex. I'm always frustrated when [...]
+
+**Describe the solution you'd like**
+A clear and concise description of what you want to happen.
+
+**Describe alternatives you've considered**
+A clear and concise description of any alternative solutions or features you've considered.
+
+**Additional context**
+Add any other context or screenshots about the feature request here.
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 965ba9d..3d30c79 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,5 +1,8 @@
# CoastSat
+[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3560436)
+[](https://gitter.im/CoastSat/community)
+
CoastSat is an open-source software toolkit written in Python that enables users to obtain time-series of shoreline position at any coastline worldwide from 30+ years (and growing) of publicly available satellite imagery.

@@ -49,7 +52,9 @@ To confirm that you have successfully activated CoastSat, your terminal command
### 1.2 Activate Google Earth Engine Python API
-With the `coastsat` environment activated, run the following command on the Anaconda Prompt to link your environment to the GEE server:
+First, you need to request access to Google Earth Engine at https://signup.earthengine.google.com/. It takes about 1 day for Google to approve requests.
+
+Once your request has been approved, with the `coastsat` environment activated, run the following command on the Anaconda Prompt to link your environment to the GEE server:
```
earthengine authenticate
@@ -124,20 +129,22 @@ Once all the shorelines have been mapped, the output is available in two differe
The figure below shows how the satellite-derived shorelines can be opened in a GIS software (QGIS) using the `.geojson` output. Note that the coordinates in the `.geojson` file are in the spatial reference system defined by the `output_epsg`.
-
+
+  +
+
#### Reference shoreline
Before running the batch shoreline detection, there is the option to manually digitize a reference shoreline on one cloud-free image. This reference shoreline helps to reject outliers and false detections when mapping shorelines as it only considers as valid shorelines the points that are within a defined distance from this reference shoreline.
- The user can manually digitize a reference shoreline on one of the images by calling:
+ The user can manually digitize one or several reference shorelines on one of the images by calling:
```
settings['reference_shoreline'] = SDS_preprocess.get_reference_sl_manual(metadata, settings)
settings['max_dist_ref'] = 100 # max distance (in meters) allowed from the reference shoreline
```
-This function allows the user to click points along the shoreline on one of the satellite images, as shown in the animation below.
+This function allows the user to click points along the shoreline on cloud-free satellite images, as shown in the animation below.
-
+
The maximum distance (in metres) allowed from the reference shoreline is defined by the parameter `max_dist_ref`. This parameter is set to a default value of 100 m. If you think that 100 m buffer from the reference shoreline will not capture the shoreline variability at your site, increase the value of this parameter. This may be the case for large nourishments or eroding/accreting coastlines.
@@ -150,6 +157,9 @@ As mentioned above, there are some additional parameters that can be modified to
- `cloud_mask_issue`: the cloud mask algorithm applied to Landsat images by USGS, namely CFMASK, does have difficulties sometimes with very bright features such as beaches or white-water in the ocean. This may result in pixels corresponding to a beach being identified as clouds and appear as masked pixels on your images. If this issue seems to be present in a large proportion of images from your local beach, you can switch this parameter to `True` and CoastSat will remove from the cloud mask the pixels that form very thin linear features, as often these are beaches and not clouds. Only activate this parameter if you observe this very specific cloud mask issue, otherwise leave to the default value of `False`.
- `sand_color`: this parameter can take 3 values: `default`, `dark` or `bright`. Only change this parameter if you are seing that with the `default` the sand pixels are not being classified as sand (in orange). If your beach has dark sand (grey/black sand beaches), you can set this parameter to `dark` and the classifier will be able to pick up the dark sand. On the other hand, if your beach has white sand and the `default` classifier is not picking it up, switch this parameter to `bright`. At this stage this option is only available for Landsat images (soon for Sentinel-2 as well).
+#### Re-training the classifier
+CoastSat's shoreline mapping alogorithm uses an image classification scheme to label each pixel into 4 classes: sand, water, white-water and other land features. While this classifier has been trained using a wide range of different beaches, it may be that it does not perform very well at specific sites that it has never seen before. You can train a new classifier with site-specific training data in a few minutes by following the Jupyter notebook in [re-train CoastSat classifier](https://github.com/kvos/CoastSat/blob/master/classification/train_new_classifier.md).
+
### 2.3 Shoreline change analysis
This section shows how to obtain time-series of shoreline change along shore-normal transects. Each transect is defined by two points, its origin and a second point that defines its length and orientation. There are 3 options to define the coordinates of the transects:
diff --git a/classification/models/NN_4classes_Landsat.pkl b/classification/models/NN_4classes_Landsat.pkl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..767fc51
Binary files /dev/null and b/classification/models/NN_4classes_Landsat.pkl differ
diff --git a/classification/models/NN_4classes_Landsat_bright.pkl b/classification/models/NN_4classes_Landsat_bright.pkl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..41d1e27
Binary files /dev/null and b/classification/models/NN_4classes_Landsat_bright.pkl differ
diff --git a/classification/models/NN_4classes_Landsat_dark.pkl b/classification/models/NN_4classes_Landsat_dark.pkl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7844794
Binary files /dev/null and b/classification/models/NN_4classes_Landsat_dark.pkl differ
diff --git a/classifiers/NN_4classes_S2.pkl b/classification/models/NN_4classes_S2.pkl
similarity index 100%
rename from classifiers/NN_4classes_S2.pkl
rename to classification/models/NN_4classes_S2.pkl
diff --git a/classification/train_new_classifier.ipynb b/classification/train_new_classifier.ipynb
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e58e26a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/train_new_classifier.ipynb
@@ -0,0 +1,436 @@
+{
+ "cells": [
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "# Train a new classifier for CoastSat\n",
+ "\n",
+ "In this notebook the CoastSat classifier is trained using satellite images from new sites. This can improve the accuracy of the shoreline detection if the users are experiencing issues with the default classifier."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "#### Initial settings"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {
+ "code_folding": [],
+ "run_control": {
+ "marked": false
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# load modules\n",
+ "%load_ext autoreload\n",
+ "%autoreload 2\n",
+ "import os, sys\n",
+ "import numpy as np\n",
+ "import pickle\n",
+ "import warnings\n",
+ "warnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\n",
+ "import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# sklearn modules\n",
+ "from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n",
+ "from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier\n",
+ "from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score\n",
+ "from sklearn.externals import joblib\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# coastsat modules\n",
+ "sys.path.insert(0, os.pardir)\n",
+ "from coastsat import SDS_download, SDS_preprocess, SDS_shoreline, SDS_tools, SDS_classify\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# plotting params\n",
+ "plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 14\n",
+ "plt.rcParams['xtick.labelsize'] = 12\n",
+ "plt.rcParams['ytick.labelsize'] = 12\n",
+ "plt.rcParams['axes.titlesize'] = 12\n",
+ "plt.rcParams['axes.labelsize'] = 12\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# filepaths \n",
+ "filepath_images = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data')\n",
+ "filepath_train = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'training_data')\n",
+ "filepath_models = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'models')\n",
+ "\n",
+ "# settings\n",
+ "settings ={'filepath_train':filepath_train, # folder where the labelled images will be stored\n",
+ " 'cloud_thresh':0.9, # percentage of cloudy pixels accepted on the image\n",
+ " 'cloud_mask_issue':True, # set to True if problems with the default cloud mask \n",
+ " 'inputs':{'filepath':filepath_images}, # folder where the images are stored\n",
+ " 'labels':{'sand':1,'white-water':2,'water':3,'other land features':4}, # labels for the classifier\n",
+ " 'colors':{'sand':[1, 0.65, 0],'white-water':[1,0,1],'water':[0.1,0.1,0.7],'other land features':[0.8,0.8,0.1]},\n",
+ " 'tolerance':0.01, # this is the pixel intensity tolerance, when using flood fill for sandy pixels\n",
+ " # set to 0 to select one pixel at a time\n",
+ " }\n",
+ " \n",
+ "# read kml files for the training sites\n",
+ "filepath_sites = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'training_sites')\n",
+ "train_sites = os.listdir(filepath_sites)\n",
+ "print('Sites for training:\\n%s\\n'%train_sites)"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "### 1. Download images\n",
+ "\n",
+ "For each site on which you want to train the classifier, save a .kml file with the region of interest (5 vertices clockwise, first and last points are the same, can be created from Google myMaps) in the folder *\\training_sites*.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "You only need a few images (~10) to train the classifier."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {
+ "code_folding": []
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# dowload images at the sites\n",
+ "dates = ['2019-01-01', '2019-07-01']\n",
+ "sat_list = 'L8'\n",
+ "for site in train_sites:\n",
+ " polygon = SDS_tools.polygon_from_kml(os.path.join(filepath_sites,site))\n",
+ " sitename = site[:site.find('.')] \n",
+ " inputs = {'polygon':polygon, 'dates':dates, 'sat_list':sat_list,\n",
+ " 'sitename':sitename, 'filepath':filepath_images}\n",
+ " print(sitename)\n",
+ " metadata = SDS_download.retrieve_images(inputs)"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "### 2. Label images\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Label the images into 4 classes: sand, white-water, water and other land features.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "The labelled images are saved in the *filepath_train* and can be visualised afterwards for quality control. If yo make a mistake, don't worry, this can be fixed later by deleting the labelled image."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {
+ "code_folding": [],
+ "run_control": {
+ "marked": true
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# label the images with an interactive annotator\n",
+ "%matplotlib qt\n",
+ "for site in train_sites:\n",
+ " settings['inputs']['sitename'] = site[:site.find('.')] \n",
+ " # load metadata\n",
+ " metadata = SDS_download.get_metadata(settings['inputs'])\n",
+ " # label images\n",
+ " SDS_classify.label_images(metadata,settings)"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "### 3. Train Classifier\n",
+ "\n",
+ "A Multilayer Perceptron is trained with *scikit-learn*. To train the classifier, the training data needs to be loaded.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "You can use the data that was labelled here and/or the original CoastSat training data."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# load labelled images\n",
+ "features = SDS_classify.load_labels(train_sites, settings)"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# you can also load the original CoastSat training data (and optionally merge it with your labelled data)\n",
+ "with open(os.path.join(settings['filepath_train'], 'CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl'), 'rb') as f:\n",
+ " features_original = pickle.load(f)\n",
+ "for key in features_original.keys():\n",
+ " print('%s : %d pixels'%(key,len(features_original[key])))"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "Run this section to combine the original training data with your labelled data:"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {
+ "code_folding": []
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# add the white-water data from the original training data\n",
+ "features['white-water'] = np.append(features['white-water'], features_original['white-water'], axis=0)\n",
+ "# or merge all the classes\n",
+ "# for key in features.keys():\n",
+ "# features[key] = np.append(features[key], features_original[key], axis=0)\n",
+ "# features = features_original \n",
+ "for key in features.keys():\n",
+ " print('%s : %d pixels'%(key,len(features[key])))"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "[OPTIONAL] As the classes do not have the same number of pixels, it is good practice to subsample the very large classes (in this case 'water' and 'other land features'):"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# subsample randomly the land and water classes\n",
+ "# as the most important class is 'sand', the number of samples should be close to the number of sand pixels\n",
+ "n_samples = 5000\n",
+ "for key in ['water', 'other land features']:\n",
+ " features[key] = features[key][np.random.choice(features[key].shape[0], n_samples, replace=False),:]\n",
+ "# print classes again\n",
+ "for key in features.keys():\n",
+ " print('%s : %d pixels'%(key,len(features[key])))"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "When the labelled data is ready, format it into X, a matrix of features, and y, a vector of labels:"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {
+ "code_folding": [],
+ "run_control": {
+ "marked": true
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# format into X (features) and y (labels) \n",
+ "classes = ['sand','white-water','water','other land features']\n",
+ "labels = [1,2,3,0]\n",
+ "X,y = SDS_classify.format_training_data(features, classes, labels)"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "Divide the dataset into train and test: train on 70% of the data and evaluate on the other 30%:"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {
+ "code_folding": [],
+ "run_control": {
+ "marked": true
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# divide in train and test and evaluate the classifier\n",
+ "X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, shuffle=True, random_state=0)\n",
+ "classifier = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(100,50), solver='adam')\n",
+ "classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)\n",
+ "print('Accuracy: %0.4f' % classifier.score(X_test,y_test))"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "[OPTIONAL] A more robust evaluation is 10-fold cross-validation (may take a few minutes to run):"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {
+ "code_folding": [],
+ "run_control": {
+ "marked": true
+ }
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# cross-validation\n",
+ "scores = cross_val_score(classifier, X, y, cv=10)\n",
+ "print('Accuracy: %0.4f (+/- %0.4f)' % (scores.mean(), scores.std() * 2))"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "Plot a confusion matrix:"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {
+ "code_folding": []
+ },
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# plot confusion matrix\n",
+ "%matplotlib inline\n",
+ "y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)\n",
+ "SDS_classify.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred,\n",
+ " classes=['other land features','sand','white-water','water'],\n",
+ " normalize=False);"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "When satisfied with the accuracy and confusion matrix, train the model using ALL the training data and save it:"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# train with all the data and save the final classifier\n",
+ "classifier = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(100,50), solver='adam')\n",
+ "classifier.fit(X,y)\n",
+ "joblib.dump(classifier, os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_test.pkl'))"
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "markdown",
+ "metadata": {},
+ "source": [
+ "### 4. Evaluate the classifier\n",
+ "\n",
+ "Load a classifier that you have trained (specify the classifiers filename) and evaluate it on the satellite images.\n",
+ "\n",
+ "This section will save the output of the classification for each site in a directory named \\evaluation."
+ ]
+ },
+ {
+ "cell_type": "code",
+ "execution_count": null,
+ "metadata": {},
+ "outputs": [],
+ "source": [
+ "# load and evaluate a classifier\n",
+ "%matplotlib qt\n",
+ "classifier = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_test.pkl'))\n",
+ "settings['output_epsg'] = 3857\n",
+ "settings['min_beach_area'] = 4500\n",
+ "settings['buffer_size'] = 200\n",
+ "settings['min_length_sl'] = 200\n",
+ "settings['cloud_thresh'] = 0.5\n",
+ "# visualise the classified images\n",
+ "for site in train_sites:\n",
+ " settings['inputs']['sitename'] = site[:site.find('.')] \n",
+ " # load metadata\n",
+ " metadata = SDS_download.get_metadata(settings['inputs'])\n",
+ " # plot the classified images\n",
+ " SDS_classify.evaluate_classifier(classifier,metadata,settings)"
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "metadata": {
+ "kernelspec": {
+ "display_name": "Python 3",
+ "language": "python",
+ "name": "python3"
+ },
+ "language_info": {
+ "codemirror_mode": {
+ "name": "ipython",
+ "version": 3
+ },
+ "file_extension": ".py",
+ "mimetype": "text/x-python",
+ "name": "python",
+ "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
+ "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
+ "version": "3.7.3"
+ },
+ "toc": {
+ "base_numbering": 1,
+ "nav_menu": {},
+ "number_sections": false,
+ "sideBar": true,
+ "skip_h1_title": false,
+ "title_cell": "Table of Contents",
+ "title_sidebar": "Contents",
+ "toc_cell": false,
+ "toc_position": {},
+ "toc_section_display": true,
+ "toc_window_display": false
+ },
+ "varInspector": {
+ "cols": {
+ "lenName": 16,
+ "lenType": 16,
+ "lenVar": 40
+ },
+ "kernels_config": {
+ "python": {
+ "delete_cmd_postfix": "",
+ "delete_cmd_prefix": "del ",
+ "library": "var_list.py",
+ "varRefreshCmd": "print(var_dic_list())"
+ },
+ "r": {
+ "delete_cmd_postfix": ") ",
+ "delete_cmd_prefix": "rm(",
+ "library": "var_list.r",
+ "varRefreshCmd": "cat(var_dic_list()) "
+ }
+ },
+ "types_to_exclude": [
+ "module",
+ "function",
+ "builtin_function_or_method",
+ "instance",
+ "_Feature"
+ ],
+ "window_display": false
+ }
+ },
+ "nbformat": 4,
+ "nbformat_minor": 2
+}
diff --git a/classification/train_new_classifier.md b/classification/train_new_classifier.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ec50e48
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/train_new_classifier.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+### Train a new CoastSat classifier
+
+CoastSat's shoreline mapping alogorithm uses an image classification scheme to label each pixel into 4 classes: sand, water, white-water and other land features. While this classifier has been trained using a wide range of different beaches, it may be that it does not perform very well at specific sites that it has never seen before.
+
+For this reason, we provide the possibility to re-train the classifier by adding labelled data from new sites. This can be done very quickly and easily by using this [Jupyter Notebook](https://github.com/kvos/CoastSat/blob/CoastSat-classifier/classification/train_new_classifier.ipynb).
+
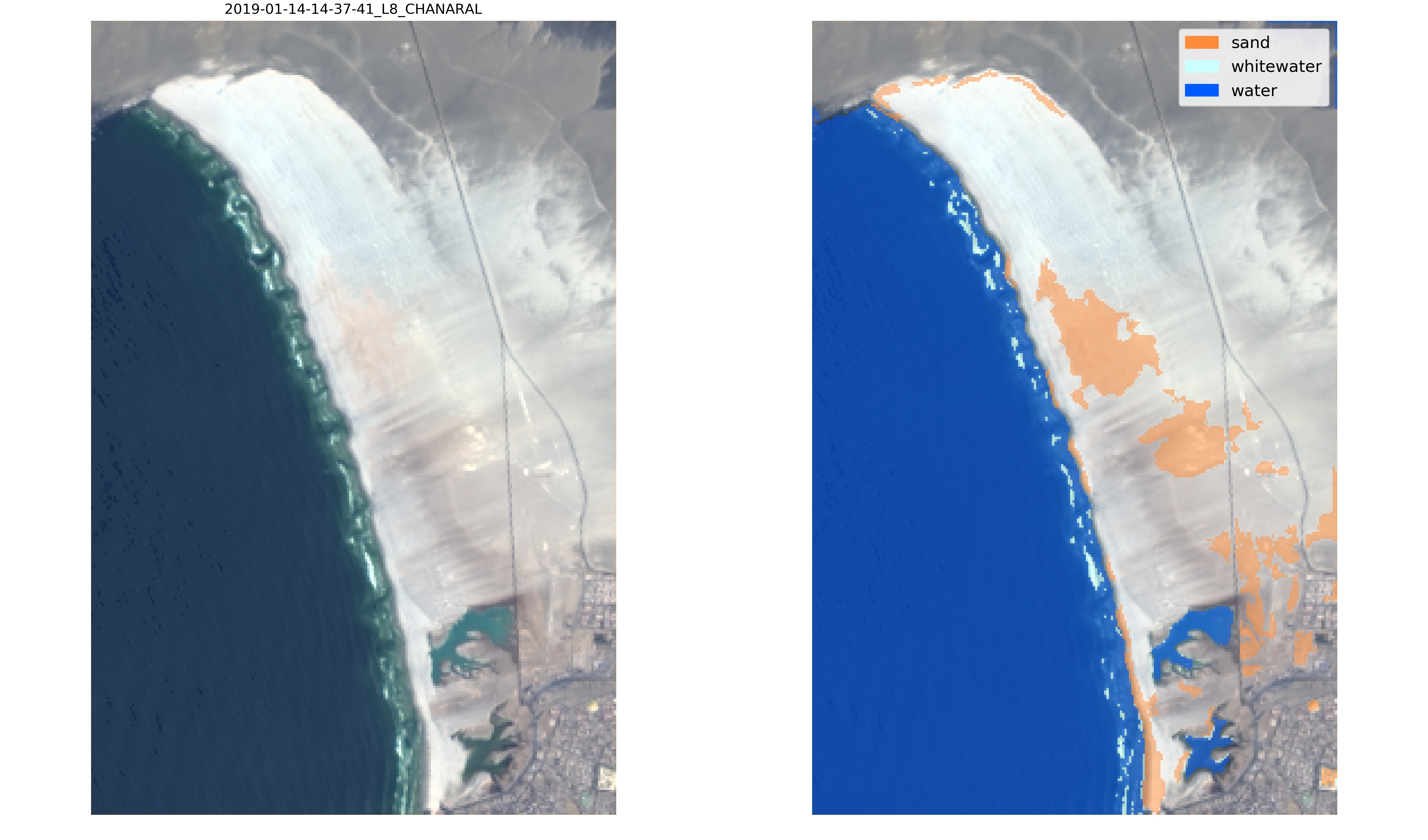
+Let's take this example, Playa Chañaral in the Atacama desert, Chile. At this beach, the sand is extremely white and the default classifier is not able to label correctly the sand pixels:
+
+
+
+To overcome this issue, we can generate training data for this site by labelling new images.
+Download the new images to be labelled and then call the function `SDS_classify.label_images(metadata,settings)`, an interactive tool will pop up for quick and efficient labelling:
+
+
+
+You only need to label sand pixels, as water and white-water looks the same everywhere in the world. You can label 2-3 images in a few minutes with the interactive tool and then the new labels can be used to re-train the classifier. The labelling tool uses *flood fill* to speed up the selection of sand pixels and you can tune the tolerance of the *flood fill* function in `settings['tolerance']`.
+
+You can then train a classifier with the newly labelled data.
+Different classification schemes exist, in this example we use a Multilayer Perceptron (Neural Network) with 2 layers, one of 100 neurons and one of 50 neurons. The training data is first divided in train and split, so that we can evaluate the accuracy of the classifier and plot a confusion matrix.
+```
+X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, shuffle=True, random_state=0)
+classifier = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(100,50), solver='adam')
+classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
+print('Accuracy: %0.4f' % classifier.score(X_test,y_test))
+y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
+label_names = ['other land features','sand','white-water','water']
+SDS_classify.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred,classes=label_names,normalize=False);
+```
+
+ +
+Finally, the new classifier can be applied to the satellite images, for visual inspection by calling the function `SDS_classify.evaluate_classifier(classifier,metadata,settings)` which will save the classified images in */evaluation*:
+
+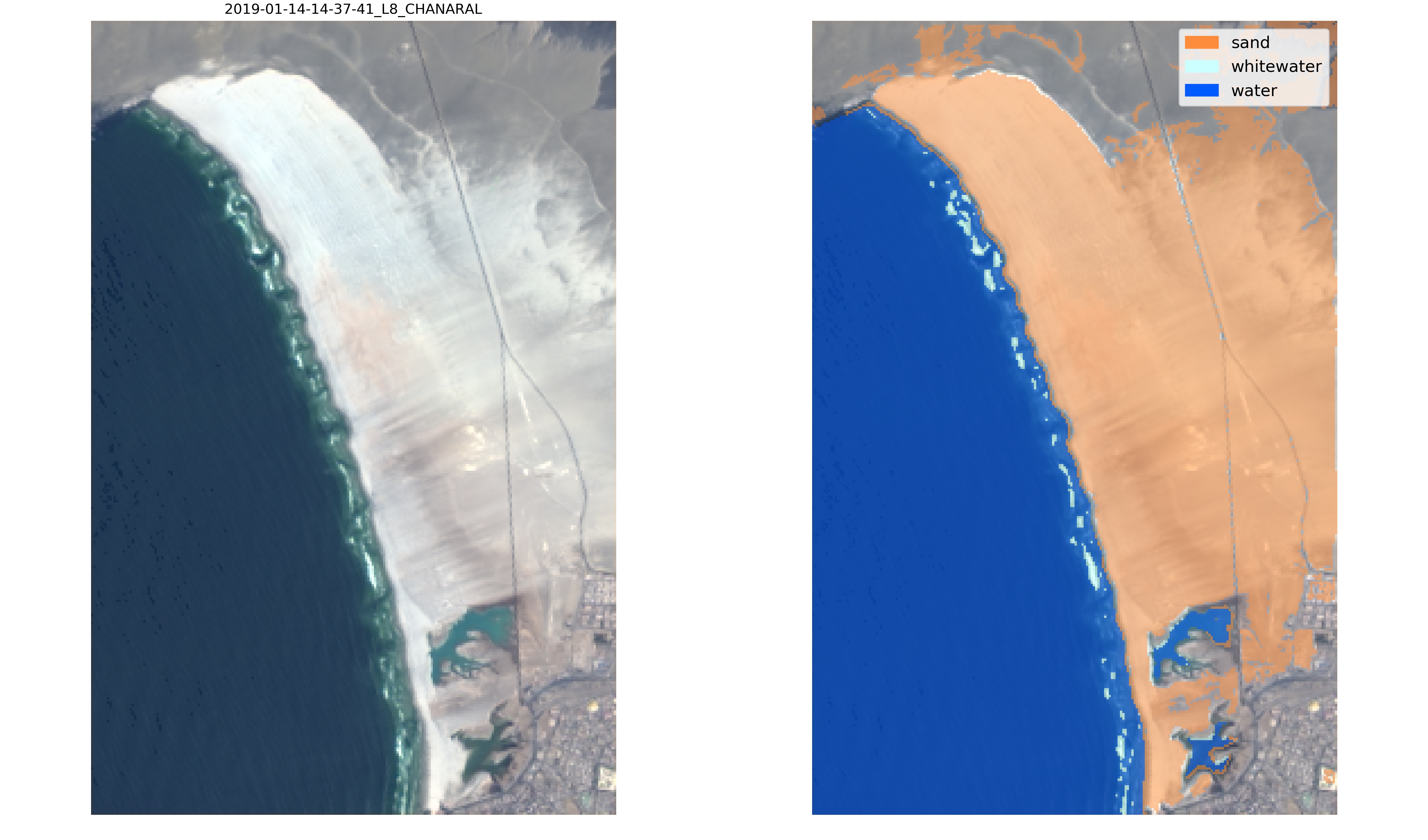
+
+Now, this new classifier labels correctly the sandy pixels of the Atacama desert and will provide more accurate satellite-derived shorelines at this beach!
diff --git a/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl b/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b6c126c
Binary files /dev/null and b/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl differ
diff --git a/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml b/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ba48549
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+ site5
+
+
+
+
+ normal
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal
+
+
+ highlight
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight
+
+
+
+ Polygon
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc
+
+
+
+ 1
+
+ 153.6170468,-28.6510018,0
+ 153.6134419,-28.6621487,0
+ 153.6297498,-28.6665921,0
+ 153.6333547,-28.655295,0
+ 153.6170468,-28.6510018,0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/classification/training_sites/NEWCASTLE.kml b/classification/training_sites/NEWCASTLE.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d2879b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/training_sites/NEWCASTLE.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+ site2
+
+
+
+
+ normal
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal
+
+
+ highlight
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight
+
+
+
+ Polygon
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc
+
+
+
+ 1
+
+ 151.7604354,-32.9330576,0
+ 151.7480758,-32.9411254,0
+ 151.7612079,-32.953226,0
+ 151.7750266,-32.9451592,0
+ 151.7604354,-32.9330576,0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/classification/training_sites/SAWTELL.kml b/classification/training_sites/SAWTELL.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4774e49
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/training_sites/SAWTELL.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+ site4
+
+
+
+
+ normal
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal
+
+
+ highlight
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight
+
+
+
+ Polygon
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc
+
+
+
+ 1
+
+ 153.0949026,-30.3586611,0
+ 153.0927568,-30.3715099,0
+ 153.1108242,-30.3727688,0
+ 153.1124979,-30.3600312,0
+ 153.0949026,-30.3586611,0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_classify.py b/coastsat/SDS_classify.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d507a55
--- /dev/null
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_classify.py
@@ -0,0 +1,624 @@
+"""
+This module contains functions to label satellite images, use the labels to
+train a pixel-wise classifier and evaluate the classifier
+
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+"""
+
+# load modules
+import os
+import numpy as np
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+import matplotlib.cm as cm
+from matplotlib.widgets import LassoSelector
+from matplotlib import path
+import pickle
+import pdb
+import warnings
+warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
+
+# image processing modules
+from skimage.segmentation import flood
+from skimage import morphology
+from pylab import ginput
+from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
+np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
+
+# CoastSat modules
+from coastsat import SDS_preprocess, SDS_shoreline, SDS_tools
+
+class SelectFromImage(object):
+ """
+ Class used to draw the lassos on the images with two methods:
+ - onselect: save the pixels inside the selection
+ - disconnect: stop drawing lassos on the image
+ """
+ # initialize lasso selection class
+ def __init__(self, ax, implot, color=[1,1,1]):
+ self.canvas = ax.figure.canvas
+ self.implot = implot
+ self.array = implot.get_array()
+ xv, yv = np.meshgrid(np.arange(self.array.shape[1]),np.arange(self.array.shape[0]))
+ self.pix = np.vstack( (xv.flatten(), yv.flatten()) ).T
+ self.ind = []
+ self.im_bool = np.zeros((self.array.shape[0], self.array.shape[1]))
+ self.color = color
+ self.lasso = LassoSelector(ax, onselect=self.onselect)
+
+ def onselect(self, verts):
+ # find pixels contained in the lasso
+ p = path.Path(verts)
+ self.ind = p.contains_points(self.pix, radius=1)
+ # color selected pixels
+ array_list = []
+ for k in range(self.array.shape[2]):
+ array2d = self.array[:,:,k]
+ lin = np.arange(array2d.size)
+ new_array2d = array2d.flatten()
+ new_array2d[lin[self.ind]] = self.color[k]
+ array_list.append(new_array2d.reshape(array2d.shape))
+ self.array = np.stack(array_list,axis=2)
+ self.implot.set_data(self.array)
+ self.canvas.draw_idle()
+ # update boolean image with selected pixels
+ vec_bool = self.im_bool.flatten()
+ vec_bool[lin[self.ind]] = 1
+ self.im_bool = vec_bool.reshape(self.im_bool.shape)
+
+ def disconnect(self):
+ self.lasso.disconnect_events()
+
+def label_images(metadata,settings):
+ """
+ Load satellite images and interactively label different classes (hard-coded)
+
+ KV WRL 2019
+
+ Arguments:
+ -----------
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'cloud_thresh': float
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
+ 'labels': dict
+ list of label names (key) and label numbers (value) for each class
+ 'flood_fill': boolean
+ True to use the flood_fill functionality when labelling sand pixels
+ 'tolerance': float
+ tolerance value for flood fill when labelling the sand pixels
+ 'filepath_train': str
+ directory in which to save the labelled data
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ Stores the labelled data in the specified directory
+
+ """
+
+ filepath_train = settings['filepath_train']
+ # initialize figure
+ fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=[17,10], tight_layout=True,sharex=True,
+ sharey=True)
+ mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
+ mng.window.showMaximized()
+
+ # loop through satellites
+ for satname in metadata.keys():
+ filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
+ filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
+ # loop through images
+ for i in range(len(filenames)):
+ # image filename
+ fn = SDS_tools.get_filenames(filenames[i],filepath, satname)
+ # read and preprocess image
+ im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn, satname, settings['cloud_mask_issue'])
+ # calculate cloud cover
+ cloud_cover = np.divide(sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int))),
+ (cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
+ # skip image if cloud cover is above threshold
+ if cloud_cover > settings['cloud_thresh'] or cloud_cover == 1:
+ continue
+ # get individual RGB image
+ im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
+ im_NDVI = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,3], im_ms[:,:,2], cloud_mask)
+ im_NDWI = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,3], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
+ # initialise labels
+ im_viz = im_RGB.copy()
+ im_labels = np.zeros([im_RGB.shape[0],im_RGB.shape[1]])
+ # show RGB image
+ ax.axis('off')
+ ax.imshow(im_RGB)
+ implot = ax.imshow(im_viz, alpha=0.6)
+ filename = filenames[i][:filenames[i].find('.')][:-4]
+ ax.set_title(filename)
+
+ ##############################################################
+ # select image to label
+ ##############################################################
+ # set a key event to accept/reject the detections (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/15033071)
+ # this variable needs to be immuatable so we can access it after the keypress event
+ key_event = {}
+ def press(event):
+ # store what key was pressed in the dictionary
+ key_event['pressed'] = event.key
+ # let the user press a key, right arrow to keep the image, left arrow to skip it
+ # to break the loop the user can press 'escape'
+ while True:
+ btn_keep = ax.text(1.1, 0.9, 'keep ⇨', size=12, ha="right", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ btn_skip = ax.text(-0.1, 0.9, '⇦ skip', size=12, ha="left", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ btn_esc = ax.text(0.5, 0, ' to quit', size=12, ha="center", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+ # after button is pressed, remove the buttons
+ btn_skip.remove()
+ btn_keep.remove()
+ btn_esc.remove()
+
+ # keep/skip image according to the pressed key, 'escape' to break the loop
+ if key_event.get('pressed') == 'right':
+ skip_image = False
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'left':
+ skip_image = True
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
+ plt.close()
+ raise StopIteration('User cancelled labelling images')
+ else:
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+
+ # if user decided to skip show the next image
+ if skip_image:
+ ax.clear()
+ continue
+ # otherwise label this image
+ else:
+ ##############################################################
+ # digitize sandy pixels
+ ##############################################################
+ ax.set_title('Click on SAND pixels (flood fill activated, tolerance = %.2f)\nwhen finished press '%settings['tolerance'])
+ # create erase button, if you click there it delets the last selection
+ btn_erase = ax.text(im_ms.shape[1], 0, 'Erase', size=20, ha='right', va='top',
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ color_sand = settings['colors']['sand']
+ sand_pixels = []
+ while 1:
+ seed = ginput(n=1, timeout=0, show_clicks=True)
+ # if empty break the loop and go to next label
+ if len(seed) == 0:
+ break
+ else:
+ # round to pixel location
+ seed = np.round(seed[0]).astype(int)
+ # if user clicks on erase, delete the last selection
+ if seed[0] > 0.95*im_ms.shape[1] and seed[1] < 0.05*im_ms.shape[0]:
+ if len(sand_pixels) > 0:
+ im_labels[sand_pixels[-1]] = 0
+ for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
+ im_viz[sand_pixels[-1],k] = im_RGB[sand_pixels[-1],k]
+ implot.set_data(im_viz)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ del sand_pixels[-1]
+
+ # otherwise label the selected sand pixels
+ else:
+ # flood fill the NDVI and the NDWI
+ fill_NDVI = flood(im_NDVI, (seed[1],seed[0]), tolerance=settings['tolerance'])
+ fill_NDWI = flood(im_NDWI, (seed[1],seed[0]), tolerance=settings['tolerance'])
+ # compute the intersection of the two masks
+ fill_sand = np.logical_and(fill_NDVI, fill_NDWI)
+ im_labels[fill_sand] = settings['labels']['sand']
+ sand_pixels.append(fill_sand)
+ # show the labelled pixels
+ for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
+ im_viz[im_labels==settings['labels']['sand'],k] = color_sand[k]
+ implot.set_data(im_viz)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+
+ ##############################################################
+ # digitize white-water pixels
+ ##############################################################
+ color_ww = settings['colors']['white-water']
+ ax.set_title('Click on individual WHITE-WATER pixels (no flood fill)\nwhen finished press ')
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ ww_pixels = []
+ while 1:
+ seed = ginput(n=1, timeout=0, show_clicks=True)
+ # if empty break the loop and go to next label
+ if len(seed) == 0:
+ break
+ else:
+ # round to pixel location
+ seed = np.round(seed[0]).astype(int)
+ # if user clicks on erase, delete the last labelled pixels
+ if seed[0] > 0.95*im_ms.shape[1] and seed[1] < 0.05*im_ms.shape[0]:
+ if len(ww_pixels) > 0:
+ im_labels[ww_pixels[-1][1],ww_pixels[-1][0]] = 0
+ for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
+ im_viz[ww_pixels[-1][1],ww_pixels[-1][0],k] = im_RGB[ww_pixels[-1][1],ww_pixels[-1][0],k]
+ implot.set_data(im_viz)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ del ww_pixels[-1]
+ else:
+ im_labels[seed[1],seed[0]] = settings['labels']['white-water']
+ for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
+ im_viz[seed[1],seed[0],k] = color_ww[k]
+ implot.set_data(im_viz)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ ww_pixels.append(seed)
+
+ im_sand_ww = im_viz.copy()
+ btn_erase.set(text=' to Erase', fontsize=12)
+
+ ##############################################################
+ # digitize water pixels (with lassos)
+ ##############################################################
+ color_water = settings['colors']['water']
+ ax.set_title('Click and hold to draw lassos and select WATER pixels\nwhen finished press ')
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ selector_water = SelectFromImage(ax, implot, color_water)
+ key_event = {}
+ while True:
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+ if key_event.get('pressed') == 'enter':
+ selector_water.disconnect()
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
+ selector_water.array = im_sand_ww
+ implot.set_data(selector_water.array)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ selector_water.implot = implot
+ selector_water.im_bool = np.zeros((selector_water.array.shape[0], selector_water.array.shape[1]))
+ selector_water.ind=[]
+ # update im_viz and im_labels
+ im_viz = selector_water.array
+ selector_water.im_bool = selector_water.im_bool.astype(bool)
+ im_labels[selector_water.im_bool] = settings['labels']['water']
+
+ im_sand_ww_water = im_viz.copy()
+
+ ##############################################################
+ # digitize land pixels (with lassos)
+ ##############################################################
+ color_land = settings['colors']['other land features']
+ ax.set_title('Click and hold to draw lassos and select OTHER LAND pixels\nwhen finished press ')
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ selector_land = SelectFromImage(ax, implot, color_land)
+ key_event = {}
+ while True:
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+ if key_event.get('pressed') == 'enter':
+ selector_land.disconnect()
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
+ selector_land.array = im_sand_ww_water
+ implot.set_data(selector_land.array)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ selector_land.implot = implot
+ selector_land.im_bool = np.zeros((selector_land.array.shape[0], selector_land.array.shape[1]))
+ selector_land.ind=[]
+ # update im_viz and im_labels
+ im_viz = selector_land.array
+ selector_land.im_bool = selector_land.im_bool.astype(bool)
+ im_labels[selector_land.im_bool] = settings['labels']['other land features']
+
+ # save labelled image
+ ax.set_title(filename)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ fp = os.path.join(filepath_train,settings['inputs']['sitename'])
+ if not os.path.exists(fp):
+ os.makedirs(fp)
+ fig.savefig(os.path.join(fp,filename+'.jpg'), dpi=150)
+ ax.clear()
+ # save labels and features
+ features = dict([])
+ for key in settings['labels'].keys():
+ im_bool = im_labels == settings['labels'][key]
+ features[key] = SDS_shoreline.calculate_features(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_bool)
+ training_data = {'labels':im_labels, 'features':features, 'label_ids':settings['labels']}
+ with open(os.path.join(fp, filename + '.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
+ pickle.dump(training_data,f)
+
+ # close figure when finished
+ plt.close(fig)
+
+def load_labels(train_sites, settings):
+ """
+ Load the labelled data from the different training sites
+
+ KV WRL 2019
+
+ Arguments:
+ -----------
+ train_sites: list of str
+ sites to be loaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'labels': dict
+ list of label names (key) and label numbers (value) for each class
+ 'filepath_train': str
+ directory in which to save the labelled data
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ features: dict
+ contains the features for each labelled pixel
+
+ """
+
+ filepath_train = settings['filepath_train']
+ # initialize the features dict
+ features = dict([])
+ n_features = 20
+ first_row = np.nan*np.ones((1,n_features))
+ for key in settings['labels'].keys():
+ features[key] = first_row
+ # loop through each site
+ for site in train_sites:
+ sitename = site[:site.find('.')]
+ filepath = os.path.join(filepath_train,sitename)
+ if os.path.exists(filepath):
+ list_files = os.listdir(filepath)
+ else:
+ continue
+ # make a new list with only the .pkl files (no .jpg)
+ list_files_pkl = []
+ for file in list_files:
+ if '.pkl' in file:
+ list_files_pkl.append(file)
+ # load and append the training data to the features dict
+ for file in list_files_pkl:
+ # read file
+ with open(os.path.join(filepath, file), 'rb') as f:
+ labelled_data = pickle.load(f)
+ for key in labelled_data['features'].keys():
+ if len(labelled_data['features'][key])>0: # check that is not empty
+ # append rows
+ features[key] = np.append(features[key],
+ labelled_data['features'][key], axis=0)
+ # remove the first row (initialized with nans) and print how many pixels
+ print('Number of pixels per class in training data:')
+ for key in features.keys():
+ features[key] = features[key][1:,:]
+ print('%s : %d pixels'%(key,len(features[key])))
+
+ return features
+
+def format_training_data(features, classes, labels):
+ """
+ Format the labelled data in an X features matrix and a y labels vector, so
+ that it can be used for training an ML model.
+
+ KV WRL 2019
+
+ Arguments:
+ -----------
+ features: dict
+ contains the features for each labelled pixel
+ classes: list of str
+ names of the classes
+ labels: list of int
+ int value associated with each class (in the same order as classes)
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ X: np.array
+ matrix features along the columns and pixels along the rows
+ y: np.array
+ vector with the labels corresponding to each row of X
+
+ """
+
+ # initialize X and y
+ X = np.nan*np.ones((1,features[classes[0]].shape[1]))
+ y = np.nan*np.ones((1,1))
+ # append row of features to X and corresponding label to y
+ for i,key in enumerate(classes):
+ y = np.append(y, labels[i]*np.ones((features[key].shape[0],1)), axis=0)
+ X = np.append(X, features[key], axis=0)
+ # remove first row
+ X = X[1:,:]; y = y[1:]
+ # replace nans with something close to 0
+ # training algotihms cannot handle nans
+ X[np.isnan(X)] = 1e-9
+
+ return X, y
+
+def plot_confusion_matrix(y_true,y_pred,classes,normalize=False,cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
+ """
+ Function copied from the scikit-learn examples (https://scikit-learn.org/stable/)
+ This function plots a confusion matrix.
+ Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`.
+
+ """
+ # compute confusion matrix
+ cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
+ if normalize:
+ cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
+ print("Normalized confusion matrix")
+ else:
+ print('Confusion matrix, without normalization')
+
+ # plot confusion matrix
+ fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6), tight_layout=True)
+ im = ax.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
+# ax.figure.colorbar(im, ax=ax)
+ ax.set(xticks=np.arange(cm.shape[1]),
+ yticks=np.arange(cm.shape[0]), ylim=[3.5,-0.5],
+ xticklabels=classes, yticklabels=classes,
+ ylabel='True label',
+ xlabel='Predicted label')
+
+ # rotate the tick labels and set their alignment.
+ plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=45, ha="right",
+ rotation_mode="anchor")
+
+ # loop over data dimensions and create text annotations.
+ fmt = '.2f' if normalize else 'd'
+ thresh = cm.max() / 2.
+ for i in range(cm.shape[0]):
+ for j in range(cm.shape[1]):
+ ax.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt),
+ ha="center", va="center",
+ color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black",
+ fontsize=12)
+ fig.tight_layout()
+ return ax
+
+def evaluate_classifier(classifier, metadata, settings):
+ """
+ Apply the image classifier to all the images and save the classified images.
+
+ KV WRL 2019
+
+ Arguments:
+ -----------
+ classifier: joblib object
+ classifier model to be used for image classification
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+ 'cloud_thresh': float
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
+ 'output_epsg': int
+ output spatial reference system as EPSG code
+ 'buffer_size': int
+ size of the buffer (m) around the sandy pixels over which the pixels
+ are considered in the thresholding algorithm
+ 'min_beach_area': int
+ minimum allowable object area (in metres^2) for the class 'sand',
+ the area is converted to number of connected pixels
+ 'min_length_sl': int
+ minimum length (in metres) of shoreline contour to be valid
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ Saves .jpg images with the output of the classification in the folder ./detection
+
+ """
+
+ # create folder called evaluation
+ fp = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'evaluation')
+ if not os.path.exists(fp):
+ os.makedirs(fp)
+
+ # initialize figure (not interactive)
+ plt.ioff()
+ fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=[17,10],sharex=True, sharey=True,
+ constrained_layout=True)
+
+ # create colormap for labels
+ cmap = cm.get_cmap('tab20c')
+ colorpalette = cmap(np.arange(0,13,1))
+ colours = np.zeros((3,4))
+ colours[0,:] = colorpalette[5]
+ colours[1,:] = np.array([204/255,1,1,1])
+ colours[2,:] = np.array([0,91/255,1,1])
+ # loop through satellites
+ for satname in metadata.keys():
+ filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
+ filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
+
+ # load classifiers and
+ if satname in ['L5','L7','L8']:
+ pixel_size = 15
+ elif satname == 'S2':
+ pixel_size = 10
+ # convert settings['min_beach_area'] and settings['buffer_size'] from metres to pixels
+ buffer_size_pixels = np.ceil(settings['buffer_size']/pixel_size)
+ min_beach_area_pixels = np.ceil(settings['min_beach_area']/pixel_size**2)
+
+ # loop through images
+ for i in range(len(filenames)):
+ # image filename
+ fn = SDS_tools.get_filenames(filenames[i],filepath, satname)
+ # read and preprocess image
+ im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn, satname, settings['cloud_mask_issue'])
+ image_epsg = metadata[satname]['epsg'][i]
+ # calculate cloud cover
+ cloud_cover = np.divide(sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int))),
+ (cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
+ # skip image if cloud cover is above threshold
+ if cloud_cover > settings['cloud_thresh']:
+ continue
+ # calculate a buffer around the reference shoreline (if any has been digitised)
+ im_ref_buffer = SDS_shoreline.create_shoreline_buffer(cloud_mask.shape, georef, image_epsg,
+ pixel_size, settings)
+ # classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
+ im_classif, im_labels = SDS_shoreline.classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask,
+ min_beach_area_pixels, classifier)
+ # there are two options to map the contours:
+ # if there are pixels in the 'sand' class --> use find_wl_contours2 (enhanced)
+ # otherwise use find_wl_contours2 (traditional)
+ try: # use try/except structure for long runs
+ if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) < 10 :
+ # compute MNDWI image (SWIR-G)
+ im_mndwi = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
+ # find water contours on MNDWI grayscale image
+ contours_mwi = SDS_shoreline.find_wl_contours1(im_mndwi, cloud_mask, im_ref_buffer)
+ else:
+ # use classification to refine threshold and extract the sand/water interface
+ contours_wi, contours_mwi = SDS_shoreline.find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels,
+ cloud_mask, buffer_size_pixels, im_ref_buffer)
+ except:
+ print('Could not map shoreline for this image: ' + filenames[i])
+ continue
+ # process the water contours into a shoreline
+ shoreline = SDS_shoreline.process_shoreline(contours_mwi, cloud_mask, georef, image_epsg, settings)
+ try:
+ sl_pix = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(SDS_tools.convert_epsg(shoreline,
+ settings['output_epsg'],
+ image_epsg)[:,[0,1]], georef)
+ except:
+ # if try fails, just add nan into the shoreline vector so the next parts can still run
+ sl_pix = np.array([[np.nan, np.nan],[np.nan, np.nan]])
+ # make a plot
+ im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
+ # create classified image
+ im_class = np.copy(im_RGB)
+ for k in range(0,im_labels.shape[2]):
+ im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],0] = colours[k,0]
+ im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],1] = colours[k,1]
+ im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],2] = colours[k,2]
+ # show images
+ ax[0].imshow(im_RGB)
+ ax[1].imshow(im_RGB)
+ ax[1].imshow(im_class, alpha=0.5)
+ ax[0].axis('off')
+ ax[1].axis('off')
+ filename = filenames[i][:filenames[i].find('.')][:-4]
+ ax[0].set_title(filename)
+ ax[0].plot(sl_pix[:,0], sl_pix[:,1], 'k.', markersize=3)
+ ax[1].plot(sl_pix[:,0], sl_pix[:,1], 'k.', markersize=3)
+ # save figure
+ fig.savefig(os.path.join(fp,settings['inputs']['sitename'] + filename[:19] +'.jpg'), dpi=150)
+ # clear axes
+ for cax in fig.axes:
+ cax.clear()
+
+ # close the figure at the end
+ plt.close()
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_download.py b/coastsat/SDS_download.py
index 224aea8..aedcc33 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_download.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_download.py
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
-"""This module contains all the functions needed to download the satellite images from the Google
-Earth Engine Server
+"""
+This module contains all the functions needed to download the satellite images
+from the Google Earth Engine server
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -15,16 +16,16 @@ import ee
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
import zipfile
import copy
-from coastsat import gdal_merge
# additional modules
-from datetime import datetime
+from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import pytz
import pickle
-import skimage.morphology as morphology
+from skimage import morphology, transform
+from scipy import ndimage
-# own modules
-from coastsat import SDS_preprocess, SDS_tools
+# CoastSat modules
+from coastsat import SDS_preprocess, SDS_tools, gdal_merge
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
@@ -35,15 +36,19 @@ def download_tif(image, polygon, bandsId, filepath):
Arguments:
-----------
- image: ee.Image
- Image object to be downloaded
- polygon: list
- polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted
- longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column
- bandsId: list of dict
- list of bands to be downloaded
- filepath: location where the temporary file should be saved
-
+ image: ee.Image
+ Image object to be downloaded
+ polygon: list
+ polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted
+ longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column
+ bandsId: list of dict
+ list of bands to be downloaded
+ filepath: location where the temporary file should be saved
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ Downloads an image in a file named data.tif
+
"""
url = ee.data.makeDownloadUrl(ee.data.getDownloadId({
@@ -60,39 +65,45 @@ def download_tif(image, polygon, bandsId, filepath):
def retrieve_images(inputs):
"""
- Downloads all images from Landsat 5, Landsat 7, Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 covering the area of
- interest and acquired between the specified dates.
- The downloaded images are in .TIF format and organised in subfolders, divided by satellite
- mission and pixel resolution.
+ Downloads all images from Landsat 5, Landsat 7, Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2
+ covering the area of interest and acquired between the specified dates.
+ The downloaded images are in .TIF format and organised in subfolders, divided
+ by satellite mission. The bands are also subdivided by pixel resolution.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- inputs: dict
- dictionnary that contains the following fields:
+ inputs: dict with the following keys
'sitename': str
- String containig the name of the site
+ name of the site
'polygon': list
polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted,
longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column,
- there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point.
- e.g. [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
+ there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point:
+ ```
+ polygon = [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
[151.3, -33.7]]]
+ ```
'dates': list of str
- list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in format 'yyyy-mm-dd'
- e.g. ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in
+ format 'yyyy-mm-dd':
+ ```
+ dates = ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ ```
'sat_list': list of str
- list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include
- e.g. ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include:
+ ```
+ sat_list = ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ ```
'filepath_data': str
- Filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
+ filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
Returns:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded: filename,
- georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
+ metadata: dict
+ contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded:
+ date, filename, georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
"""
@@ -710,178 +721,199 @@ def retrieve_images(inputs):
def merge_overlapping_images(metadata,inputs):
"""
- When the area of interest is located at the boundary between 2 images, there will be overlap
- between the 2 images and both will be downloaded from Google Earth Engine. This function
- merges the 2 images, so that the area of interest is covered by only 1 image.
+ Merge simultaneous overlapping images that cover the area of interest.
+ When the area of interest is located at the boundary between 2 images, there
+ will be overlap between the 2 images and both will be downloaded from Google
+ Earth Engine. This function merges the 2 images, so that the area of interest
+ is covered by only 1 image.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
- inputs: dict
- dictionnary that contains the following fields:
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ inputs: dict with the following keys
'sitename': str
- String containig the name of the site
+ name of the site
'polygon': list
polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted,
longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column,
- there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point.
- e.g. [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
+ there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point:
+ ```
+ polygon = [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
[151.3, -33.7]]]
+ ```
'dates': list of str
- list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in format 'yyyy-mm-dd'
- e.g. ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in
+ format 'yyyy-mm-dd':
+ ```
+ dates = ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ ```
'sat_list': list of str
- list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include
- e.g. ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include:
+ ```
+ sat_list = ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ ```
'filepath_data': str
- Filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
+ filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
Returns:
-----------
- metadata_updated: dict
- updated metadata with the information of the merged images
+ metadata_updated: dict
+ updated metadata
"""
-
- # only for Sentinel-2 at this stage (not sure if this is needed for Landsat images)
+
+ # only for Sentinel-2 at this stage (not sure if this is needed for Landsat images)
sat = 'S2'
filepath = os.path.join(inputs['filepath'], inputs['sitename'])
-
- # find the images that are overlapping (same date in S2 filenames)
filenames = metadata[sat]['filenames']
- filenames_copy = filenames.copy()
- # loop through all the filenames and find the pairs of overlapping images (same date and time of acquisition)
+ # find the pairs of images that are within 5 minutes of each other
+ time_delta = 5*60 # 5 minutes in seconds
+ dates = metadata[sat]['dates'].copy()
pairs = []
- for i,fn in enumerate(filenames):
- filenames_copy[i] = []
- # find duplicate
- boolvec = [fn[:22] == _[:22] for _ in filenames_copy]
- if np.any(boolvec):
+ for i,date in enumerate(metadata[sat]['dates']):
+ # dummy value so it does not match it again
+ dates[i] = pytz.utc.localize(datetime(1,1,1) + timedelta(days=i+1))
+ # calculate time difference
+ time_diff = np.array([np.abs((date - _).total_seconds()) for _ in dates])
+ # find the matching times and add to pairs list
+ boolvec = time_diff <= time_delta
+ if np.sum(boolvec) == 0:
+ continue
+ else:
idx_dup = np.where(boolvec)[0][0]
- if len(filenames[i]) > len(filenames[idx_dup]):
- pairs.append([idx_dup,i])
- else:
- pairs.append([i,idx_dup])
+ pairs.append([i,idx_dup])
- # for each pair of images, merge them into one complete image
+ # for each pair of image, create a mask and add no_data into the .tif file (this is needed before merging .tif files)
for i,pair in enumerate(pairs):
-
fn_im = []
- for index in range(len(pair)):
- # read image
+ for index in range(len(pair)):
+ # get filenames of all the files corresponding to the each image in the pair
fn_im.append([os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', '10m', filenames[pair[index]]),
os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', '20m', filenames[pair[index]].replace('10m','20m')),
os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', '60m', filenames[pair[index]].replace('10m','60m')),
os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', 'meta', filenames[pair[index]].replace('_10m','').replace('.tif','.txt'))])
+ # read that image
im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn_im[index], sat, False)
-
+ # im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
+
# in Sentinel2 images close to the edge of the image there are some artefacts,
# that are squares with constant pixel intensities. They need to be masked in the
# raster (GEOTIFF). It can be done using the image standard deviation, which
- # indicates values close to 0 for the artefacts.
-
- # First mask the 10m bands
+ # indicates values close to 0 for the artefacts.
if len(im_ms) > 0:
+ # calculate image std for the first 10m band
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_ms[:,:,0],1)
+ # convert to binary
im_binary = np.logical_or(im_std < 1e-6, np.isnan(im_std))
- mask = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
+ # dilate to fill the edges (which have high std)
+ mask10 = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
+ # mask all 10m bands
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
- im_ms[mask,k] = np.nan
+ im_ms[mask10,k] = np.nan
+ # mask the 10m .tif file (add no_data where mask is True)
+ SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][0], mask10)
- SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][0], mask)
-
- # Then mask the 20m band
+ # create another mask for the 20m band (SWIR1)
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_extra,1)
im_binary = np.logical_or(im_std < 1e-6, np.isnan(im_std))
- mask = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
- im_extra[mask] = np.nan
+ mask20 = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
+ im_extra[mask20] = np.nan
+ # mask the 20m .tif file (im_extra)
+ SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][1], mask20)
- SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][1], mask)
+ # use the 20m mask to create a mask for the 60m QA band (by resampling)
+ mask60 = ndimage.zoom(mask20,zoom=1/3,order=0)
+ mask60 = transform.resize(mask60, im_QA.shape, mode='constant', order=0,
+ preserve_range=True)
+ mask60 = mask60.astype(bool)
+ # mask the 60m .tif file (im_QA)
+ SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][2], mask60)
+
else:
continue
# make a figure for quality control
-# plt.figure()
-# plt.subplot(221)
-# plt.imshow(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]])
-# plt.title('imRGB')
-# plt.subplot(222)
-# plt.imshow(im20, cmap='gray')
-# plt.title('im20')
-# plt.subplot(223)
-# plt.imshow(imQA, cmap='gray')
-# plt.title('imQA')
-# plt.subplot(224)
-# plt.title(fn_im[index][0][-30:])
-
- # merge masked 10m bands
- fn_merged = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'merged.tif')
+ # fig,ax= plt.subplots(2,2,tight_layout=True)
+ # ax[0,0].imshow(im_RGB)
+ # ax[0,0].set_title('RGB original')
+ # ax[1,0].imshow(mask10)
+ # ax[1,0].set_title('Mask 10m')
+ # ax[0,1].imshow(mask20)
+ # ax[0,1].set_title('Mask 20m')
+ # ax[1,1].imshow(mask60)
+ # ax[1,1].set_title('Mask 60 m')
+
+ # once all the pairs of .tif files have been masked with no_data, merge the using gdal_merge
+ fn_merged = os.path.join(filepath, 'merged.tif')
+
+ # merge masked 10m bands and remove duplicate file
gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', '0', fn_im[0][0], fn_im[1][0]])
os.chmod(fn_im[0][0], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[0][0])
os.chmod(fn_im[1][0], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[1][0])
+ os.chmod(fn_merged, 0o777)
os.rename(fn_merged, fn_im[0][0])
# merge masked 20m band (SWIR band)
- fn_merged = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'merged.tif')
gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', '0', fn_im[0][1], fn_im[1][1]])
os.chmod(fn_im[0][1], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[0][1])
os.chmod(fn_im[1][1], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[1][1])
+ os.chmod(fn_merged, 0o777)
os.rename(fn_merged, fn_im[0][1])
# merge QA band (60m band)
- fn_merged = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'merged.tif')
- gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', 'nan', fn_im[0][2], fn_im[1][2]])
+ gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', '0', fn_im[0][2], fn_im[1][2]])
os.chmod(fn_im[0][2], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[0][2])
os.chmod(fn_im[1][2], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[1][2])
+ os.chmod(fn_merged, 0o777)
os.rename(fn_merged, fn_im[0][2])
# remove the metadata .txt file of the duplicate image
os.chmod(fn_im[1][3], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[1][3])
-
+
print('%d pairs of overlapping Sentinel-2 images were merged' % len(pairs))
- # update the metadata dict (delete all the duplicates)
+ # update the metadata dict
metadata_updated = copy.deepcopy(metadata)
- filenames_copy = metadata_updated[sat]['filenames']
- index_list = []
- for i in range(len(filenames_copy)):
- if filenames_copy[i].find('dup') == -1:
- index_list.append(i)
+ idx_removed = []
+ idx_kept = []
+ for pair in pairs: idx_removed.append(pair[1])
+ for idx in np.arange(0,len(metadata[sat]['dates'])):
+ if not idx in idx_removed: idx_kept.append(idx)
for key in metadata_updated[sat].keys():
- metadata_updated[sat][key] = [metadata_updated[sat][key][_] for _ in index_list]
+ metadata_updated[sat][key] = [metadata_updated[sat][key][_] for _ in idx_kept]
- return metadata_updated
+ return metadata_updated
def get_metadata(inputs):
"""
- Gets the metadata from the downloaded .txt files in the \meta folders.
+ Gets the metadata from the downloaded images by parsing .txt files located
+ in the \meta subfolder.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- inputs: dict
- dictionnary that contains the following fields:
+ inputs: dict with the following fields
'sitename': str
- String containig the name of the site
+ name of the site
'filepath_data': str
- Filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
+ filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
Returns:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded: filename,
- georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
+ metadata: dict
+ contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded:
+ date, filename, georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
"""
# directory containing the images
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_preprocess.py b/coastsat/SDS_preprocess.py
index 4fe1d32..eabc489 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_preprocess.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_preprocess.py
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
-"""This module contains all the functions needed to preprocess the satellite images before the
-shoreline can be extracted. This includes creating a cloud mask and
+"""
+This module contains all the functions needed to preprocess the satellite images
+ before the shorelines can be extracted. This includes creating a cloud mask and
pansharpening/downsampling the multispectral bands.
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -24,7 +25,7 @@ import pickle
import geopandas as gpd
from shapely import geometry
-# own modules
+# CoastSat modules
from coastsat import SDS_tools
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
@@ -37,17 +38,19 @@ def create_cloud_mask(im_QA, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
Arguments:
-----------
- im_QA: np.array
- Image containing the QA band
- satname: string
- short name for the satellite (L5, L7, L8 or S2)
- cloud_mask_issue: boolean
- True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
+ im_QA: np.array
+ Image containing the QA band
+ satname: string
+ short name for the satellite: ```'L5', 'L7', 'L8' or 'S2'```
+ cloud_mask_issue: boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being
+ erroneously masked on the images
Returns:
-----------
- cloud_mask : np.array
- A boolean array with True if a pixel is cloudy and False otherwise
+ cloud_mask : np.array
+ boolean array with True if a pixel is cloudy and False otherwise
+
"""
# convert QA bits (the bits allocated to cloud cover vary depending on the satellite mission)
@@ -76,20 +79,22 @@ def create_cloud_mask(im_QA, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
def hist_match(source, template):
"""
- Adjust the pixel values of a grayscale image such that its histogram matches that of a
- target image.
+ Adjust the pixel values of a grayscale image such that its histogram matches
+ that of a target image.
Arguments:
-----------
- source: np.array
- Image to transform; the histogram is computed over the flattened
- array
- template: np.array
- Template image; can have different dimensions to source
+ source: np.array
+ Image to transform; the histogram is computed over the flattened
+ array
+ template: np.array
+ Template image; can have different dimensions to source
+
Returns:
-----------
- matched: np.array
- The transformed output image
+ matched: np.array
+ The transformed output image
+
"""
oldshape = source.shape
@@ -119,25 +124,27 @@ def hist_match(source, template):
def pansharpen(im_ms, im_pan, cloud_mask):
"""
Pansharpens a multispectral image, using the panchromatic band and a cloud mask.
- A PCA is applied to the image, then the 1st PC is replaced with the panchromatic band.
- Note that it is essential to match the histrograms of the 1st PC and the panchromatic band
- before replacing and inverting the PCA.
+ A PCA is applied to the image, then the 1st PC is replaced, after histogram
+ matching with the panchromatic band. Note that it is essential to match the
+ histrograms of the 1st PC and the panchromatic band before replacing and
+ inverting the PCA.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- Multispectral image to pansharpen (3D)
- im_pan: np.array
- Panchromatic band (2D)
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_ms: np.array
+ Multispectral image to pansharpen (3D)
+ im_pan: np.array
+ Panchromatic band (2D)
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
Returns:
-----------
- im_ms_ps: np.ndarray
- Pansharpened multispectral image (3D)
+ im_ms_ps: np.ndarray
+ Pansharpened multispectral image (3D)
+
"""
# reshape image into vector and apply cloud mask
@@ -172,17 +179,17 @@ def rescale_image_intensity(im, cloud_mask, prob_high):
Arguments:
-----------
- im: np.array
- Image to rescale, can be 3D (multispectral) or 2D (single band)
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- prob_high: float
- probability of exceedence used to calculate the upper percentile
+ im: np.array
+ Image to rescale, can be 3D (multispectral) or 2D (single band)
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ prob_high: float
+ probability of exceedence used to calculate the upper percentile
Returns:
-----------
- im_adj: np.array
- The rescaled image
+ im_adj: np.array
+ rescaled image
"""
# lower percentile is set to 0
@@ -221,40 +228,41 @@ def rescale_image_intensity(im, cloud_mask, prob_high):
def preprocess_single(fn, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
"""
- Reads the image and outputs the pansharpened/down-sampled multispectral bands, the
- georeferencing vector of the image (coordinates of the upper left pixel), the cloud mask and
- the QA band. For Landsat 7-8 it also outputs the panchromatic band and for Sentinel-2 it also
- outputs the 20m SWIR band.
+ Reads the image and outputs the pansharpened/down-sampled multispectral bands,
+ the georeferencing vector of the image (coordinates of the upper left pixel),
+ the cloud mask, the QA band and a no_data image.
+ For Landsat 7-8 it also outputs the panchromatic band and for Sentinel-2 it
+ also outputs the 20m SWIR band.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- fn: str or list of str
- filename of the .TIF file containing the image
- for L7, L8 and S2 this is a list of filenames, one filename for each band at different
- resolution (30m and 15m for Landsat 7-8, 10m, 20m, 60m for Sentinel-2)
- satname: str
- name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
- cloud_mask_issue: boolean
- True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
+ fn: str or list of str
+ filename of the .TIF file containing the image. For L7, L8 and S2 this
+ is a list of filenames, one filename for each band at different
+ resolution (30m and 15m for Landsat 7-8, 10m, 20m, 60m for Sentinel-2)
+ satname: str
+ name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
+ cloud_mask_issue: boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
Returns:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- 3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale] defining the
- coordinates of the top-left pixel of the image
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- im_extra : np.array
- 2D array containing the 20m resolution SWIR band for Sentinel-2 and the 15m resolution
- panchromatic band for Landsat 7 and Landsat 8. This field is empty for Landsat 5.
- im_QA: np.array
- 2D array containing the QA band, from which the cloud_mask can be computed.
- im_nodata: np.array
- 2D array with True where no data values (-inf) are located
+ im_ms: np.array
+ 3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale] defining the
+ coordinates of the top-left pixel of the image
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_extra : np.array
+ 2D array containing the 20m resolution SWIR band for Sentinel-2 and the 15m resolution
+ panchromatic band for Landsat 7 and Landsat 8. This field is empty for Landsat 5.
+ im_QA: np.array
+ 2D array containing the QA band, from which the cloud_mask can be computed.
+ im_nodata: np.array
+ 2D array with True where no data values (-inf) are located
"""
@@ -510,20 +518,21 @@ def preprocess_single(fn, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
def create_jpg(im_ms, cloud_mask, date, satname, filepath):
"""
Saves a .jpg file with the RGB image as well as the NIR and SWIR1 grayscale images.
- This functions can be modified to obtain different visualisations of the multispectral images.
+ This functions can be modified to obtain different visualisations of the
+ multispectral images.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- 3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- date: str
- String containing the date at which the image was acquired
- satname: str
- name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
+ im_ms: np.array
+ 3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ date: str
+ string containing the date at which the image was acquired
+ satname: str
+ name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
Returns:
-----------
@@ -573,7 +582,7 @@ def create_jpg(im_ms, cloud_mask, date, satname, filepath):
plt.close()
-def save_jpg(metadata, settings):
+def save_jpg(metadata, settings, **kwargs):
"""
Saves a .jpg image for all the images contained in metadata.
@@ -581,22 +590,24 @@ def save_jpg(metadata, settings):
Arguments:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- cloud_thresh: float
- value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in the image that is accepted
- sitename: string
- name of the site (also name of the folder where the images are stored)
- cloud_mask_issue: boolean
- True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
-
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+ 'cloud_thresh': float
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
+
Returns:
-----------
-
+ Stores the images as .jpg in a folder named /preprocessed
+
"""
-
+
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
cloud_thresh = settings['cloud_thresh']
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
@@ -626,6 +637,7 @@ def save_jpg(metadata, settings):
continue
# save .jpg with date and satellite in the title
date = filenames[i][:19]
+ plt.ioff() # turning interactive plotting off
create_jpg(im_ms, cloud_mask, date, satname, filepath_jpg)
# print the location where the images have been saved
@@ -634,44 +646,50 @@ def save_jpg(metadata, settings):
def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
"""
- Allows the user to manually digitize a reference shoreline that is used seed the shoreline
- detection algorithm. The reference shoreline helps to detect the outliers, making the shoreline
- detection more robust.
+ Allows the user to manually digitize a reference shoreline that is used seed
+ the shoreline detection algorithm. The reference shoreline helps to detect
+ the outliers, making the shoreline detection more robust.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
'cloud_thresh': float
- value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in the image that is accepted
- 'sitename': string
- name of the site (also name of the folder where the images are stored)
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
'output_epsg': int
- epsg code of the desired spatial reference system
+ output spatial reference system as EPSG code
Returns:
-----------
- reference_shoreline: np.array
- coordinates of the reference shoreline that was manually digitized
+ reference_shoreline: np.array
+ coordinates of the reference shoreline that was manually digitized.
+ This is also saved as a .pkl and .geojson file.
"""
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
-
+ pts_coords = []
# check if reference shoreline already exists in the corresponding folder
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename)
filename = sitename + '_reference_shoreline.pkl'
+ # if it exist, load it and return it
if filename in os.listdir(filepath):
print('Reference shoreline already exists and was loaded')
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_reference_shoreline.pkl'), 'rb') as f:
refsl = pickle.load(f)
return refsl
-
+
+ # otherwise get the user to manually digitise a shoreline on S2, L8 or L5 images (no L7 because of scan line error)
else:
# first try to use S2 images (10m res for manually digitizing the reference shoreline)
if 'S2' in metadata.keys():
@@ -690,8 +708,12 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
else:
- raise Exception('You cannot digitize the shoreline on L7 images, add another L8, S2 or L5 to your dataset.')
-
+ raise Exception('You cannot digitize the shoreline on L7 images (because of gaps in the images), add another L8, S2 or L5 to your dataset.')
+
+ # create figure
+ fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=[18,9], tight_layout=True)
+ mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
+ mng.window.showMaximized()
# loop trhough the images
for i in range(len(filenames)):
@@ -711,37 +733,55 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
im_RGB = rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
# plot the image RGB on a figure
- fig = plt.figure()
- fig.set_size_inches([18,9])
- fig.set_tight_layout(True)
- plt.axis('off')
- plt.imshow(im_RGB)
+ ax.axis('off')
+ ax.imshow(im_RGB)
# decide if the image if good enough for digitizing the shoreline
- plt.title('click if image is clear enough to digitize the shoreline.\n' +
- 'If not (too cloudy) click on to get another image', fontsize=14)
- keep_button = plt.text(0, 0.9, 'keep', size=16, ha="left", va="top",
- transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
- bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
- skip_button = plt.text(1, 0.9, 'skip', size=16, ha="right", va="top",
- transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
- bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
- mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
- mng.window.showMaximized()
-
- # let user click on the image once
- pt_input = ginput(n=1, timeout=1e9, show_clicks=False)
- pt_input = np.array(pt_input)
-
- # if clicks next to , show another image
- if pt_input[0][0] > im_ms.shape[1]/2:
- plt.close()
+ ax.set_title('Press if image is clear enough to digitize the shoreline.\n' +
+ 'If the image is cloudy press to get another image', fontsize=14)
+ # set a key event to accept/reject the detections (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/15033071)
+ # this variable needs to be immuatable so we can access it after the keypress event
+ skip_image = False
+ key_event = {}
+ def press(event):
+ # store what key was pressed in the dictionary
+ key_event['pressed'] = event.key
+ # let the user press a key, right arrow to keep the image, left arrow to skip it
+ # to break the loop the user can press 'escape'
+ while True:
+ btn_keep = plt.text(1.1, 0.9, 'keep ⇨', size=12, ha="right", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ btn_skip = plt.text(-0.1, 0.9, '⇦ skip', size=12, ha="left", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ btn_esc = plt.text(0.5, 0, ' to quit', size=12, ha="center", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ plt.draw()
+ fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+ # after button is pressed, remove the buttons
+ btn_skip.remove()
+ btn_keep.remove()
+ btn_esc.remove()
+ # keep/skip image according to the pressed key, 'escape' to break the loop
+ if key_event.get('pressed') == 'right':
+ skip_image = False
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'left':
+ skip_image = True
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
+ plt.close()
+ raise StopIteration('User cancelled checking shoreline detection')
+ else:
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+
+ if skip_image:
+ ax.clear()
continue
-
else:
- # remove keep and skip buttons
- keep_button.set_visible(False)
- skip_button.set_visible(False)
# create two new buttons
add_button = plt.text(0, 0.9, 'add', size=16, ha="left", va="top",
transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
@@ -749,7 +789,6 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
end_button = plt.text(1, 0.9, 'end', size=16, ha="right", va="top",
transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
-
# add multiple reference shorelines (until user clicks on button)
pts_sl = np.expand_dims(np.array([np.nan, np.nan]),axis=0)
geoms = []
@@ -757,7 +796,7 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
add_button.set_visible(False)
end_button.set_visible(False)
# update title (instructions)
- plt.title('Click points along the shoreline (enough points to capture the beach curvature).\n' +
+ ax.set_title('Click points along the shoreline (enough points to capture the beach curvature).\n' +
'Start at one end of the beach.\n' + 'When finished digitizing, click ',
fontsize=14)
plt.draw()
@@ -791,14 +830,14 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
# convert to pixel coordinates and plot
pts_pix_interp = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(pts_world_interp, georef)
pts_sl = np.append(pts_sl, pts_world_interp, axis=0)
- plt.plot(pts_pix_interp[:,0], pts_pix_interp[:,1], 'r--')
- plt.plot(pts_pix_interp[0,0], pts_pix_interp[0,1],'ko')
- plt.plot(pts_pix_interp[-1,0], pts_pix_interp[-1,1],'ko')
+ ax.plot(pts_pix_interp[:,0], pts_pix_interp[:,1], 'r--')
+ ax.plot(pts_pix_interp[0,0], pts_pix_interp[0,1],'ko')
+ ax.plot(pts_pix_interp[-1,0], pts_pix_interp[-1,1],'ko')
# update title and buttons
add_button.set_visible(True)
end_button.set_visible(True)
- plt.title('click to digitize another shoreline or to finish and save the shoreline(s)',
+ ax.set_title('click on to digitize another shoreline or on to finish and save the shoreline(s)',
fontsize=14)
plt.draw()
@@ -845,5 +884,10 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
print('Reference shoreline has been saved in ' + filepath)
break
+
+ # check if a shoreline was digitised
+ if len(pts_coords) == 0:
+ raise Exception('No cloud free images are available to digitise the reference shoreline,'+
+ 'download more images and try again')
return pts_coords
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_shoreline.py b/coastsat/SDS_shoreline.py
index 92383b1..0e45273 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_shoreline.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_shoreline.py
@@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
-"""This module contains all the functions needed for extracting satellite-derived shorelines (SDS)
+"""
+This module contains all the functions needed for extracting satellite-derived
+shorelines (SDS)
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -26,7 +28,7 @@ from matplotlib import gridspec
from pylab import ginput
import pickle
-# own modules
+# CoastSat modules
from coastsat import SDS_tools, SDS_preprocess
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
@@ -37,24 +39,27 @@ np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
def calculate_features(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_bool):
"""
- Calculates a range of features on the image that are used for the supervised classification.
- The features include spectral normalized-difference indices and standard deviation of the image.
+ Calculates features on the image that are used for the supervised classification.
+ The features include spectral normalized-difference indices and standard
+ deviation of the image for all the bands and indices.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- im_bool: np.array
- 2D array of boolean indicating where on the image to calculate the features
-
- Returns: -----------
- features: np.array
- matrix containing each feature (columns) calculated for all
- the pixels (rows) indicated in im_bool
+ im_ms: np.array
+ RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_bool: np.array
+ 2D array of boolean indicating where on the image to calculate the features
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ features: np.array
+ matrix containing each feature (columns) calculated for all
+ the pixels (rows) indicated in im_bool
+
"""
# add all the multispectral bands
@@ -103,27 +108,29 @@ def classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask, min_beach_area, clf):
- water --> label = 3
- other (vegetation, buildings, rocks...) --> label = 0
- The classifier is a Neural Network previously trained.
+ The classifier is a Neural Network that is already trained.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- Pansharpened RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
- im_extra:
- only used for Landsat 7 and 8 where im_extra is the panchromatic band
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- min_beach_area: int
- minimum number of pixels that have to be connected to belong to the SAND class
- clf: classifier
-
- Returns: -----------
- im_classif: np.array
- 2D image containing labels
- im_labels: np.array of booleans
- 3D image containing a boolean image for each class (im_classif == label)
+ im_ms: np.array
+ Pansharpened RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
+ im_extra:
+ only used for Landsat 7 and 8 where im_extra is the panchromatic band
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ min_beach_area: int
+ minimum number of pixels that have to be connected to belong to the SAND class
+ clf: joblib object
+ pre-trained classifier
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ im_classif: np.array
+ 2D image containing labels
+ im_labels: np.array of booleans
+ 3D image containing a boolean image for each class (im_classif == label)
"""
@@ -163,24 +170,26 @@ def classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask, min_beach_area, clf):
def find_wl_contours1(im_ndwi, cloud_mask, im_ref_buffer):
"""
- Traditional method for shorelien detection.
- Finds the water line by thresholding the Normalized Difference Water Index and applying
- the Marching Squares Algorithm to contour the iso-value corresponding to the threshold.
+ Traditional method for shoreline detection using a global threshold.
+ Finds the water line by thresholding the Normalized Difference Water Index
+ and applying the Marching Squares Algorithm to contour the iso-value
+ corresponding to the threshold.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ndwi: np.ndarray
- Image (2D) with the NDWI (water index)
- cloud_mask: np.ndarray
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- im_ref_buffer: np.array
- Binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
-
- Returns: -----------
- contours_wl: list of np.arrays
- contains the (row,column) coordinates of the contour lines
+ im_ndwi: np.ndarray
+ Image (2D) with the NDWI (water index)
+ cloud_mask: np.ndarray
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_ref_buffer: np.array
+ Binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ contours_wl: list of np.arrays
+ contains the coordinates of the contour lines
"""
@@ -212,32 +221,33 @@ def find_wl_contours1(im_ndwi, cloud_mask, im_ref_buffer):
def find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels, cloud_mask, buffer_size, im_ref_buffer):
"""
- New robust method for extracting shorelines. Incorporates the classification component to
- refine the treshold and make it specific to the sand/water interface.
+ New robust method for extracting shorelines. Incorporates the classification
+ component to refine the treshold and make it specific to the sand/water interface.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
- im_labels: np.array
- 3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- buffer_size: int
- size of the buffer around the sandy beach over which the pixels are considered in the
- thresholding algorithm.
- im_ref_buffer: np.array
- Binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
-
- Returns: -----------
- contours_wi: list of np.arrays
- contains the (row,column) coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
- NDWI (Normalized Difference Water Index) image
- contours_mwi: list of np.arrays
- contains the (row,column) coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
- MNDWI (Modified Normalized Difference Water Index) image
+ im_ms: np.array
+ RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
+ im_labels: np.array
+ 3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ buffer_size: int
+ size of the buffer around the sandy beach over which the pixels are considered in the
+ thresholding algorithm.
+ im_ref_buffer: np.array
+ binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ contours_wi: list of np.arrays
+ contains the coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
+ NDWI (Normalized Difference Water Index) image
+ contours_mwi: list of np.arrays
+ contains the coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
+ MNDWI (Modified Normalized Difference Water Index) image
"""
@@ -318,33 +328,33 @@ def find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels, cloud_mask, buffer_size, im_ref_buffer):
def create_shoreline_buffer(im_shape, georef, image_epsg, pixel_size, settings):
"""
- Creates a buffer around the reference shoreline. The size of the buffer is given by
- settings['max_dist_ref'].
+ Creates a buffer around the reference shoreline. The size of the buffer is
+ given by settings['max_dist_ref'].
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_shape: np.array
- size of the image (rows,columns)
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- image_epsg: int
- spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
- pixel_size: int
- size of the pixel in metres (15 for Landsat, 10 for Sentinel-2)
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- output_epsg: int
+ im_shape: np.array
+ size of the image (rows,columns)
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ image_epsg: int
+ spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
+ pixel_size: int
+ size of the pixel in metres (15 for Landsat, 10 for Sentinel-2)
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'output_epsg': int
output spatial reference system
- reference_shoreline: np.array
+ 'reference_shoreline': np.array
coordinates of the reference shoreline
- max_dist_ref: int
+ 'max_dist_ref': int
maximum distance from the reference shoreline in metres
- Returns: -----------
- im_buffer: np.array
- binary image, True where the buffer is, False otherwise
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ im_buffer: np.array
+ binary image, True where the buffer is, False otherwise
"""
# initialise the image buffer
@@ -358,6 +368,12 @@ def create_shoreline_buffer(im_shape, georef, image_epsg, pixel_size, settings):
ref_sl_pix = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(ref_sl_conv, georef)
ref_sl_pix_rounded = np.round(ref_sl_pix).astype(int)
+ # make sure that the pixel coordinates of the reference shoreline are inside the image
+ idx_row = np.logical_and(ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,0] > 0, ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,0] < im_shape[1])
+ idx_col = np.logical_and(ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,1] > 0, ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,1] < im_shape[0])
+ idx_inside = np.logical_and(idx_row, idx_col)
+ ref_sl_pix_rounded = ref_sl_pix_rounded[idx_inside,:]
+
# create binary image of the reference shoreline (1 where the shoreline is 0 otherwise)
im_binary = np.zeros(im_shape)
for j in range(len(ref_sl_pix_rounded)):
@@ -373,33 +389,32 @@ def create_shoreline_buffer(im_shape, georef, image_epsg, pixel_size, settings):
def process_shoreline(contours, cloud_mask, georef, image_epsg, settings):
"""
- Converts the contours from image coordinates to world coordinates. This function also removes
- the contours that are too small to be a shoreline (based on the parameter
- settings['min_length_sl'])
+ Converts the contours from image coordinates to world coordinates.
+ This function also removes the contours that are too small to be a shoreline
+ (based on the parameter settings['min_length_sl'])
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- contours: np.array or list of np.array
- image contours as detected by the function find_contours
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- image_epsg: int
- spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- output_epsg: int
+ contours: np.array or list of np.array
+ image contours as detected by the function find_contours
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ image_epsg: int
+ spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'output_epsg': int
output spatial reference system
- min_length_sl: float
- minimum length of shoreline perimeter to be kept (in meters)
+ 'min_length_sl': float
+ minimum length of shoreline contour to be kept (in meters)
Returns:
-----------
- shoreline: np.array
- array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
+ shoreline: np.array
+ array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
"""
@@ -445,36 +460,44 @@ def process_shoreline(contours, cloud_mask, georef, image_epsg, settings):
def show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,image_epsg, georef,
settings, date, satname):
"""
- Shows the detected shoreline to the user for visual quality control. The user can select "keep"
- if the shoreline detection is correct or "skip" if it is incorrect.
+ Shows the detected shoreline to the user for visual quality control.
+ The user can accept/reject the detected shorelines by using keep/skip
+ buttons.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- im_labels: np.array
- 3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
- shoreline: np.array
- array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
- image_epsg: int
- spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- date: string
- date at which the image was taken
- satname: string
- indicates the satname (L5,L7,L8 or S2)
+ im_ms: np.array
+ RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_labels: np.array
+ 3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
+ shoreline: np.array
+ array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
+ image_epsg: int
+ spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ date: string
+ date at which the image was taken
+ satname: string
+ indicates the satname (L5,L7,L8 or S2)
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+ 'output_epsg': int
+ output spatial reference system as EPSG code
+ 'check_detection': bool
+ if True, lets user manually accept/reject the mapped shorelines
+ 'save_figure': bool
+ if True, saves a -jpg file for each mapped shoreline
Returns:
-----------
- skip_image: boolean
- True if the user wants to skip the image, False otherwise.
+ skip_image: boolean
+ True if the user wants to skip the image, False otherwise
"""
@@ -520,26 +543,26 @@ def show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,image_epsg, georef,
else:
# else create a new figure
fig = plt.figure()
- fig.set_size_inches([12.53, 9.3])
+ fig.set_size_inches([18, 9])
mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
mng.window.showMaximized()
# according to the image shape, decide whether it is better to have the images
# in vertical subplots or horizontal subplots
- if im_RGB.shape[1] > 2*im_RGB.shape[0]:
+ if im_RGB.shape[1] > 1.5*im_RGB.shape[0]:
# vertical subplots
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(3, 1)
gs.update(bottom=0.03, top=0.97, left=0.03, right=0.97)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,0])
- ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1,0])
- ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[2,0])
+ ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1,0], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
+ ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[2,0], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
else:
# horizontal subplots
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(1, 3)
gs.update(bottom=0.05, top=0.95, left=0.05, right=0.95)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,0])
- ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,1])
- ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,2])
+ ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,1], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
+ ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,2], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
# change the color of nans to either black (0.0) or white (1.0) or somewhere in between
nan_color = 1.0
@@ -634,42 +657,50 @@ def show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,image_epsg, georef,
def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
"""
- Extracts shorelines from satellite images.
+ Main function to extract shorelines from satellite images
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
-
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- sitename: str
- String containig the name of the site
- cloud_mask_issue: boolean
- True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
- buffer_size: int
- size of the buffer (m) around the sandy beach over which the pixels are considered in the
- thresholding algorithm
- min_beach_area: int
- minimum allowable object area (in metres^2) for the class 'sand'
- cloud_thresh: float
- value between 0 and 1 defining the maximum percentage of cloud cover allowed in the images
- output_epsg: int
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+ 'cloud_thresh': float
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
+ 'buffer_size': int
+ size of the buffer (m) around the sandy pixels over which the pixels
+ are considered in the thresholding algorithm
+ 'min_beach_area': int
+ minimum allowable object area (in metres^2) for the class 'sand',
+ the area is converted to number of connected pixels
+ 'min_length_sl': int
+ minimum length (in metres) of shoreline contour to be valid
+ 'sand_color': str
+ default', 'dark' (for grey/black sand beaches) or 'bright' (for white sand beaches)
+ 'output_epsg': int
output spatial reference system as EPSG code
- check_detection: boolean
- True to show each invidual detection and let the user validate the mapped shoreline
-
+ 'check_detection': bool
+ if True, lets user manually accept/reject the mapped shorelines
+ 'save_figure': bool
+ if True, saves a -jpg file for each mapped shoreline
+
Returns:
-----------
- output: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates.
+ output: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates + metadata
"""
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
+ filepath_models = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classification', 'models')
# initialise output structure
output = dict([])
# create a subfolder to store the .jpg images showing the detection
@@ -700,15 +731,15 @@ def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
if satname in ['L5','L7','L8']:
pixel_size = 15
if settings['sand_color'] == 'dark':
- clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classifiers', 'NN_4classes_Landsat_dark.pkl'))
+ clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_dark.pkl'))
elif settings['sand_color'] == 'bright':
- clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classifiers', 'NN_4classes_Landsat_bright.pkl'))
+ clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_bright.pkl'))
else:
- clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classifiers', 'NN_4classes_Landsat.pkl'))
+ clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat.pkl'))
elif satname == 'S2':
pixel_size = 10
- clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classifiers', 'NN_4classes_S2.pkl'))
+ clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_S2.pkl'))
# convert settings['min_beach_area'] and settings['buffer_size'] from metres to pixels
buffer_size_pixels = np.ceil(settings['buffer_size']/pixel_size)
@@ -743,11 +774,6 @@ def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
im_ref_buffer = create_shoreline_buffer(cloud_mask.shape, georef, image_epsg,
pixel_size, settings)
- # when running the automated mode, skip image if cloudy pixels are found in the shoreline buffer
- if not settings['check_detection'] and 'reference_shoreline' in settings.keys():
- if sum(sum(np.logical_and(im_ref_buffer, cloud_mask_adv))) > 0:
- continue
-
# classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
im_classif, im_labels = classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask,
min_beach_area_pixels, clf)
@@ -756,7 +782,7 @@ def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
# if there are pixels in the 'sand' class --> use find_wl_contours2 (enhanced)
# otherwise use find_wl_contours2 (traditional)
try: # use try/except structure for long runs
- if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) == 0 :
+ if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) < 10 :
# compute MNDWI image (SWIR-G)
im_mndwi = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
# find water contours on MNDWI grayscale image
@@ -777,6 +803,8 @@ def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
# if settings['save_figure'] = True, saves a figure for each mapped shoreline
if settings['check_detection'] or settings['save_figure']:
date = filenames[i][:19]
+ if not settings['check_detection']:
+ plt.ioff() # turning interactive plotting off
skip_image = show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,
image_epsg, georef, settings, date, satname)
# if the user decides to skip the image, continue and do not save the mapped shoreline
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_tools.py b/coastsat/SDS_tools.py
index 7e86598..478795c 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_tools.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_tools.py
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
-"""This module contains utilities to work with satellite images'
+"""
+This module contains utilities to work with satellite images
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -14,7 +15,7 @@ from osgeo import gdal, osr
import geopandas as gpd
from shapely import geometry
import skimage.transform as transform
-from scipy.ndimage.filters import uniform_filter
+from astropy.convolution import convolve
###################################################################################################
# COORDINATES CONVERSION FUNCTIONS
@@ -22,21 +23,22 @@ from scipy.ndimage.filters import uniform_filter
def convert_pix2world(points, georef):
"""
- Converts pixel coordinates (row,columns) to world projected coordinates
- performing an affine transformation.
+ Converts pixel coordinates (pixel row and column) to world projected
+ coordinates performing an affine transformation.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- points: np.array or list of np.array
- array with 2 columns (rows first and columns second)
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ points: np.array or list of np.array
+ array with 2 columns (row first and column second)
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- Returns: -----------
- points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
- converted coordinates, first columns with X and second column with Y
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
+ converted coordinates, first columns with X and second column with Y
"""
@@ -47,13 +49,15 @@ def convert_pix2world(points, georef):
# create affine transformation
tform = transform.AffineTransform(aff_mat)
+ # if list of arrays
if type(points) is list:
points_converted = []
# iterate over the list
for i, arr in enumerate(points):
tmp = arr[:,[1,0]]
points_converted.append(tform(tmp))
-
+
+ # if single array
elif type(points) is np.ndarray:
tmp = points[:,[1,0]]
points_converted = tform(tmp)
@@ -65,22 +69,23 @@ def convert_pix2world(points, georef):
def convert_world2pix(points, georef):
"""
- Converts world projected coordinates (X,Y) to image coordinates (row,column)
- performing an affine transformation.
+ Converts world projected coordinates (X,Y) to image coordinates
+ (pixel row and column) performing an affine transformation.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- points: np.array or list of np.array
- array with 2 columns (rows first and columns second)
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ points: np.array or list of np.array
+ array with 2 columns (X,Y)
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- Returns: -----------
- points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
- converted coordinates, first columns with row and second column with column
-
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
+ converted coordinates (pixel row and column)
+
"""
# make affine transformation matrix
@@ -90,12 +95,14 @@ def convert_world2pix(points, georef):
# create affine transformation
tform = transform.AffineTransform(aff_mat)
+ # if list of arrays
if type(points) is list:
points_converted = []
# iterate over the list
for i, arr in enumerate(points):
points_converted.append(tform.inverse(points))
+ # if single array
elif type(points) is np.ndarray:
points_converted = tform.inverse(points)
@@ -108,22 +115,23 @@ def convert_world2pix(points, georef):
def convert_epsg(points, epsg_in, epsg_out):
"""
- Converts from one spatial reference to another using the epsg codes.
+ Converts from one spatial reference to another using the epsg codes
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- points: np.array or list of np.ndarray
- array with 2 columns (rows first and columns second)
- epsg_in: int
- epsg code of the spatial reference in which the input is
- epsg_out: int
- epsg code of the spatial reference in which the output will be
+ points: np.array or list of np.ndarray
+ array with 2 columns (rows first and columns second)
+ epsg_in: int
+ epsg code of the spatial reference in which the input is
+ epsg_out: int
+ epsg code of the spatial reference in which the output will be
- Returns: -----------
- points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
- converted coordinates
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
+ converted coordinates from epsg_in to epsg_out
"""
@@ -134,18 +142,18 @@ def convert_epsg(points, epsg_in, epsg_out):
outSpatialRef.ImportFromEPSG(epsg_out)
# create a coordinates transform
coordTransform = osr.CoordinateTransformation(inSpatialRef, outSpatialRef)
- # transform points
+ # if list of arrays
if type(points) is list:
points_converted = []
# iterate over the list
for i, arr in enumerate(points):
points_converted.append(np.array(coordTransform.TransformPoints(arr)))
+ # if single array
elif type(points) is np.ndarray:
points_converted = np.array(coordTransform.TransformPoints(points))
else:
raise Exception('invalid input type')
-
return points_converted
###################################################################################################
@@ -160,14 +168,18 @@ def nd_index(im1, im2, cloud_mask):
Arguments:
-----------
- im1, im2: np.array
- Images (2D) with which to calculate the ND index
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
-
- Returns: -----------
- im_nd: np.array
- Image (2D) containing the ND index
+ im1: np.array
+ first image (2D) with which to calculate the ND index
+ im2: np.array
+ second image (2D) with which to calculate the ND index
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ im_nd: np.array
+ Image (2D) containing the ND index
+
"""
# reshape the cloud mask
@@ -188,20 +200,21 @@ def nd_index(im1, im2, cloud_mask):
def image_std(image, radius):
"""
- Calculates the standard deviation of an image, using a moving window of specified radius.
+ Calculates the standard deviation of an image, using a moving window of
+ specified radius. Uses astropy's convolution library'
Arguments:
-----------
- image: np.array
- 2D array containing the pixel intensities of a single-band image
- radius: int
- radius defining the moving window used to calculate the standard deviation. For example,
- radius = 1 will produce a 3x3 moving window.
+ image: np.array
+ 2D array containing the pixel intensities of a single-band image
+ radius: int
+ radius defining the moving window used to calculate the standard deviation.
+ For example, radius = 1 will produce a 3x3 moving window.
Returns:
-----------
- win_std: np.array
- 2D array containing the standard deviation of the image
+ win_std: np.array
+ 2D array containing the standard deviation of the image
"""
@@ -211,9 +224,11 @@ def image_std(image, radius):
image_padded = np.pad(image, radius, 'reflect')
# window size
win_rows, win_cols = radius*2 + 1, radius*2 + 1
- # calculate std
- win_mean = uniform_filter(image_padded, (win_rows, win_cols))
- win_sqr_mean = uniform_filter(image_padded**2, (win_rows, win_cols))
+ # calculate std with uniform filters
+ win_mean = convolve(image_padded, np.ones((win_rows,win_cols)), boundary='extend',
+ normalize_kernel=True, nan_treatment='interpolate', preserve_nan=True)
+ win_sqr_mean = convolve(image_padded**2, np.ones((win_rows,win_cols)), boundary='extend',
+ normalize_kernel=True, nan_treatment='interpolate', preserve_nan=True)
win_var = win_sqr_mean - win_mean**2
win_std = np.sqrt(win_var)
# remove padding
@@ -227,14 +242,14 @@ def mask_raster(fn, mask):
Arguments:
-----------
- fn: str
- filepath + filename of the .tif raster
- mask: np.array
- array of boolean where True indicates the pixels that are to be masked
+ fn: str
+ filepath + filename of the .tif raster
+ mask: np.array
+ array of boolean where True indicates the pixels that are to be masked
Returns:
-----------
- overwrites the .tif file directly
+ Overwrites the .tif file directly
"""
@@ -264,27 +279,38 @@ def get_filepath(inputs,satname):
Arguments:
-----------
- inputs: dict
- dictionnary that contains the following fields:
+ inputs: dict with the following keys
'sitename': str
- String containig the name of the site
+ name of the site
'polygon': list
- polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted
- longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column
+ polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted,
+ longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column,
+ there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point:
+ ```
+ polygon = [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
+ [151.3, -33.7]]]
+ ```
'dates': list of str
- list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in format 'yyyy-mm-dd'
- e.g. ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in
+ format 'yyyy-mm-dd':
+ ```
+ dates = ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ ```
'sat_list': list of str
- list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include
- e.g. ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
- satname: str
- short name of the satellite mission
+ list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include:
+ ```
+ sat_list = ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ ```
+ 'filepath_data': str
+ filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
+ satname: str
+ short name of the satellite mission ('L5','L7','L8','S2')
Returns:
-----------
- filepath: str or list of str
- contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
-
+ filepath: str or list of str
+ contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
+
"""
sitename = inputs['sitename']
@@ -320,17 +346,17 @@ def get_filenames(filename, filepath, satname):
Arguments:
-----------
- filename: str
- name of the downloaded satellite image as found in the metadata
- filepath: str or list of str
- contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
- satname: str
- short name of the satellite mission
+ filename: str
+ name of the downloaded satellite image as found in the metadata
+ filepath: str or list of str
+ contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
+ satname: str
+ short name of the satellite mission
Returns:
-----------
- fn: str or list of str
- contains the filepath + filenames to access the satellite image
+ fn: str or list of str
+ contains the filepath + filenames to access the satellite image
"""
@@ -351,19 +377,20 @@ def get_filenames(filename, filepath, satname):
def merge_output(output):
"""
- Function to merge the output dictionnary, which has one key per satellite mission into a
- dictionnary containing all the shorelines and dates ordered chronologically.
+ Function to merge the output dictionnary, which has one key per satellite mission
+ into a dictionnary containing all the shorelines and dates ordered chronologically.
Arguments:
-----------
- output: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates, organised by satellite mission
-
+ output: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates, organised by
+ satellite mission
+
Returns:
-----------
- output_all: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines in a single list sorted by date
-
+ output_all: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines in a single list sorted by date
+
"""
# initialize output dict
@@ -401,9 +428,10 @@ def polygon_from_kml(fn):
fn: str
filepath + filename of the kml file to be read
- Returns: -----------
- polygon: list
- coordinates extracted from the .kml file
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ polygon: list
+ coordinates extracted from the .kml file
"""
@@ -428,13 +456,13 @@ def transects_from_geojson(filename):
Arguments:
-----------
- filename: str
- contains the path and filename of the geojson file to be loaded
+ filename: str
+ contains the path and filename of the geojson file to be loaded
Returns:
-----------
- transects: dict
- contains the X and Y coordinates of each transect.
+ transects: dict
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of each transect
"""
@@ -458,11 +486,13 @@ def output_to_gdf(output):
output: dict
contains the coordinates of the mapped shorelines + attributes
- Returns: -----------
- gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
-
-
- """
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
+ contains the shorelines + attirbutes
+
+ """
+
# loop through the mapped shorelines
counter = 0
for i in range(len(output['shorelines'])):
@@ -498,11 +528,13 @@ def transects_to_gdf(transects):
transects: dict
contains the coordinates of the transects
- Returns: -----------
- gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
- """
+ """
+
# loop through the mapped shorelines
for i,key in enumerate(list(transects.keys())):
# save the geometry + attributes
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_transects.py b/coastsat/SDS_transects.py
index 6e7221f..472e36a 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_transects.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_transects.py
@@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
-"""This module contains functions to analyze the shoreline data along transects'
+"""
+This module contains functions to analyze the 2D shorelines along shore-normal
+transects
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -14,28 +16,33 @@ import skimage.transform as transform
from pylab import ginput
import geopandas as gpd
-# own modules
+# CoastSat modules
from coastsat import SDS_tools
def create_transect(origin, orientation, length):
"""
- Create a 2D transect of points with 1m interval.
+ Create a transect given an origin, orientation and length.
+ Points are spaced at 1m intervals.
+
+ KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- origin: np.array
- contains the X and Y coordinates of the origin of the transect
- orientation: int
- angle of the transect (anti-clockwise from North) in degrees
- length: int
- length of the transect in metres
+ origin: np.array
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of the origin of the transect
+ orientation: int
+ angle of the transect (anti-clockwise from North) in degrees
+ length: int
+ length of the transect in metres
Returns:
-----------
- transect: np.array
- contains the X and Y coordinates of the transect
+ transect: np.array
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of the transect
- """
+ """
+
+ # origin of the transect
x0 = origin[0]
y0 = origin[1]
# orientation of the transect
@@ -54,25 +61,29 @@ def create_transect(origin, orientation, length):
def draw_transects(output, settings):
"""
- Allows the user to draw shore-normal transects over the mapped shorelines.
+ Draw shore-normal transects interactively on top of the mapped shorelines
Arguments:
-----------
- output: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates.
- settings: dict
- contains the inputs
+ output: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding metadata
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+
Returns:
-----------
- transects: dict
- contains the X and Y coordinates of all the transects drawn. These are also saved
- as a .geojson (+ a .jpg figure showing the location of the transects)
+ transects: dict
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of all the transects drawn.
+ Also saves the coordinates as a .geojson as well as a .jpg figure
+ showing the location of the transects.
- """
+ """
+
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
filepath = os.path.join(settings['inputs']['filepath'], sitename)
- # plot all shorelines
+ # plot the mapped shorelines
fig1 = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig1.add_subplot(111)
ax1.axis('equal')
@@ -90,7 +101,7 @@ def draw_transects(output, settings):
ax1.set_title('Click two points to define each transect (first point is the origin of the transect).\n'+
'When all transects have been defined, click on ', fontsize=16)
- # initialise variable
+ # initialise transects dict
transects = dict([])
counter = 0
# loop until user breaks it by click
@@ -99,14 +110,20 @@ def draw_transects(output, settings):
pts = ginput(n=2, timeout=1e9)
if len(pts) > 0:
origin = pts[0]
+ # if user presses , no points are selected
else:
+ # save figure as .jpg
fig1.gca().set_title('Transect locations', fontsize=16)
fig1.savefig(os.path.join(filepath, 'jpg_files', sitename + '_transect_locations.jpg'), dpi=200)
plt.title('Transect coordinates saved as ' + sitename + '_transects.geojson')
plt.draw()
+ # wait 3 seconds for user to visualise the transects that are saved
ginput(n=1, timeout=3, show_clicks=True)
plt.close(fig1)
+ # break the loop
break
+
+ # add selectect points to the transect dict
counter = counter + 1
transect = np.array([pts[0], pts[1]])
@@ -126,40 +143,40 @@ def draw_transects(output, settings):
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
plt.draw()
- # save as transects.geojson (for GIS)
+ # save transects.geojson
gdf = SDS_tools.transects_to_gdf(transects)
# set projection
gdf.crs = {'init':'epsg:'+str(settings['output_epsg'])}
# save as geojson
gdf.to_file(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_transects.geojson'), driver='GeoJSON', encoding='utf-8')
+ # print the location of the files
print('Transect locations saved in ' + filepath)
return transects
def compute_intersection(output, transects, settings):
"""
- Computes the intersection between the 2D mapped shorelines and the transects, to generate
- time-series of cross-shore distance along each transect.
+ Computes the intersection between the 2D shorelines and the shore-normal.
+ transects. It returns time-series of cross-shore distance along each transect.
Arguments:
-----------
- output: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates.
- transects: dict
- contains the X and Y coordinates of the transects (first and last point needed for each
- transect).
- settings: dict
- contains parameters defining :
- along_dist: alongshore distance to caluclate the intersection (median of points
- within this distance).
-
+ output: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding metadata
+ transects: dict
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of each transect
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'along_dist': int
+ alongshore distance considered caluclate the intersection
+
Returns:
-----------
- cross_dist: dict
- time-series of cross-shore distance along each of the transects. These are not tidally
- corrected.
+ cross_dist: dict
+ time-series of cross-shore distance along each of the transects.
+ Not tidally corrected.
- """
+ """
+
shorelines = output['shorelines']
along_dist = settings['along_dist']
diff --git a/environment.yml b/environment.yml
index f816bd4..2b23b22 100644
--- a/environment.yml
+++ b/environment.yml
@@ -16,3 +16,4 @@ dependencies:
- scipy=1.2.1
- spyder=3.3.4
- notebook=5.7.8
+ - astropy
diff --git a/examples/NARRA_polygon.kml b/examples/NARRA_polygon.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ab57b18
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/NARRA_polygon.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+ NARRA
+
+
+
+
+ normal
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal
+
+
+ highlight
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight
+
+
+
+ Polygon 1
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc
+
+
+
+ 1
+
+ 151.2957545,-33.7012561,0
+ 151.297557,-33.7388075,0
+ 151.312234,-33.7390216,0
+ 151.311204,-33.701399,0
+ 151.2957545,-33.7012561,0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Finally, the new classifier can be applied to the satellite images, for visual inspection by calling the function `SDS_classify.evaluate_classifier(classifier,metadata,settings)` which will save the classified images in */evaluation*:
+
+
+
+Now, this new classifier labels correctly the sandy pixels of the Atacama desert and will provide more accurate satellite-derived shorelines at this beach!
diff --git a/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl b/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b6c126c
Binary files /dev/null and b/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl differ
diff --git a/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml b/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ba48549
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+ site5
+
+
+
+
+ normal
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal
+
+
+ highlight
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight
+
+
+
+ Polygon
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc
+
+
+
+ 1
+
+ 153.6170468,-28.6510018,0
+ 153.6134419,-28.6621487,0
+ 153.6297498,-28.6665921,0
+ 153.6333547,-28.655295,0
+ 153.6170468,-28.6510018,0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/classification/training_sites/NEWCASTLE.kml b/classification/training_sites/NEWCASTLE.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d2879b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/training_sites/NEWCASTLE.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+ site2
+
+
+
+
+ normal
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal
+
+
+ highlight
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight
+
+
+
+ Polygon
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc
+
+
+
+ 1
+
+ 151.7604354,-32.9330576,0
+ 151.7480758,-32.9411254,0
+ 151.7612079,-32.953226,0
+ 151.7750266,-32.9451592,0
+ 151.7604354,-32.9330576,0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/classification/training_sites/SAWTELL.kml b/classification/training_sites/SAWTELL.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4774e49
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/training_sites/SAWTELL.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+ site4
+
+
+
+
+ normal
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal
+
+
+ highlight
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight
+
+
+
+ Polygon
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc
+
+
+
+ 1
+
+ 153.0949026,-30.3586611,0
+ 153.0927568,-30.3715099,0
+ 153.1108242,-30.3727688,0
+ 153.1124979,-30.3600312,0
+ 153.0949026,-30.3586611,0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_classify.py b/coastsat/SDS_classify.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d507a55
--- /dev/null
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_classify.py
@@ -0,0 +1,624 @@
+"""
+This module contains functions to label satellite images, use the labels to
+train a pixel-wise classifier and evaluate the classifier
+
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+"""
+
+# load modules
+import os
+import numpy as np
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+import matplotlib.cm as cm
+from matplotlib.widgets import LassoSelector
+from matplotlib import path
+import pickle
+import pdb
+import warnings
+warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
+
+# image processing modules
+from skimage.segmentation import flood
+from skimage import morphology
+from pylab import ginput
+from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
+np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
+
+# CoastSat modules
+from coastsat import SDS_preprocess, SDS_shoreline, SDS_tools
+
+class SelectFromImage(object):
+ """
+ Class used to draw the lassos on the images with two methods:
+ - onselect: save the pixels inside the selection
+ - disconnect: stop drawing lassos on the image
+ """
+ # initialize lasso selection class
+ def __init__(self, ax, implot, color=[1,1,1]):
+ self.canvas = ax.figure.canvas
+ self.implot = implot
+ self.array = implot.get_array()
+ xv, yv = np.meshgrid(np.arange(self.array.shape[1]),np.arange(self.array.shape[0]))
+ self.pix = np.vstack( (xv.flatten(), yv.flatten()) ).T
+ self.ind = []
+ self.im_bool = np.zeros((self.array.shape[0], self.array.shape[1]))
+ self.color = color
+ self.lasso = LassoSelector(ax, onselect=self.onselect)
+
+ def onselect(self, verts):
+ # find pixels contained in the lasso
+ p = path.Path(verts)
+ self.ind = p.contains_points(self.pix, radius=1)
+ # color selected pixels
+ array_list = []
+ for k in range(self.array.shape[2]):
+ array2d = self.array[:,:,k]
+ lin = np.arange(array2d.size)
+ new_array2d = array2d.flatten()
+ new_array2d[lin[self.ind]] = self.color[k]
+ array_list.append(new_array2d.reshape(array2d.shape))
+ self.array = np.stack(array_list,axis=2)
+ self.implot.set_data(self.array)
+ self.canvas.draw_idle()
+ # update boolean image with selected pixels
+ vec_bool = self.im_bool.flatten()
+ vec_bool[lin[self.ind]] = 1
+ self.im_bool = vec_bool.reshape(self.im_bool.shape)
+
+ def disconnect(self):
+ self.lasso.disconnect_events()
+
+def label_images(metadata,settings):
+ """
+ Load satellite images and interactively label different classes (hard-coded)
+
+ KV WRL 2019
+
+ Arguments:
+ -----------
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'cloud_thresh': float
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
+ 'labels': dict
+ list of label names (key) and label numbers (value) for each class
+ 'flood_fill': boolean
+ True to use the flood_fill functionality when labelling sand pixels
+ 'tolerance': float
+ tolerance value for flood fill when labelling the sand pixels
+ 'filepath_train': str
+ directory in which to save the labelled data
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ Stores the labelled data in the specified directory
+
+ """
+
+ filepath_train = settings['filepath_train']
+ # initialize figure
+ fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=[17,10], tight_layout=True,sharex=True,
+ sharey=True)
+ mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
+ mng.window.showMaximized()
+
+ # loop through satellites
+ for satname in metadata.keys():
+ filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
+ filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
+ # loop through images
+ for i in range(len(filenames)):
+ # image filename
+ fn = SDS_tools.get_filenames(filenames[i],filepath, satname)
+ # read and preprocess image
+ im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn, satname, settings['cloud_mask_issue'])
+ # calculate cloud cover
+ cloud_cover = np.divide(sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int))),
+ (cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
+ # skip image if cloud cover is above threshold
+ if cloud_cover > settings['cloud_thresh'] or cloud_cover == 1:
+ continue
+ # get individual RGB image
+ im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
+ im_NDVI = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,3], im_ms[:,:,2], cloud_mask)
+ im_NDWI = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,3], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
+ # initialise labels
+ im_viz = im_RGB.copy()
+ im_labels = np.zeros([im_RGB.shape[0],im_RGB.shape[1]])
+ # show RGB image
+ ax.axis('off')
+ ax.imshow(im_RGB)
+ implot = ax.imshow(im_viz, alpha=0.6)
+ filename = filenames[i][:filenames[i].find('.')][:-4]
+ ax.set_title(filename)
+
+ ##############################################################
+ # select image to label
+ ##############################################################
+ # set a key event to accept/reject the detections (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/15033071)
+ # this variable needs to be immuatable so we can access it after the keypress event
+ key_event = {}
+ def press(event):
+ # store what key was pressed in the dictionary
+ key_event['pressed'] = event.key
+ # let the user press a key, right arrow to keep the image, left arrow to skip it
+ # to break the loop the user can press 'escape'
+ while True:
+ btn_keep = ax.text(1.1, 0.9, 'keep ⇨', size=12, ha="right", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ btn_skip = ax.text(-0.1, 0.9, '⇦ skip', size=12, ha="left", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ btn_esc = ax.text(0.5, 0, ' to quit', size=12, ha="center", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+ # after button is pressed, remove the buttons
+ btn_skip.remove()
+ btn_keep.remove()
+ btn_esc.remove()
+
+ # keep/skip image according to the pressed key, 'escape' to break the loop
+ if key_event.get('pressed') == 'right':
+ skip_image = False
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'left':
+ skip_image = True
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
+ plt.close()
+ raise StopIteration('User cancelled labelling images')
+ else:
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+
+ # if user decided to skip show the next image
+ if skip_image:
+ ax.clear()
+ continue
+ # otherwise label this image
+ else:
+ ##############################################################
+ # digitize sandy pixels
+ ##############################################################
+ ax.set_title('Click on SAND pixels (flood fill activated, tolerance = %.2f)\nwhen finished press '%settings['tolerance'])
+ # create erase button, if you click there it delets the last selection
+ btn_erase = ax.text(im_ms.shape[1], 0, 'Erase', size=20, ha='right', va='top',
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ color_sand = settings['colors']['sand']
+ sand_pixels = []
+ while 1:
+ seed = ginput(n=1, timeout=0, show_clicks=True)
+ # if empty break the loop and go to next label
+ if len(seed) == 0:
+ break
+ else:
+ # round to pixel location
+ seed = np.round(seed[0]).astype(int)
+ # if user clicks on erase, delete the last selection
+ if seed[0] > 0.95*im_ms.shape[1] and seed[1] < 0.05*im_ms.shape[0]:
+ if len(sand_pixels) > 0:
+ im_labels[sand_pixels[-1]] = 0
+ for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
+ im_viz[sand_pixels[-1],k] = im_RGB[sand_pixels[-1],k]
+ implot.set_data(im_viz)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ del sand_pixels[-1]
+
+ # otherwise label the selected sand pixels
+ else:
+ # flood fill the NDVI and the NDWI
+ fill_NDVI = flood(im_NDVI, (seed[1],seed[0]), tolerance=settings['tolerance'])
+ fill_NDWI = flood(im_NDWI, (seed[1],seed[0]), tolerance=settings['tolerance'])
+ # compute the intersection of the two masks
+ fill_sand = np.logical_and(fill_NDVI, fill_NDWI)
+ im_labels[fill_sand] = settings['labels']['sand']
+ sand_pixels.append(fill_sand)
+ # show the labelled pixels
+ for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
+ im_viz[im_labels==settings['labels']['sand'],k] = color_sand[k]
+ implot.set_data(im_viz)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+
+ ##############################################################
+ # digitize white-water pixels
+ ##############################################################
+ color_ww = settings['colors']['white-water']
+ ax.set_title('Click on individual WHITE-WATER pixels (no flood fill)\nwhen finished press ')
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ ww_pixels = []
+ while 1:
+ seed = ginput(n=1, timeout=0, show_clicks=True)
+ # if empty break the loop and go to next label
+ if len(seed) == 0:
+ break
+ else:
+ # round to pixel location
+ seed = np.round(seed[0]).astype(int)
+ # if user clicks on erase, delete the last labelled pixels
+ if seed[0] > 0.95*im_ms.shape[1] and seed[1] < 0.05*im_ms.shape[0]:
+ if len(ww_pixels) > 0:
+ im_labels[ww_pixels[-1][1],ww_pixels[-1][0]] = 0
+ for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
+ im_viz[ww_pixels[-1][1],ww_pixels[-1][0],k] = im_RGB[ww_pixels[-1][1],ww_pixels[-1][0],k]
+ implot.set_data(im_viz)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ del ww_pixels[-1]
+ else:
+ im_labels[seed[1],seed[0]] = settings['labels']['white-water']
+ for k in range(im_viz.shape[2]):
+ im_viz[seed[1],seed[0],k] = color_ww[k]
+ implot.set_data(im_viz)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ ww_pixels.append(seed)
+
+ im_sand_ww = im_viz.copy()
+ btn_erase.set(text=' to Erase', fontsize=12)
+
+ ##############################################################
+ # digitize water pixels (with lassos)
+ ##############################################################
+ color_water = settings['colors']['water']
+ ax.set_title('Click and hold to draw lassos and select WATER pixels\nwhen finished press ')
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ selector_water = SelectFromImage(ax, implot, color_water)
+ key_event = {}
+ while True:
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+ if key_event.get('pressed') == 'enter':
+ selector_water.disconnect()
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
+ selector_water.array = im_sand_ww
+ implot.set_data(selector_water.array)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ selector_water.implot = implot
+ selector_water.im_bool = np.zeros((selector_water.array.shape[0], selector_water.array.shape[1]))
+ selector_water.ind=[]
+ # update im_viz and im_labels
+ im_viz = selector_water.array
+ selector_water.im_bool = selector_water.im_bool.astype(bool)
+ im_labels[selector_water.im_bool] = settings['labels']['water']
+
+ im_sand_ww_water = im_viz.copy()
+
+ ##############################################################
+ # digitize land pixels (with lassos)
+ ##############################################################
+ color_land = settings['colors']['other land features']
+ ax.set_title('Click and hold to draw lassos and select OTHER LAND pixels\nwhen finished press ')
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ selector_land = SelectFromImage(ax, implot, color_land)
+ key_event = {}
+ while True:
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+ if key_event.get('pressed') == 'enter':
+ selector_land.disconnect()
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
+ selector_land.array = im_sand_ww_water
+ implot.set_data(selector_land.array)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ selector_land.implot = implot
+ selector_land.im_bool = np.zeros((selector_land.array.shape[0], selector_land.array.shape[1]))
+ selector_land.ind=[]
+ # update im_viz and im_labels
+ im_viz = selector_land.array
+ selector_land.im_bool = selector_land.im_bool.astype(bool)
+ im_labels[selector_land.im_bool] = settings['labels']['other land features']
+
+ # save labelled image
+ ax.set_title(filename)
+ fig.canvas.draw_idle()
+ fp = os.path.join(filepath_train,settings['inputs']['sitename'])
+ if not os.path.exists(fp):
+ os.makedirs(fp)
+ fig.savefig(os.path.join(fp,filename+'.jpg'), dpi=150)
+ ax.clear()
+ # save labels and features
+ features = dict([])
+ for key in settings['labels'].keys():
+ im_bool = im_labels == settings['labels'][key]
+ features[key] = SDS_shoreline.calculate_features(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_bool)
+ training_data = {'labels':im_labels, 'features':features, 'label_ids':settings['labels']}
+ with open(os.path.join(fp, filename + '.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
+ pickle.dump(training_data,f)
+
+ # close figure when finished
+ plt.close(fig)
+
+def load_labels(train_sites, settings):
+ """
+ Load the labelled data from the different training sites
+
+ KV WRL 2019
+
+ Arguments:
+ -----------
+ train_sites: list of str
+ sites to be loaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'labels': dict
+ list of label names (key) and label numbers (value) for each class
+ 'filepath_train': str
+ directory in which to save the labelled data
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ features: dict
+ contains the features for each labelled pixel
+
+ """
+
+ filepath_train = settings['filepath_train']
+ # initialize the features dict
+ features = dict([])
+ n_features = 20
+ first_row = np.nan*np.ones((1,n_features))
+ for key in settings['labels'].keys():
+ features[key] = first_row
+ # loop through each site
+ for site in train_sites:
+ sitename = site[:site.find('.')]
+ filepath = os.path.join(filepath_train,sitename)
+ if os.path.exists(filepath):
+ list_files = os.listdir(filepath)
+ else:
+ continue
+ # make a new list with only the .pkl files (no .jpg)
+ list_files_pkl = []
+ for file in list_files:
+ if '.pkl' in file:
+ list_files_pkl.append(file)
+ # load and append the training data to the features dict
+ for file in list_files_pkl:
+ # read file
+ with open(os.path.join(filepath, file), 'rb') as f:
+ labelled_data = pickle.load(f)
+ for key in labelled_data['features'].keys():
+ if len(labelled_data['features'][key])>0: # check that is not empty
+ # append rows
+ features[key] = np.append(features[key],
+ labelled_data['features'][key], axis=0)
+ # remove the first row (initialized with nans) and print how many pixels
+ print('Number of pixels per class in training data:')
+ for key in features.keys():
+ features[key] = features[key][1:,:]
+ print('%s : %d pixels'%(key,len(features[key])))
+
+ return features
+
+def format_training_data(features, classes, labels):
+ """
+ Format the labelled data in an X features matrix and a y labels vector, so
+ that it can be used for training an ML model.
+
+ KV WRL 2019
+
+ Arguments:
+ -----------
+ features: dict
+ contains the features for each labelled pixel
+ classes: list of str
+ names of the classes
+ labels: list of int
+ int value associated with each class (in the same order as classes)
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ X: np.array
+ matrix features along the columns and pixels along the rows
+ y: np.array
+ vector with the labels corresponding to each row of X
+
+ """
+
+ # initialize X and y
+ X = np.nan*np.ones((1,features[classes[0]].shape[1]))
+ y = np.nan*np.ones((1,1))
+ # append row of features to X and corresponding label to y
+ for i,key in enumerate(classes):
+ y = np.append(y, labels[i]*np.ones((features[key].shape[0],1)), axis=0)
+ X = np.append(X, features[key], axis=0)
+ # remove first row
+ X = X[1:,:]; y = y[1:]
+ # replace nans with something close to 0
+ # training algotihms cannot handle nans
+ X[np.isnan(X)] = 1e-9
+
+ return X, y
+
+def plot_confusion_matrix(y_true,y_pred,classes,normalize=False,cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
+ """
+ Function copied from the scikit-learn examples (https://scikit-learn.org/stable/)
+ This function plots a confusion matrix.
+ Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`.
+
+ """
+ # compute confusion matrix
+ cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
+ if normalize:
+ cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
+ print("Normalized confusion matrix")
+ else:
+ print('Confusion matrix, without normalization')
+
+ # plot confusion matrix
+ fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6), tight_layout=True)
+ im = ax.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
+# ax.figure.colorbar(im, ax=ax)
+ ax.set(xticks=np.arange(cm.shape[1]),
+ yticks=np.arange(cm.shape[0]), ylim=[3.5,-0.5],
+ xticklabels=classes, yticklabels=classes,
+ ylabel='True label',
+ xlabel='Predicted label')
+
+ # rotate the tick labels and set their alignment.
+ plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=45, ha="right",
+ rotation_mode="anchor")
+
+ # loop over data dimensions and create text annotations.
+ fmt = '.2f' if normalize else 'd'
+ thresh = cm.max() / 2.
+ for i in range(cm.shape[0]):
+ for j in range(cm.shape[1]):
+ ax.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt),
+ ha="center", va="center",
+ color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black",
+ fontsize=12)
+ fig.tight_layout()
+ return ax
+
+def evaluate_classifier(classifier, metadata, settings):
+ """
+ Apply the image classifier to all the images and save the classified images.
+
+ KV WRL 2019
+
+ Arguments:
+ -----------
+ classifier: joblib object
+ classifier model to be used for image classification
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+ 'cloud_thresh': float
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
+ 'output_epsg': int
+ output spatial reference system as EPSG code
+ 'buffer_size': int
+ size of the buffer (m) around the sandy pixels over which the pixels
+ are considered in the thresholding algorithm
+ 'min_beach_area': int
+ minimum allowable object area (in metres^2) for the class 'sand',
+ the area is converted to number of connected pixels
+ 'min_length_sl': int
+ minimum length (in metres) of shoreline contour to be valid
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ Saves .jpg images with the output of the classification in the folder ./detection
+
+ """
+
+ # create folder called evaluation
+ fp = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'evaluation')
+ if not os.path.exists(fp):
+ os.makedirs(fp)
+
+ # initialize figure (not interactive)
+ plt.ioff()
+ fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=[17,10],sharex=True, sharey=True,
+ constrained_layout=True)
+
+ # create colormap for labels
+ cmap = cm.get_cmap('tab20c')
+ colorpalette = cmap(np.arange(0,13,1))
+ colours = np.zeros((3,4))
+ colours[0,:] = colorpalette[5]
+ colours[1,:] = np.array([204/255,1,1,1])
+ colours[2,:] = np.array([0,91/255,1,1])
+ # loop through satellites
+ for satname in metadata.keys():
+ filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
+ filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
+
+ # load classifiers and
+ if satname in ['L5','L7','L8']:
+ pixel_size = 15
+ elif satname == 'S2':
+ pixel_size = 10
+ # convert settings['min_beach_area'] and settings['buffer_size'] from metres to pixels
+ buffer_size_pixels = np.ceil(settings['buffer_size']/pixel_size)
+ min_beach_area_pixels = np.ceil(settings['min_beach_area']/pixel_size**2)
+
+ # loop through images
+ for i in range(len(filenames)):
+ # image filename
+ fn = SDS_tools.get_filenames(filenames[i],filepath, satname)
+ # read and preprocess image
+ im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn, satname, settings['cloud_mask_issue'])
+ image_epsg = metadata[satname]['epsg'][i]
+ # calculate cloud cover
+ cloud_cover = np.divide(sum(sum(cloud_mask.astype(int))),
+ (cloud_mask.shape[0]*cloud_mask.shape[1]))
+ # skip image if cloud cover is above threshold
+ if cloud_cover > settings['cloud_thresh']:
+ continue
+ # calculate a buffer around the reference shoreline (if any has been digitised)
+ im_ref_buffer = SDS_shoreline.create_shoreline_buffer(cloud_mask.shape, georef, image_epsg,
+ pixel_size, settings)
+ # classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
+ im_classif, im_labels = SDS_shoreline.classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask,
+ min_beach_area_pixels, classifier)
+ # there are two options to map the contours:
+ # if there are pixels in the 'sand' class --> use find_wl_contours2 (enhanced)
+ # otherwise use find_wl_contours2 (traditional)
+ try: # use try/except structure for long runs
+ if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) < 10 :
+ # compute MNDWI image (SWIR-G)
+ im_mndwi = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
+ # find water contours on MNDWI grayscale image
+ contours_mwi = SDS_shoreline.find_wl_contours1(im_mndwi, cloud_mask, im_ref_buffer)
+ else:
+ # use classification to refine threshold and extract the sand/water interface
+ contours_wi, contours_mwi = SDS_shoreline.find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels,
+ cloud_mask, buffer_size_pixels, im_ref_buffer)
+ except:
+ print('Could not map shoreline for this image: ' + filenames[i])
+ continue
+ # process the water contours into a shoreline
+ shoreline = SDS_shoreline.process_shoreline(contours_mwi, cloud_mask, georef, image_epsg, settings)
+ try:
+ sl_pix = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(SDS_tools.convert_epsg(shoreline,
+ settings['output_epsg'],
+ image_epsg)[:,[0,1]], georef)
+ except:
+ # if try fails, just add nan into the shoreline vector so the next parts can still run
+ sl_pix = np.array([[np.nan, np.nan],[np.nan, np.nan]])
+ # make a plot
+ im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
+ # create classified image
+ im_class = np.copy(im_RGB)
+ for k in range(0,im_labels.shape[2]):
+ im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],0] = colours[k,0]
+ im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],1] = colours[k,1]
+ im_class[im_labels[:,:,k],2] = colours[k,2]
+ # show images
+ ax[0].imshow(im_RGB)
+ ax[1].imshow(im_RGB)
+ ax[1].imshow(im_class, alpha=0.5)
+ ax[0].axis('off')
+ ax[1].axis('off')
+ filename = filenames[i][:filenames[i].find('.')][:-4]
+ ax[0].set_title(filename)
+ ax[0].plot(sl_pix[:,0], sl_pix[:,1], 'k.', markersize=3)
+ ax[1].plot(sl_pix[:,0], sl_pix[:,1], 'k.', markersize=3)
+ # save figure
+ fig.savefig(os.path.join(fp,settings['inputs']['sitename'] + filename[:19] +'.jpg'), dpi=150)
+ # clear axes
+ for cax in fig.axes:
+ cax.clear()
+
+ # close the figure at the end
+ plt.close()
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_download.py b/coastsat/SDS_download.py
index 224aea8..aedcc33 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_download.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_download.py
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
-"""This module contains all the functions needed to download the satellite images from the Google
-Earth Engine Server
+"""
+This module contains all the functions needed to download the satellite images
+from the Google Earth Engine server
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -15,16 +16,16 @@ import ee
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
import zipfile
import copy
-from coastsat import gdal_merge
# additional modules
-from datetime import datetime
+from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import pytz
import pickle
-import skimage.morphology as morphology
+from skimage import morphology, transform
+from scipy import ndimage
-# own modules
-from coastsat import SDS_preprocess, SDS_tools
+# CoastSat modules
+from coastsat import SDS_preprocess, SDS_tools, gdal_merge
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
@@ -35,15 +36,19 @@ def download_tif(image, polygon, bandsId, filepath):
Arguments:
-----------
- image: ee.Image
- Image object to be downloaded
- polygon: list
- polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted
- longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column
- bandsId: list of dict
- list of bands to be downloaded
- filepath: location where the temporary file should be saved
-
+ image: ee.Image
+ Image object to be downloaded
+ polygon: list
+ polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted
+ longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column
+ bandsId: list of dict
+ list of bands to be downloaded
+ filepath: location where the temporary file should be saved
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ Downloads an image in a file named data.tif
+
"""
url = ee.data.makeDownloadUrl(ee.data.getDownloadId({
@@ -60,39 +65,45 @@ def download_tif(image, polygon, bandsId, filepath):
def retrieve_images(inputs):
"""
- Downloads all images from Landsat 5, Landsat 7, Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 covering the area of
- interest and acquired between the specified dates.
- The downloaded images are in .TIF format and organised in subfolders, divided by satellite
- mission and pixel resolution.
+ Downloads all images from Landsat 5, Landsat 7, Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2
+ covering the area of interest and acquired between the specified dates.
+ The downloaded images are in .TIF format and organised in subfolders, divided
+ by satellite mission. The bands are also subdivided by pixel resolution.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- inputs: dict
- dictionnary that contains the following fields:
+ inputs: dict with the following keys
'sitename': str
- String containig the name of the site
+ name of the site
'polygon': list
polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted,
longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column,
- there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point.
- e.g. [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
+ there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point:
+ ```
+ polygon = [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
[151.3, -33.7]]]
+ ```
'dates': list of str
- list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in format 'yyyy-mm-dd'
- e.g. ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in
+ format 'yyyy-mm-dd':
+ ```
+ dates = ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ ```
'sat_list': list of str
- list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include
- e.g. ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include:
+ ```
+ sat_list = ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ ```
'filepath_data': str
- Filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
+ filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
Returns:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded: filename,
- georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
+ metadata: dict
+ contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded:
+ date, filename, georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
"""
@@ -710,178 +721,199 @@ def retrieve_images(inputs):
def merge_overlapping_images(metadata,inputs):
"""
- When the area of interest is located at the boundary between 2 images, there will be overlap
- between the 2 images and both will be downloaded from Google Earth Engine. This function
- merges the 2 images, so that the area of interest is covered by only 1 image.
+ Merge simultaneous overlapping images that cover the area of interest.
+ When the area of interest is located at the boundary between 2 images, there
+ will be overlap between the 2 images and both will be downloaded from Google
+ Earth Engine. This function merges the 2 images, so that the area of interest
+ is covered by only 1 image.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
- inputs: dict
- dictionnary that contains the following fields:
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ inputs: dict with the following keys
'sitename': str
- String containig the name of the site
+ name of the site
'polygon': list
polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted,
longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column,
- there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point.
- e.g. [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
+ there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point:
+ ```
+ polygon = [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
[151.3, -33.7]]]
+ ```
'dates': list of str
- list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in format 'yyyy-mm-dd'
- e.g. ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in
+ format 'yyyy-mm-dd':
+ ```
+ dates = ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ ```
'sat_list': list of str
- list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include
- e.g. ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include:
+ ```
+ sat_list = ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ ```
'filepath_data': str
- Filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
+ filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
Returns:
-----------
- metadata_updated: dict
- updated metadata with the information of the merged images
+ metadata_updated: dict
+ updated metadata
"""
-
- # only for Sentinel-2 at this stage (not sure if this is needed for Landsat images)
+
+ # only for Sentinel-2 at this stage (not sure if this is needed for Landsat images)
sat = 'S2'
filepath = os.path.join(inputs['filepath'], inputs['sitename'])
-
- # find the images that are overlapping (same date in S2 filenames)
filenames = metadata[sat]['filenames']
- filenames_copy = filenames.copy()
- # loop through all the filenames and find the pairs of overlapping images (same date and time of acquisition)
+ # find the pairs of images that are within 5 minutes of each other
+ time_delta = 5*60 # 5 minutes in seconds
+ dates = metadata[sat]['dates'].copy()
pairs = []
- for i,fn in enumerate(filenames):
- filenames_copy[i] = []
- # find duplicate
- boolvec = [fn[:22] == _[:22] for _ in filenames_copy]
- if np.any(boolvec):
+ for i,date in enumerate(metadata[sat]['dates']):
+ # dummy value so it does not match it again
+ dates[i] = pytz.utc.localize(datetime(1,1,1) + timedelta(days=i+1))
+ # calculate time difference
+ time_diff = np.array([np.abs((date - _).total_seconds()) for _ in dates])
+ # find the matching times and add to pairs list
+ boolvec = time_diff <= time_delta
+ if np.sum(boolvec) == 0:
+ continue
+ else:
idx_dup = np.where(boolvec)[0][0]
- if len(filenames[i]) > len(filenames[idx_dup]):
- pairs.append([idx_dup,i])
- else:
- pairs.append([i,idx_dup])
+ pairs.append([i,idx_dup])
- # for each pair of images, merge them into one complete image
+ # for each pair of image, create a mask and add no_data into the .tif file (this is needed before merging .tif files)
for i,pair in enumerate(pairs):
-
fn_im = []
- for index in range(len(pair)):
- # read image
+ for index in range(len(pair)):
+ # get filenames of all the files corresponding to the each image in the pair
fn_im.append([os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', '10m', filenames[pair[index]]),
os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', '20m', filenames[pair[index]].replace('10m','20m')),
os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', '60m', filenames[pair[index]].replace('10m','60m')),
os.path.join(filepath, 'S2', 'meta', filenames[pair[index]].replace('_10m','').replace('.tif','.txt'))])
+ # read that image
im_ms, georef, cloud_mask, im_extra, im_QA, im_nodata = SDS_preprocess.preprocess_single(fn_im[index], sat, False)
-
+ # im_RGB = SDS_preprocess.rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
+
# in Sentinel2 images close to the edge of the image there are some artefacts,
# that are squares with constant pixel intensities. They need to be masked in the
# raster (GEOTIFF). It can be done using the image standard deviation, which
- # indicates values close to 0 for the artefacts.
-
- # First mask the 10m bands
+ # indicates values close to 0 for the artefacts.
if len(im_ms) > 0:
+ # calculate image std for the first 10m band
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_ms[:,:,0],1)
+ # convert to binary
im_binary = np.logical_or(im_std < 1e-6, np.isnan(im_std))
- mask = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
+ # dilate to fill the edges (which have high std)
+ mask10 = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
+ # mask all 10m bands
for k in range(im_ms.shape[2]):
- im_ms[mask,k] = np.nan
+ im_ms[mask10,k] = np.nan
+ # mask the 10m .tif file (add no_data where mask is True)
+ SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][0], mask10)
- SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][0], mask)
-
- # Then mask the 20m band
+ # create another mask for the 20m band (SWIR1)
im_std = SDS_tools.image_std(im_extra,1)
im_binary = np.logical_or(im_std < 1e-6, np.isnan(im_std))
- mask = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
- im_extra[mask] = np.nan
+ mask20 = morphology.dilation(im_binary, morphology.square(3))
+ im_extra[mask20] = np.nan
+ # mask the 20m .tif file (im_extra)
+ SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][1], mask20)
- SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][1], mask)
+ # use the 20m mask to create a mask for the 60m QA band (by resampling)
+ mask60 = ndimage.zoom(mask20,zoom=1/3,order=0)
+ mask60 = transform.resize(mask60, im_QA.shape, mode='constant', order=0,
+ preserve_range=True)
+ mask60 = mask60.astype(bool)
+ # mask the 60m .tif file (im_QA)
+ SDS_tools.mask_raster(fn_im[index][2], mask60)
+
else:
continue
# make a figure for quality control
-# plt.figure()
-# plt.subplot(221)
-# plt.imshow(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]])
-# plt.title('imRGB')
-# plt.subplot(222)
-# plt.imshow(im20, cmap='gray')
-# plt.title('im20')
-# plt.subplot(223)
-# plt.imshow(imQA, cmap='gray')
-# plt.title('imQA')
-# plt.subplot(224)
-# plt.title(fn_im[index][0][-30:])
-
- # merge masked 10m bands
- fn_merged = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'merged.tif')
+ # fig,ax= plt.subplots(2,2,tight_layout=True)
+ # ax[0,0].imshow(im_RGB)
+ # ax[0,0].set_title('RGB original')
+ # ax[1,0].imshow(mask10)
+ # ax[1,0].set_title('Mask 10m')
+ # ax[0,1].imshow(mask20)
+ # ax[0,1].set_title('Mask 20m')
+ # ax[1,1].imshow(mask60)
+ # ax[1,1].set_title('Mask 60 m')
+
+ # once all the pairs of .tif files have been masked with no_data, merge the using gdal_merge
+ fn_merged = os.path.join(filepath, 'merged.tif')
+
+ # merge masked 10m bands and remove duplicate file
gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', '0', fn_im[0][0], fn_im[1][0]])
os.chmod(fn_im[0][0], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[0][0])
os.chmod(fn_im[1][0], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[1][0])
+ os.chmod(fn_merged, 0o777)
os.rename(fn_merged, fn_im[0][0])
# merge masked 20m band (SWIR band)
- fn_merged = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'merged.tif')
gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', '0', fn_im[0][1], fn_im[1][1]])
os.chmod(fn_im[0][1], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[0][1])
os.chmod(fn_im[1][1], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[1][1])
+ os.chmod(fn_merged, 0o777)
os.rename(fn_merged, fn_im[0][1])
# merge QA band (60m band)
- fn_merged = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'merged.tif')
- gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', 'nan', fn_im[0][2], fn_im[1][2]])
+ gdal_merge.main(['', '-o', fn_merged, '-n', '0', fn_im[0][2], fn_im[1][2]])
os.chmod(fn_im[0][2], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[0][2])
os.chmod(fn_im[1][2], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[1][2])
+ os.chmod(fn_merged, 0o777)
os.rename(fn_merged, fn_im[0][2])
# remove the metadata .txt file of the duplicate image
os.chmod(fn_im[1][3], 0o777)
os.remove(fn_im[1][3])
-
+
print('%d pairs of overlapping Sentinel-2 images were merged' % len(pairs))
- # update the metadata dict (delete all the duplicates)
+ # update the metadata dict
metadata_updated = copy.deepcopy(metadata)
- filenames_copy = metadata_updated[sat]['filenames']
- index_list = []
- for i in range(len(filenames_copy)):
- if filenames_copy[i].find('dup') == -1:
- index_list.append(i)
+ idx_removed = []
+ idx_kept = []
+ for pair in pairs: idx_removed.append(pair[1])
+ for idx in np.arange(0,len(metadata[sat]['dates'])):
+ if not idx in idx_removed: idx_kept.append(idx)
for key in metadata_updated[sat].keys():
- metadata_updated[sat][key] = [metadata_updated[sat][key][_] for _ in index_list]
+ metadata_updated[sat][key] = [metadata_updated[sat][key][_] for _ in idx_kept]
- return metadata_updated
+ return metadata_updated
def get_metadata(inputs):
"""
- Gets the metadata from the downloaded .txt files in the \meta folders.
+ Gets the metadata from the downloaded images by parsing .txt files located
+ in the \meta subfolder.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- inputs: dict
- dictionnary that contains the following fields:
+ inputs: dict with the following fields
'sitename': str
- String containig the name of the site
+ name of the site
'filepath_data': str
- Filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
+ filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
Returns:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded: filename,
- georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
+ metadata: dict
+ contains the information about the satellite images that were downloaded:
+ date, filename, georeferencing accuracy and image coordinate reference system
"""
# directory containing the images
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_preprocess.py b/coastsat/SDS_preprocess.py
index 4fe1d32..eabc489 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_preprocess.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_preprocess.py
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
-"""This module contains all the functions needed to preprocess the satellite images before the
-shoreline can be extracted. This includes creating a cloud mask and
+"""
+This module contains all the functions needed to preprocess the satellite images
+ before the shorelines can be extracted. This includes creating a cloud mask and
pansharpening/downsampling the multispectral bands.
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -24,7 +25,7 @@ import pickle
import geopandas as gpd
from shapely import geometry
-# own modules
+# CoastSat modules
from coastsat import SDS_tools
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
@@ -37,17 +38,19 @@ def create_cloud_mask(im_QA, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
Arguments:
-----------
- im_QA: np.array
- Image containing the QA band
- satname: string
- short name for the satellite (L5, L7, L8 or S2)
- cloud_mask_issue: boolean
- True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
+ im_QA: np.array
+ Image containing the QA band
+ satname: string
+ short name for the satellite: ```'L5', 'L7', 'L8' or 'S2'```
+ cloud_mask_issue: boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being
+ erroneously masked on the images
Returns:
-----------
- cloud_mask : np.array
- A boolean array with True if a pixel is cloudy and False otherwise
+ cloud_mask : np.array
+ boolean array with True if a pixel is cloudy and False otherwise
+
"""
# convert QA bits (the bits allocated to cloud cover vary depending on the satellite mission)
@@ -76,20 +79,22 @@ def create_cloud_mask(im_QA, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
def hist_match(source, template):
"""
- Adjust the pixel values of a grayscale image such that its histogram matches that of a
- target image.
+ Adjust the pixel values of a grayscale image such that its histogram matches
+ that of a target image.
Arguments:
-----------
- source: np.array
- Image to transform; the histogram is computed over the flattened
- array
- template: np.array
- Template image; can have different dimensions to source
+ source: np.array
+ Image to transform; the histogram is computed over the flattened
+ array
+ template: np.array
+ Template image; can have different dimensions to source
+
Returns:
-----------
- matched: np.array
- The transformed output image
+ matched: np.array
+ The transformed output image
+
"""
oldshape = source.shape
@@ -119,25 +124,27 @@ def hist_match(source, template):
def pansharpen(im_ms, im_pan, cloud_mask):
"""
Pansharpens a multispectral image, using the panchromatic band and a cloud mask.
- A PCA is applied to the image, then the 1st PC is replaced with the panchromatic band.
- Note that it is essential to match the histrograms of the 1st PC and the panchromatic band
- before replacing and inverting the PCA.
+ A PCA is applied to the image, then the 1st PC is replaced, after histogram
+ matching with the panchromatic band. Note that it is essential to match the
+ histrograms of the 1st PC and the panchromatic band before replacing and
+ inverting the PCA.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- Multispectral image to pansharpen (3D)
- im_pan: np.array
- Panchromatic band (2D)
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_ms: np.array
+ Multispectral image to pansharpen (3D)
+ im_pan: np.array
+ Panchromatic band (2D)
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
Returns:
-----------
- im_ms_ps: np.ndarray
- Pansharpened multispectral image (3D)
+ im_ms_ps: np.ndarray
+ Pansharpened multispectral image (3D)
+
"""
# reshape image into vector and apply cloud mask
@@ -172,17 +179,17 @@ def rescale_image_intensity(im, cloud_mask, prob_high):
Arguments:
-----------
- im: np.array
- Image to rescale, can be 3D (multispectral) or 2D (single band)
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- prob_high: float
- probability of exceedence used to calculate the upper percentile
+ im: np.array
+ Image to rescale, can be 3D (multispectral) or 2D (single band)
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ prob_high: float
+ probability of exceedence used to calculate the upper percentile
Returns:
-----------
- im_adj: np.array
- The rescaled image
+ im_adj: np.array
+ rescaled image
"""
# lower percentile is set to 0
@@ -221,40 +228,41 @@ def rescale_image_intensity(im, cloud_mask, prob_high):
def preprocess_single(fn, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
"""
- Reads the image and outputs the pansharpened/down-sampled multispectral bands, the
- georeferencing vector of the image (coordinates of the upper left pixel), the cloud mask and
- the QA band. For Landsat 7-8 it also outputs the panchromatic band and for Sentinel-2 it also
- outputs the 20m SWIR band.
+ Reads the image and outputs the pansharpened/down-sampled multispectral bands,
+ the georeferencing vector of the image (coordinates of the upper left pixel),
+ the cloud mask, the QA band and a no_data image.
+ For Landsat 7-8 it also outputs the panchromatic band and for Sentinel-2 it
+ also outputs the 20m SWIR band.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- fn: str or list of str
- filename of the .TIF file containing the image
- for L7, L8 and S2 this is a list of filenames, one filename for each band at different
- resolution (30m and 15m for Landsat 7-8, 10m, 20m, 60m for Sentinel-2)
- satname: str
- name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
- cloud_mask_issue: boolean
- True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
+ fn: str or list of str
+ filename of the .TIF file containing the image. For L7, L8 and S2 this
+ is a list of filenames, one filename for each band at different
+ resolution (30m and 15m for Landsat 7-8, 10m, 20m, 60m for Sentinel-2)
+ satname: str
+ name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
+ cloud_mask_issue: boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
Returns:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- 3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale] defining the
- coordinates of the top-left pixel of the image
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- im_extra : np.array
- 2D array containing the 20m resolution SWIR band for Sentinel-2 and the 15m resolution
- panchromatic band for Landsat 7 and Landsat 8. This field is empty for Landsat 5.
- im_QA: np.array
- 2D array containing the QA band, from which the cloud_mask can be computed.
- im_nodata: np.array
- 2D array with True where no data values (-inf) are located
+ im_ms: np.array
+ 3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale] defining the
+ coordinates of the top-left pixel of the image
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_extra : np.array
+ 2D array containing the 20m resolution SWIR band for Sentinel-2 and the 15m resolution
+ panchromatic band for Landsat 7 and Landsat 8. This field is empty for Landsat 5.
+ im_QA: np.array
+ 2D array containing the QA band, from which the cloud_mask can be computed.
+ im_nodata: np.array
+ 2D array with True where no data values (-inf) are located
"""
@@ -510,20 +518,21 @@ def preprocess_single(fn, satname, cloud_mask_issue):
def create_jpg(im_ms, cloud_mask, date, satname, filepath):
"""
Saves a .jpg file with the RGB image as well as the NIR and SWIR1 grayscale images.
- This functions can be modified to obtain different visualisations of the multispectral images.
+ This functions can be modified to obtain different visualisations of the
+ multispectral images.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- 3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- date: str
- String containing the date at which the image was acquired
- satname: str
- name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
+ im_ms: np.array
+ 3D array containing the pansharpened/down-sampled bands (B,G,R,NIR,SWIR1)
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ date: str
+ string containing the date at which the image was acquired
+ satname: str
+ name of the satellite mission (e.g., 'L5')
Returns:
-----------
@@ -573,7 +582,7 @@ def create_jpg(im_ms, cloud_mask, date, satname, filepath):
plt.close()
-def save_jpg(metadata, settings):
+def save_jpg(metadata, settings, **kwargs):
"""
Saves a .jpg image for all the images contained in metadata.
@@ -581,22 +590,24 @@ def save_jpg(metadata, settings):
Arguments:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- cloud_thresh: float
- value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in the image that is accepted
- sitename: string
- name of the site (also name of the folder where the images are stored)
- cloud_mask_issue: boolean
- True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
-
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+ 'cloud_thresh': float
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
+
Returns:
-----------
-
+ Stores the images as .jpg in a folder named /preprocessed
+
"""
-
+
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
cloud_thresh = settings['cloud_thresh']
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
@@ -626,6 +637,7 @@ def save_jpg(metadata, settings):
continue
# save .jpg with date and satellite in the title
date = filenames[i][:19]
+ plt.ioff() # turning interactive plotting off
create_jpg(im_ms, cloud_mask, date, satname, filepath_jpg)
# print the location where the images have been saved
@@ -634,44 +646,50 @@ def save_jpg(metadata, settings):
def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
"""
- Allows the user to manually digitize a reference shoreline that is used seed the shoreline
- detection algorithm. The reference shoreline helps to detect the outliers, making the shoreline
- detection more robust.
+ Allows the user to manually digitize a reference shoreline that is used seed
+ the shoreline detection algorithm. The reference shoreline helps to detect
+ the outliers, making the shoreline detection more robust.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
'cloud_thresh': float
- value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in the image that is accepted
- 'sitename': string
- name of the site (also name of the folder where the images are stored)
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
'output_epsg': int
- epsg code of the desired spatial reference system
+ output spatial reference system as EPSG code
Returns:
-----------
- reference_shoreline: np.array
- coordinates of the reference shoreline that was manually digitized
+ reference_shoreline: np.array
+ coordinates of the reference shoreline that was manually digitized.
+ This is also saved as a .pkl and .geojson file.
"""
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
-
+ pts_coords = []
# check if reference shoreline already exists in the corresponding folder
filepath = os.path.join(filepath_data, sitename)
filename = sitename + '_reference_shoreline.pkl'
+ # if it exist, load it and return it
if filename in os.listdir(filepath):
print('Reference shoreline already exists and was loaded')
with open(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_reference_shoreline.pkl'), 'rb') as f:
refsl = pickle.load(f)
return refsl
-
+
+ # otherwise get the user to manually digitise a shoreline on S2, L8 or L5 images (no L7 because of scan line error)
else:
# first try to use S2 images (10m res for manually digitizing the reference shoreline)
if 'S2' in metadata.keys():
@@ -690,8 +708,12 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
filepath = SDS_tools.get_filepath(settings['inputs'],satname)
filenames = metadata[satname]['filenames']
else:
- raise Exception('You cannot digitize the shoreline on L7 images, add another L8, S2 or L5 to your dataset.')
-
+ raise Exception('You cannot digitize the shoreline on L7 images (because of gaps in the images), add another L8, S2 or L5 to your dataset.')
+
+ # create figure
+ fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=[18,9], tight_layout=True)
+ mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
+ mng.window.showMaximized()
# loop trhough the images
for i in range(len(filenames)):
@@ -711,37 +733,55 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
im_RGB = rescale_image_intensity(im_ms[:,:,[2,1,0]], cloud_mask, 99.9)
# plot the image RGB on a figure
- fig = plt.figure()
- fig.set_size_inches([18,9])
- fig.set_tight_layout(True)
- plt.axis('off')
- plt.imshow(im_RGB)
+ ax.axis('off')
+ ax.imshow(im_RGB)
# decide if the image if good enough for digitizing the shoreline
- plt.title('click if image is clear enough to digitize the shoreline.\n' +
- 'If not (too cloudy) click on to get another image', fontsize=14)
- keep_button = plt.text(0, 0.9, 'keep', size=16, ha="left", va="top",
- transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
- bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
- skip_button = plt.text(1, 0.9, 'skip', size=16, ha="right", va="top",
- transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
- bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
- mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
- mng.window.showMaximized()
-
- # let user click on the image once
- pt_input = ginput(n=1, timeout=1e9, show_clicks=False)
- pt_input = np.array(pt_input)
-
- # if clicks next to , show another image
- if pt_input[0][0] > im_ms.shape[1]/2:
- plt.close()
+ ax.set_title('Press if image is clear enough to digitize the shoreline.\n' +
+ 'If the image is cloudy press to get another image', fontsize=14)
+ # set a key event to accept/reject the detections (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/15033071)
+ # this variable needs to be immuatable so we can access it after the keypress event
+ skip_image = False
+ key_event = {}
+ def press(event):
+ # store what key was pressed in the dictionary
+ key_event['pressed'] = event.key
+ # let the user press a key, right arrow to keep the image, left arrow to skip it
+ # to break the loop the user can press 'escape'
+ while True:
+ btn_keep = plt.text(1.1, 0.9, 'keep ⇨', size=12, ha="right", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ btn_skip = plt.text(-0.1, 0.9, '⇦ skip', size=12, ha="left", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ btn_esc = plt.text(0.5, 0, ' to quit', size=12, ha="center", va="top",
+ transform=ax.transAxes,
+ bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
+ plt.draw()
+ fig.canvas.mpl_connect('key_press_event', press)
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+ # after button is pressed, remove the buttons
+ btn_skip.remove()
+ btn_keep.remove()
+ btn_esc.remove()
+ # keep/skip image according to the pressed key, 'escape' to break the loop
+ if key_event.get('pressed') == 'right':
+ skip_image = False
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'left':
+ skip_image = True
+ break
+ elif key_event.get('pressed') == 'escape':
+ plt.close()
+ raise StopIteration('User cancelled checking shoreline detection')
+ else:
+ plt.waitforbuttonpress()
+
+ if skip_image:
+ ax.clear()
continue
-
else:
- # remove keep and skip buttons
- keep_button.set_visible(False)
- skip_button.set_visible(False)
# create two new buttons
add_button = plt.text(0, 0.9, 'add', size=16, ha="left", va="top",
transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
@@ -749,7 +789,6 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
end_button = plt.text(1, 0.9, 'end', size=16, ha="right", va="top",
transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
-
# add multiple reference shorelines (until user clicks on button)
pts_sl = np.expand_dims(np.array([np.nan, np.nan]),axis=0)
geoms = []
@@ -757,7 +796,7 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
add_button.set_visible(False)
end_button.set_visible(False)
# update title (instructions)
- plt.title('Click points along the shoreline (enough points to capture the beach curvature).\n' +
+ ax.set_title('Click points along the shoreline (enough points to capture the beach curvature).\n' +
'Start at one end of the beach.\n' + 'When finished digitizing, click ',
fontsize=14)
plt.draw()
@@ -791,14 +830,14 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
# convert to pixel coordinates and plot
pts_pix_interp = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(pts_world_interp, georef)
pts_sl = np.append(pts_sl, pts_world_interp, axis=0)
- plt.plot(pts_pix_interp[:,0], pts_pix_interp[:,1], 'r--')
- plt.plot(pts_pix_interp[0,0], pts_pix_interp[0,1],'ko')
- plt.plot(pts_pix_interp[-1,0], pts_pix_interp[-1,1],'ko')
+ ax.plot(pts_pix_interp[:,0], pts_pix_interp[:,1], 'r--')
+ ax.plot(pts_pix_interp[0,0], pts_pix_interp[0,1],'ko')
+ ax.plot(pts_pix_interp[-1,0], pts_pix_interp[-1,1],'ko')
# update title and buttons
add_button.set_visible(True)
end_button.set_visible(True)
- plt.title('click to digitize another shoreline or to finish and save the shoreline(s)',
+ ax.set_title('click on to digitize another shoreline or on to finish and save the shoreline(s)',
fontsize=14)
plt.draw()
@@ -845,5 +884,10 @@ def get_reference_sl(metadata, settings):
print('Reference shoreline has been saved in ' + filepath)
break
+
+ # check if a shoreline was digitised
+ if len(pts_coords) == 0:
+ raise Exception('No cloud free images are available to digitise the reference shoreline,'+
+ 'download more images and try again')
return pts_coords
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_shoreline.py b/coastsat/SDS_shoreline.py
index 92383b1..0e45273 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_shoreline.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_shoreline.py
@@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
-"""This module contains all the functions needed for extracting satellite-derived shorelines (SDS)
+"""
+This module contains all the functions needed for extracting satellite-derived
+shorelines (SDS)
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -26,7 +28,7 @@ from matplotlib import gridspec
from pylab import ginput
import pickle
-# own modules
+# CoastSat modules
from coastsat import SDS_tools, SDS_preprocess
np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
@@ -37,24 +39,27 @@ np.seterr(all='ignore') # raise/ignore divisions by 0 and nans
def calculate_features(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_bool):
"""
- Calculates a range of features on the image that are used for the supervised classification.
- The features include spectral normalized-difference indices and standard deviation of the image.
+ Calculates features on the image that are used for the supervised classification.
+ The features include spectral normalized-difference indices and standard
+ deviation of the image for all the bands and indices.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- im_bool: np.array
- 2D array of boolean indicating where on the image to calculate the features
-
- Returns: -----------
- features: np.array
- matrix containing each feature (columns) calculated for all
- the pixels (rows) indicated in im_bool
+ im_ms: np.array
+ RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_bool: np.array
+ 2D array of boolean indicating where on the image to calculate the features
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ features: np.array
+ matrix containing each feature (columns) calculated for all
+ the pixels (rows) indicated in im_bool
+
"""
# add all the multispectral bands
@@ -103,27 +108,29 @@ def classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask, min_beach_area, clf):
- water --> label = 3
- other (vegetation, buildings, rocks...) --> label = 0
- The classifier is a Neural Network previously trained.
+ The classifier is a Neural Network that is already trained.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- Pansharpened RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
- im_extra:
- only used for Landsat 7 and 8 where im_extra is the panchromatic band
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- min_beach_area: int
- minimum number of pixels that have to be connected to belong to the SAND class
- clf: classifier
-
- Returns: -----------
- im_classif: np.array
- 2D image containing labels
- im_labels: np.array of booleans
- 3D image containing a boolean image for each class (im_classif == label)
+ im_ms: np.array
+ Pansharpened RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
+ im_extra:
+ only used for Landsat 7 and 8 where im_extra is the panchromatic band
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ min_beach_area: int
+ minimum number of pixels that have to be connected to belong to the SAND class
+ clf: joblib object
+ pre-trained classifier
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ im_classif: np.array
+ 2D image containing labels
+ im_labels: np.array of booleans
+ 3D image containing a boolean image for each class (im_classif == label)
"""
@@ -163,24 +170,26 @@ def classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask, min_beach_area, clf):
def find_wl_contours1(im_ndwi, cloud_mask, im_ref_buffer):
"""
- Traditional method for shorelien detection.
- Finds the water line by thresholding the Normalized Difference Water Index and applying
- the Marching Squares Algorithm to contour the iso-value corresponding to the threshold.
+ Traditional method for shoreline detection using a global threshold.
+ Finds the water line by thresholding the Normalized Difference Water Index
+ and applying the Marching Squares Algorithm to contour the iso-value
+ corresponding to the threshold.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ndwi: np.ndarray
- Image (2D) with the NDWI (water index)
- cloud_mask: np.ndarray
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- im_ref_buffer: np.array
- Binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
-
- Returns: -----------
- contours_wl: list of np.arrays
- contains the (row,column) coordinates of the contour lines
+ im_ndwi: np.ndarray
+ Image (2D) with the NDWI (water index)
+ cloud_mask: np.ndarray
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_ref_buffer: np.array
+ Binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ contours_wl: list of np.arrays
+ contains the coordinates of the contour lines
"""
@@ -212,32 +221,33 @@ def find_wl_contours1(im_ndwi, cloud_mask, im_ref_buffer):
def find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels, cloud_mask, buffer_size, im_ref_buffer):
"""
- New robust method for extracting shorelines. Incorporates the classification component to
- refine the treshold and make it specific to the sand/water interface.
+ New robust method for extracting shorelines. Incorporates the classification
+ component to refine the treshold and make it specific to the sand/water interface.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
- im_labels: np.array
- 3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- buffer_size: int
- size of the buffer around the sandy beach over which the pixels are considered in the
- thresholding algorithm.
- im_ref_buffer: np.array
- Binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
-
- Returns: -----------
- contours_wi: list of np.arrays
- contains the (row,column) coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
- NDWI (Normalized Difference Water Index) image
- contours_mwi: list of np.arrays
- contains the (row,column) coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
- MNDWI (Modified Normalized Difference Water Index) image
+ im_ms: np.array
+ RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
+ im_labels: np.array
+ 3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ buffer_size: int
+ size of the buffer around the sandy beach over which the pixels are considered in the
+ thresholding algorithm.
+ im_ref_buffer: np.array
+ binary image containing a buffer around the reference shoreline
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ contours_wi: list of np.arrays
+ contains the coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
+ NDWI (Normalized Difference Water Index) image
+ contours_mwi: list of np.arrays
+ contains the coordinates of the contour lines extracted from the
+ MNDWI (Modified Normalized Difference Water Index) image
"""
@@ -318,33 +328,33 @@ def find_wl_contours2(im_ms, im_labels, cloud_mask, buffer_size, im_ref_buffer):
def create_shoreline_buffer(im_shape, georef, image_epsg, pixel_size, settings):
"""
- Creates a buffer around the reference shoreline. The size of the buffer is given by
- settings['max_dist_ref'].
+ Creates a buffer around the reference shoreline. The size of the buffer is
+ given by settings['max_dist_ref'].
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_shape: np.array
- size of the image (rows,columns)
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- image_epsg: int
- spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
- pixel_size: int
- size of the pixel in metres (15 for Landsat, 10 for Sentinel-2)
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- output_epsg: int
+ im_shape: np.array
+ size of the image (rows,columns)
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ image_epsg: int
+ spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
+ pixel_size: int
+ size of the pixel in metres (15 for Landsat, 10 for Sentinel-2)
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'output_epsg': int
output spatial reference system
- reference_shoreline: np.array
+ 'reference_shoreline': np.array
coordinates of the reference shoreline
- max_dist_ref: int
+ 'max_dist_ref': int
maximum distance from the reference shoreline in metres
- Returns: -----------
- im_buffer: np.array
- binary image, True where the buffer is, False otherwise
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ im_buffer: np.array
+ binary image, True where the buffer is, False otherwise
"""
# initialise the image buffer
@@ -358,6 +368,12 @@ def create_shoreline_buffer(im_shape, georef, image_epsg, pixel_size, settings):
ref_sl_pix = SDS_tools.convert_world2pix(ref_sl_conv, georef)
ref_sl_pix_rounded = np.round(ref_sl_pix).astype(int)
+ # make sure that the pixel coordinates of the reference shoreline are inside the image
+ idx_row = np.logical_and(ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,0] > 0, ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,0] < im_shape[1])
+ idx_col = np.logical_and(ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,1] > 0, ref_sl_pix_rounded[:,1] < im_shape[0])
+ idx_inside = np.logical_and(idx_row, idx_col)
+ ref_sl_pix_rounded = ref_sl_pix_rounded[idx_inside,:]
+
# create binary image of the reference shoreline (1 where the shoreline is 0 otherwise)
im_binary = np.zeros(im_shape)
for j in range(len(ref_sl_pix_rounded)):
@@ -373,33 +389,32 @@ def create_shoreline_buffer(im_shape, georef, image_epsg, pixel_size, settings):
def process_shoreline(contours, cloud_mask, georef, image_epsg, settings):
"""
- Converts the contours from image coordinates to world coordinates. This function also removes
- the contours that are too small to be a shoreline (based on the parameter
- settings['min_length_sl'])
+ Converts the contours from image coordinates to world coordinates.
+ This function also removes the contours that are too small to be a shoreline
+ (based on the parameter settings['min_length_sl'])
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- contours: np.array or list of np.array
- image contours as detected by the function find_contours
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- image_epsg: int
- spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- output_epsg: int
+ contours: np.array or list of np.array
+ image contours as detected by the function find_contours
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ image_epsg: int
+ spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'output_epsg': int
output spatial reference system
- min_length_sl: float
- minimum length of shoreline perimeter to be kept (in meters)
+ 'min_length_sl': float
+ minimum length of shoreline contour to be kept (in meters)
Returns:
-----------
- shoreline: np.array
- array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
+ shoreline: np.array
+ array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
"""
@@ -445,36 +460,44 @@ def process_shoreline(contours, cloud_mask, georef, image_epsg, settings):
def show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,image_epsg, georef,
settings, date, satname):
"""
- Shows the detected shoreline to the user for visual quality control. The user can select "keep"
- if the shoreline detection is correct or "skip" if it is incorrect.
+ Shows the detected shoreline to the user for visual quality control.
+ The user can accept/reject the detected shorelines by using keep/skip
+ buttons.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- im_ms: np.array
- RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
- im_labels: np.array
- 3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
- shoreline: np.array
- array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
- image_epsg: int
- spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- date: string
- date at which the image was taken
- satname: string
- indicates the satname (L5,L7,L8 or S2)
+ im_ms: np.array
+ RGB + downsampled NIR and SWIR
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+ im_labels: np.array
+ 3D image containing a boolean image for each class in the order (sand, swash, water)
+ shoreline: np.array
+ array of points with the X and Y coordinates of the shoreline
+ image_epsg: int
+ spatial reference system of the image from which the contours were extracted
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ date: string
+ date at which the image was taken
+ satname: string
+ indicates the satname (L5,L7,L8 or S2)
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+ 'output_epsg': int
+ output spatial reference system as EPSG code
+ 'check_detection': bool
+ if True, lets user manually accept/reject the mapped shorelines
+ 'save_figure': bool
+ if True, saves a -jpg file for each mapped shoreline
Returns:
-----------
- skip_image: boolean
- True if the user wants to skip the image, False otherwise.
+ skip_image: boolean
+ True if the user wants to skip the image, False otherwise
"""
@@ -520,26 +543,26 @@ def show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,image_epsg, georef,
else:
# else create a new figure
fig = plt.figure()
- fig.set_size_inches([12.53, 9.3])
+ fig.set_size_inches([18, 9])
mng = plt.get_current_fig_manager()
mng.window.showMaximized()
# according to the image shape, decide whether it is better to have the images
# in vertical subplots or horizontal subplots
- if im_RGB.shape[1] > 2*im_RGB.shape[0]:
+ if im_RGB.shape[1] > 1.5*im_RGB.shape[0]:
# vertical subplots
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(3, 1)
gs.update(bottom=0.03, top=0.97, left=0.03, right=0.97)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,0])
- ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1,0])
- ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[2,0])
+ ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1,0], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
+ ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[2,0], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
else:
# horizontal subplots
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(1, 3)
gs.update(bottom=0.05, top=0.95, left=0.05, right=0.95)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,0])
- ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,1])
- ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,2])
+ ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,1], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
+ ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0,2], sharex=ax1, sharey=ax1)
# change the color of nans to either black (0.0) or white (1.0) or somewhere in between
nan_color = 1.0
@@ -634,42 +657,50 @@ def show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,image_epsg, georef,
def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
"""
- Extracts shorelines from satellite images.
+ Main function to extract shorelines from satellite images
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- metadata: dict
- contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
-
- settings: dict
- contains the following fields:
- sitename: str
- String containig the name of the site
- cloud_mask_issue: boolean
- True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels are being masked on the images
- buffer_size: int
- size of the buffer (m) around the sandy beach over which the pixels are considered in the
- thresholding algorithm
- min_beach_area: int
- minimum allowable object area (in metres^2) for the class 'sand'
- cloud_thresh: float
- value between 0 and 1 defining the maximum percentage of cloud cover allowed in the images
- output_epsg: int
+ metadata: dict
+ contains all the information about the satellite images that were downloaded
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+ 'cloud_thresh': float
+ value between 0 and 1 indicating the maximum cloud fraction in
+ the cropped image that is accepted
+ 'cloud_mask_issue': boolean
+ True if there is an issue with the cloud mask and sand pixels
+ are erroneously being masked on the images
+ 'buffer_size': int
+ size of the buffer (m) around the sandy pixels over which the pixels
+ are considered in the thresholding algorithm
+ 'min_beach_area': int
+ minimum allowable object area (in metres^2) for the class 'sand',
+ the area is converted to number of connected pixels
+ 'min_length_sl': int
+ minimum length (in metres) of shoreline contour to be valid
+ 'sand_color': str
+ default', 'dark' (for grey/black sand beaches) or 'bright' (for white sand beaches)
+ 'output_epsg': int
output spatial reference system as EPSG code
- check_detection: boolean
- True to show each invidual detection and let the user validate the mapped shoreline
-
+ 'check_detection': bool
+ if True, lets user manually accept/reject the mapped shorelines
+ 'save_figure': bool
+ if True, saves a -jpg file for each mapped shoreline
+
Returns:
-----------
- output: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates.
+ output: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates + metadata
"""
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
filepath_data = settings['inputs']['filepath']
+ filepath_models = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classification', 'models')
# initialise output structure
output = dict([])
# create a subfolder to store the .jpg images showing the detection
@@ -700,15 +731,15 @@ def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
if satname in ['L5','L7','L8']:
pixel_size = 15
if settings['sand_color'] == 'dark':
- clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classifiers', 'NN_4classes_Landsat_dark.pkl'))
+ clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_dark.pkl'))
elif settings['sand_color'] == 'bright':
- clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classifiers', 'NN_4classes_Landsat_bright.pkl'))
+ clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat_bright.pkl'))
else:
- clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classifiers', 'NN_4classes_Landsat.pkl'))
+ clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_Landsat.pkl'))
elif satname == 'S2':
pixel_size = 10
- clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'classifiers', 'NN_4classes_S2.pkl'))
+ clf = joblib.load(os.path.join(filepath_models, 'NN_4classes_S2.pkl'))
# convert settings['min_beach_area'] and settings['buffer_size'] from metres to pixels
buffer_size_pixels = np.ceil(settings['buffer_size']/pixel_size)
@@ -743,11 +774,6 @@ def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
im_ref_buffer = create_shoreline_buffer(cloud_mask.shape, georef, image_epsg,
pixel_size, settings)
- # when running the automated mode, skip image if cloudy pixels are found in the shoreline buffer
- if not settings['check_detection'] and 'reference_shoreline' in settings.keys():
- if sum(sum(np.logical_and(im_ref_buffer, cloud_mask_adv))) > 0:
- continue
-
# classify image in 4 classes (sand, whitewater, water, other) with NN classifier
im_classif, im_labels = classify_image_NN(im_ms, im_extra, cloud_mask,
min_beach_area_pixels, clf)
@@ -756,7 +782,7 @@ def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
# if there are pixels in the 'sand' class --> use find_wl_contours2 (enhanced)
# otherwise use find_wl_contours2 (traditional)
try: # use try/except structure for long runs
- if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) == 0 :
+ if sum(sum(im_labels[:,:,0])) < 10 :
# compute MNDWI image (SWIR-G)
im_mndwi = SDS_tools.nd_index(im_ms[:,:,4], im_ms[:,:,1], cloud_mask)
# find water contours on MNDWI grayscale image
@@ -777,6 +803,8 @@ def extract_shorelines(metadata, settings):
# if settings['save_figure'] = True, saves a figure for each mapped shoreline
if settings['check_detection'] or settings['save_figure']:
date = filenames[i][:19]
+ if not settings['check_detection']:
+ plt.ioff() # turning interactive plotting off
skip_image = show_detection(im_ms, cloud_mask, im_labels, shoreline,
image_epsg, georef, settings, date, satname)
# if the user decides to skip the image, continue and do not save the mapped shoreline
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_tools.py b/coastsat/SDS_tools.py
index 7e86598..478795c 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_tools.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_tools.py
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
-"""This module contains utilities to work with satellite images'
+"""
+This module contains utilities to work with satellite images
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -14,7 +15,7 @@ from osgeo import gdal, osr
import geopandas as gpd
from shapely import geometry
import skimage.transform as transform
-from scipy.ndimage.filters import uniform_filter
+from astropy.convolution import convolve
###################################################################################################
# COORDINATES CONVERSION FUNCTIONS
@@ -22,21 +23,22 @@ from scipy.ndimage.filters import uniform_filter
def convert_pix2world(points, georef):
"""
- Converts pixel coordinates (row,columns) to world projected coordinates
- performing an affine transformation.
+ Converts pixel coordinates (pixel row and column) to world projected
+ coordinates performing an affine transformation.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- points: np.array or list of np.array
- array with 2 columns (rows first and columns second)
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ points: np.array or list of np.array
+ array with 2 columns (row first and column second)
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- Returns: -----------
- points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
- converted coordinates, first columns with X and second column with Y
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
+ converted coordinates, first columns with X and second column with Y
"""
@@ -47,13 +49,15 @@ def convert_pix2world(points, georef):
# create affine transformation
tform = transform.AffineTransform(aff_mat)
+ # if list of arrays
if type(points) is list:
points_converted = []
# iterate over the list
for i, arr in enumerate(points):
tmp = arr[:,[1,0]]
points_converted.append(tform(tmp))
-
+
+ # if single array
elif type(points) is np.ndarray:
tmp = points[:,[1,0]]
points_converted = tform(tmp)
@@ -65,22 +69,23 @@ def convert_pix2world(points, georef):
def convert_world2pix(points, georef):
"""
- Converts world projected coordinates (X,Y) to image coordinates (row,column)
- performing an affine transformation.
+ Converts world projected coordinates (X,Y) to image coordinates
+ (pixel row and column) performing an affine transformation.
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- points: np.array or list of np.array
- array with 2 columns (rows first and columns second)
- georef: np.array
- vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
+ points: np.array or list of np.array
+ array with 2 columns (X,Y)
+ georef: np.array
+ vector of 6 elements [Xtr, Xscale, Xshear, Ytr, Yshear, Yscale]
- Returns: -----------
- points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
- converted coordinates, first columns with row and second column with column
-
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
+ converted coordinates (pixel row and column)
+
"""
# make affine transformation matrix
@@ -90,12 +95,14 @@ def convert_world2pix(points, georef):
# create affine transformation
tform = transform.AffineTransform(aff_mat)
+ # if list of arrays
if type(points) is list:
points_converted = []
# iterate over the list
for i, arr in enumerate(points):
points_converted.append(tform.inverse(points))
+ # if single array
elif type(points) is np.ndarray:
points_converted = tform.inverse(points)
@@ -108,22 +115,23 @@ def convert_world2pix(points, georef):
def convert_epsg(points, epsg_in, epsg_out):
"""
- Converts from one spatial reference to another using the epsg codes.
+ Converts from one spatial reference to another using the epsg codes
KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- points: np.array or list of np.ndarray
- array with 2 columns (rows first and columns second)
- epsg_in: int
- epsg code of the spatial reference in which the input is
- epsg_out: int
- epsg code of the spatial reference in which the output will be
+ points: np.array or list of np.ndarray
+ array with 2 columns (rows first and columns second)
+ epsg_in: int
+ epsg code of the spatial reference in which the input is
+ epsg_out: int
+ epsg code of the spatial reference in which the output will be
- Returns: -----------
- points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
- converted coordinates
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ points_converted: np.array or list of np.array
+ converted coordinates from epsg_in to epsg_out
"""
@@ -134,18 +142,18 @@ def convert_epsg(points, epsg_in, epsg_out):
outSpatialRef.ImportFromEPSG(epsg_out)
# create a coordinates transform
coordTransform = osr.CoordinateTransformation(inSpatialRef, outSpatialRef)
- # transform points
+ # if list of arrays
if type(points) is list:
points_converted = []
# iterate over the list
for i, arr in enumerate(points):
points_converted.append(np.array(coordTransform.TransformPoints(arr)))
+ # if single array
elif type(points) is np.ndarray:
points_converted = np.array(coordTransform.TransformPoints(points))
else:
raise Exception('invalid input type')
-
return points_converted
###################################################################################################
@@ -160,14 +168,18 @@ def nd_index(im1, im2, cloud_mask):
Arguments:
-----------
- im1, im2: np.array
- Images (2D) with which to calculate the ND index
- cloud_mask: np.array
- 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
-
- Returns: -----------
- im_nd: np.array
- Image (2D) containing the ND index
+ im1: np.array
+ first image (2D) with which to calculate the ND index
+ im2: np.array
+ second image (2D) with which to calculate the ND index
+ cloud_mask: np.array
+ 2D cloud mask with True where cloud pixels are
+
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ im_nd: np.array
+ Image (2D) containing the ND index
+
"""
# reshape the cloud mask
@@ -188,20 +200,21 @@ def nd_index(im1, im2, cloud_mask):
def image_std(image, radius):
"""
- Calculates the standard deviation of an image, using a moving window of specified radius.
+ Calculates the standard deviation of an image, using a moving window of
+ specified radius. Uses astropy's convolution library'
Arguments:
-----------
- image: np.array
- 2D array containing the pixel intensities of a single-band image
- radius: int
- radius defining the moving window used to calculate the standard deviation. For example,
- radius = 1 will produce a 3x3 moving window.
+ image: np.array
+ 2D array containing the pixel intensities of a single-band image
+ radius: int
+ radius defining the moving window used to calculate the standard deviation.
+ For example, radius = 1 will produce a 3x3 moving window.
Returns:
-----------
- win_std: np.array
- 2D array containing the standard deviation of the image
+ win_std: np.array
+ 2D array containing the standard deviation of the image
"""
@@ -211,9 +224,11 @@ def image_std(image, radius):
image_padded = np.pad(image, radius, 'reflect')
# window size
win_rows, win_cols = radius*2 + 1, radius*2 + 1
- # calculate std
- win_mean = uniform_filter(image_padded, (win_rows, win_cols))
- win_sqr_mean = uniform_filter(image_padded**2, (win_rows, win_cols))
+ # calculate std with uniform filters
+ win_mean = convolve(image_padded, np.ones((win_rows,win_cols)), boundary='extend',
+ normalize_kernel=True, nan_treatment='interpolate', preserve_nan=True)
+ win_sqr_mean = convolve(image_padded**2, np.ones((win_rows,win_cols)), boundary='extend',
+ normalize_kernel=True, nan_treatment='interpolate', preserve_nan=True)
win_var = win_sqr_mean - win_mean**2
win_std = np.sqrt(win_var)
# remove padding
@@ -227,14 +242,14 @@ def mask_raster(fn, mask):
Arguments:
-----------
- fn: str
- filepath + filename of the .tif raster
- mask: np.array
- array of boolean where True indicates the pixels that are to be masked
+ fn: str
+ filepath + filename of the .tif raster
+ mask: np.array
+ array of boolean where True indicates the pixels that are to be masked
Returns:
-----------
- overwrites the .tif file directly
+ Overwrites the .tif file directly
"""
@@ -264,27 +279,38 @@ def get_filepath(inputs,satname):
Arguments:
-----------
- inputs: dict
- dictionnary that contains the following fields:
+ inputs: dict with the following keys
'sitename': str
- String containig the name of the site
+ name of the site
'polygon': list
- polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted
- longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column
+ polygon containing the lon/lat coordinates to be extracted,
+ longitudes in the first column and latitudes in the second column,
+ there are 5 pairs of lat/lon with the fifth point equal to the first point:
+ ```
+ polygon = [[[151.3, -33.7],[151.4, -33.7],[151.4, -33.8],[151.3, -33.8],
+ [151.3, -33.7]]]
+ ```
'dates': list of str
- list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in format 'yyyy-mm-dd'
- e.g. ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ list that contains 2 strings with the initial and final dates in
+ format 'yyyy-mm-dd':
+ ```
+ dates = ['1987-01-01', '2018-01-01']
+ ```
'sat_list': list of str
- list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include
- e.g. ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
- satname: str
- short name of the satellite mission
+ list that contains the names of the satellite missions to include:
+ ```
+ sat_list = ['L5', 'L7', 'L8', 'S2']
+ ```
+ 'filepath_data': str
+ filepath to the directory where the images are downloaded
+ satname: str
+ short name of the satellite mission ('L5','L7','L8','S2')
Returns:
-----------
- filepath: str or list of str
- contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
-
+ filepath: str or list of str
+ contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
+
"""
sitename = inputs['sitename']
@@ -320,17 +346,17 @@ def get_filenames(filename, filepath, satname):
Arguments:
-----------
- filename: str
- name of the downloaded satellite image as found in the metadata
- filepath: str or list of str
- contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
- satname: str
- short name of the satellite mission
+ filename: str
+ name of the downloaded satellite image as found in the metadata
+ filepath: str or list of str
+ contains the filepath(s) to the folder(s) containing the satellite images
+ satname: str
+ short name of the satellite mission
Returns:
-----------
- fn: str or list of str
- contains the filepath + filenames to access the satellite image
+ fn: str or list of str
+ contains the filepath + filenames to access the satellite image
"""
@@ -351,19 +377,20 @@ def get_filenames(filename, filepath, satname):
def merge_output(output):
"""
- Function to merge the output dictionnary, which has one key per satellite mission into a
- dictionnary containing all the shorelines and dates ordered chronologically.
+ Function to merge the output dictionnary, which has one key per satellite mission
+ into a dictionnary containing all the shorelines and dates ordered chronologically.
Arguments:
-----------
- output: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates, organised by satellite mission
-
+ output: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates, organised by
+ satellite mission
+
Returns:
-----------
- output_all: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines in a single list sorted by date
-
+ output_all: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines in a single list sorted by date
+
"""
# initialize output dict
@@ -401,9 +428,10 @@ def polygon_from_kml(fn):
fn: str
filepath + filename of the kml file to be read
- Returns: -----------
- polygon: list
- coordinates extracted from the .kml file
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ polygon: list
+ coordinates extracted from the .kml file
"""
@@ -428,13 +456,13 @@ def transects_from_geojson(filename):
Arguments:
-----------
- filename: str
- contains the path and filename of the geojson file to be loaded
+ filename: str
+ contains the path and filename of the geojson file to be loaded
Returns:
-----------
- transects: dict
- contains the X and Y coordinates of each transect.
+ transects: dict
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of each transect
"""
@@ -458,11 +486,13 @@ def output_to_gdf(output):
output: dict
contains the coordinates of the mapped shorelines + attributes
- Returns: -----------
- gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
-
-
- """
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
+ contains the shorelines + attirbutes
+
+ """
+
# loop through the mapped shorelines
counter = 0
for i in range(len(output['shorelines'])):
@@ -498,11 +528,13 @@ def transects_to_gdf(transects):
transects: dict
contains the coordinates of the transects
- Returns: -----------
- gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
+ Returns:
+ -----------
+ gdf_all: gpd.GeoDataFrame
- """
+ """
+
# loop through the mapped shorelines
for i,key in enumerate(list(transects.keys())):
# save the geometry + attributes
diff --git a/coastsat/SDS_transects.py b/coastsat/SDS_transects.py
index 6e7221f..472e36a 100644
--- a/coastsat/SDS_transects.py
+++ b/coastsat/SDS_transects.py
@@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
-"""This module contains functions to analyze the shoreline data along transects'
+"""
+This module contains functions to analyze the 2D shorelines along shore-normal
+transects
- Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
+Author: Kilian Vos, Water Research Laboratory, University of New South Wales
"""
# load modules
@@ -14,28 +16,33 @@ import skimage.transform as transform
from pylab import ginput
import geopandas as gpd
-# own modules
+# CoastSat modules
from coastsat import SDS_tools
def create_transect(origin, orientation, length):
"""
- Create a 2D transect of points with 1m interval.
+ Create a transect given an origin, orientation and length.
+ Points are spaced at 1m intervals.
+
+ KV WRL 2018
Arguments:
-----------
- origin: np.array
- contains the X and Y coordinates of the origin of the transect
- orientation: int
- angle of the transect (anti-clockwise from North) in degrees
- length: int
- length of the transect in metres
+ origin: np.array
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of the origin of the transect
+ orientation: int
+ angle of the transect (anti-clockwise from North) in degrees
+ length: int
+ length of the transect in metres
Returns:
-----------
- transect: np.array
- contains the X and Y coordinates of the transect
+ transect: np.array
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of the transect
- """
+ """
+
+ # origin of the transect
x0 = origin[0]
y0 = origin[1]
# orientation of the transect
@@ -54,25 +61,29 @@ def create_transect(origin, orientation, length):
def draw_transects(output, settings):
"""
- Allows the user to draw shore-normal transects over the mapped shorelines.
+ Draw shore-normal transects interactively on top of the mapped shorelines
Arguments:
-----------
- output: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates.
- settings: dict
- contains the inputs
+ output: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding metadata
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'inputs': dict
+ input parameters (sitename, filepath, polygon, dates, sat_list)
+
Returns:
-----------
- transects: dict
- contains the X and Y coordinates of all the transects drawn. These are also saved
- as a .geojson (+ a .jpg figure showing the location of the transects)
+ transects: dict
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of all the transects drawn.
+ Also saves the coordinates as a .geojson as well as a .jpg figure
+ showing the location of the transects.
- """
+ """
+
sitename = settings['inputs']['sitename']
filepath = os.path.join(settings['inputs']['filepath'], sitename)
- # plot all shorelines
+ # plot the mapped shorelines
fig1 = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig1.add_subplot(111)
ax1.axis('equal')
@@ -90,7 +101,7 @@ def draw_transects(output, settings):
ax1.set_title('Click two points to define each transect (first point is the origin of the transect).\n'+
'When all transects have been defined, click on ', fontsize=16)
- # initialise variable
+ # initialise transects dict
transects = dict([])
counter = 0
# loop until user breaks it by click
@@ -99,14 +110,20 @@ def draw_transects(output, settings):
pts = ginput(n=2, timeout=1e9)
if len(pts) > 0:
origin = pts[0]
+ # if user presses , no points are selected
else:
+ # save figure as .jpg
fig1.gca().set_title('Transect locations', fontsize=16)
fig1.savefig(os.path.join(filepath, 'jpg_files', sitename + '_transect_locations.jpg'), dpi=200)
plt.title('Transect coordinates saved as ' + sitename + '_transects.geojson')
plt.draw()
+ # wait 3 seconds for user to visualise the transects that are saved
ginput(n=1, timeout=3, show_clicks=True)
plt.close(fig1)
+ # break the loop
break
+
+ # add selectect points to the transect dict
counter = counter + 1
transect = np.array([pts[0], pts[1]])
@@ -126,40 +143,40 @@ def draw_transects(output, settings):
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", ec='k',fc='w'))
plt.draw()
- # save as transects.geojson (for GIS)
+ # save transects.geojson
gdf = SDS_tools.transects_to_gdf(transects)
# set projection
gdf.crs = {'init':'epsg:'+str(settings['output_epsg'])}
# save as geojson
gdf.to_file(os.path.join(filepath, sitename + '_transects.geojson'), driver='GeoJSON', encoding='utf-8')
+ # print the location of the files
print('Transect locations saved in ' + filepath)
return transects
def compute_intersection(output, transects, settings):
"""
- Computes the intersection between the 2D mapped shorelines and the transects, to generate
- time-series of cross-shore distance along each transect.
+ Computes the intersection between the 2D shorelines and the shore-normal.
+ transects. It returns time-series of cross-shore distance along each transect.
Arguments:
-----------
- output: dict
- contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding dates.
- transects: dict
- contains the X and Y coordinates of the transects (first and last point needed for each
- transect).
- settings: dict
- contains parameters defining :
- along_dist: alongshore distance to caluclate the intersection (median of points
- within this distance).
-
+ output: dict
+ contains the extracted shorelines and corresponding metadata
+ transects: dict
+ contains the X and Y coordinates of each transect
+ settings: dict with the following keys
+ 'along_dist': int
+ alongshore distance considered caluclate the intersection
+
Returns:
-----------
- cross_dist: dict
- time-series of cross-shore distance along each of the transects. These are not tidally
- corrected.
+ cross_dist: dict
+ time-series of cross-shore distance along each of the transects.
+ Not tidally corrected.
- """
+ """
+
shorelines = output['shorelines']
along_dist = settings['along_dist']
diff --git a/environment.yml b/environment.yml
index f816bd4..2b23b22 100644
--- a/environment.yml
+++ b/environment.yml
@@ -16,3 +16,4 @@ dependencies:
- scipy=1.2.1
- spyder=3.3.4
- notebook=5.7.8
+ - astropy
diff --git a/examples/NARRA_polygon.kml b/examples/NARRA_polygon.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ab57b18
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/NARRA_polygon.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+ NARRA
+
+
+
+
+ normal
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-normal
+
+
+ highlight
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc-highlight
+
+
+
+ Polygon 1
+ #poly-000000-1200-77-nodesc
+
+
+
+ 1
+
+ 151.2957545,-33.7012561,0
+ 151.297557,-33.7388075,0
+ 151.312234,-33.7390216,0
+ 151.311204,-33.701399,0
+ 151.2957545,-33.7012561,0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
 +
+ +
+ +
+Finally, the new classifier can be applied to the satellite images, for visual inspection by calling the function `SDS_classify.evaluate_classifier(classifier,metadata,settings)` which will save the classified images in */evaluation*:
+
+
+
+Now, this new classifier labels correctly the sandy pixels of the Atacama desert and will provide more accurate satellite-derived shorelines at this beach!
diff --git a/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl b/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b6c126c
Binary files /dev/null and b/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl differ
diff --git a/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml b/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ba48549
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+
+
+Finally, the new classifier can be applied to the satellite images, for visual inspection by calling the function `SDS_classify.evaluate_classifier(classifier,metadata,settings)` which will save the classified images in */evaluation*:
+
+
+
+Now, this new classifier labels correctly the sandy pixels of the Atacama desert and will provide more accurate satellite-derived shorelines at this beach!
diff --git a/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl b/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b6c126c
Binary files /dev/null and b/classification/training_data/CoastSat_training_set_L8.pkl differ
diff --git a/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml b/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ba48549
--- /dev/null
+++ b/classification/training_sites/BYRON.kml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+
+